Digital print paper features a smooth, coated surface designed for crisp ink resolution but offers moderate ink absorption, whereas blotting paper has a highly porous structure that rapidly absorbs excess ink to prevent smudging. Choosing between the two depends on the need for image clarity versus efficient ink drying in writing or printing applications.
Table of Comparison
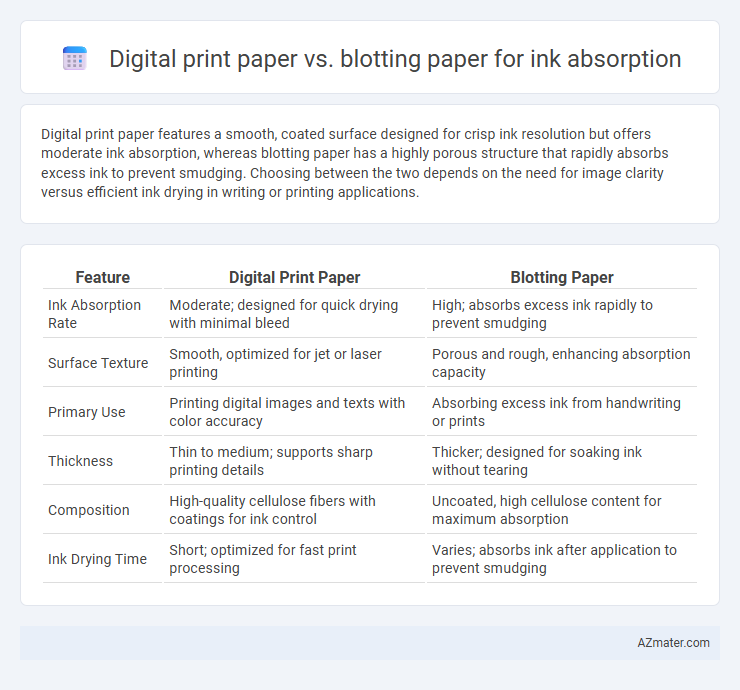
| Feature | Digital Print Paper | Blotting Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Ink Absorption Rate | Moderate; designed for quick drying with minimal bleed | High; absorbs excess ink rapidly to prevent smudging |
| Surface Texture | Smooth, optimized for jet or laser printing | Porous and rough, enhancing absorption capacity |
| Primary Use | Printing digital images and texts with color accuracy | Absorbing excess ink from handwriting or prints |
| Thickness | Thin to medium; supports sharp printing details | Thicker; designed for soaking ink without tearing |
| Composition | High-quality cellulose fibers with coatings for ink control | Uncoated, high cellulose content for maximum absorption |
| Ink Drying Time | Short; optimized for fast print processing | Varies; absorbs ink after application to prevent smudging |
Introduction to Ink Absorption in Paper Types
Digital print paper features a smooth, coated surface engineered for precise ink placement and rapid drying, allowing for high-resolution images with minimal ink bleed. Blotting paper, characterized by its highly porous and absorbent texture, quickly soaks up excess ink to prevent smudging but lacks the controlled ink distribution of print papers. Understanding ink absorption involves analyzing factors like fiber composition, porosity, and surface treatment, which directly impact ink retention, drying time, and image clarity on different paper types.
What is Digital Print Paper?
Digital print paper is specifically engineered to optimize ink absorption for high-resolution inkjet and laser printing, delivering sharp, vibrant images with minimal bleed and quick drying times. Unlike blotting paper, which is designed to absorb excess ink rapidly to prevent smudging in handwritten documents, digital print paper balances absorption and gloss to maintain image clarity and color accuracy. This specialized paper typically features a smooth surface and a coating that enhances inkjet ink adhesion, making it ideal for digital printing applications.
Understanding Blotting Paper: Definition and Uses
Blotting paper is a highly absorbent, lightweight paper designed specifically to absorb excess ink from writing surfaces, preventing smudging and ensuring cleaner lines. Unlike digital print paper, which is optimized for smooth ink adherence and image clarity, blotting paper rapidly soaks up wet ink, making it essential for traditional writing with fountain pens or calligraphy. Its porous texture allows it to function effectively in drying ink without disturbing the original marks on the paper.
Composition and Structure Differences
Digital print paper is usually composed of tightly packed cellulose fibers with a smooth, coated surface designed to prevent ink bleed and allow precise ink jet droplet absorption, optimizing color sharpness and detail. Blotting paper consists of loosely arranged, highly porous cellulose fibers that rapidly absorb excess ink through capillary action, preventing smudging but lacking the fine structural control necessary for high-resolution printing. The dense, coated structure of digital print paper contrasts sharply with the open, absorbent matrix of blotting paper, making each suited to different ink absorption purposes.
Ink Absorption Mechanism: Digital Print Paper vs Blotting Paper
Digital print paper absorbs ink primarily through its coated surface designed for quick drying and precise color retention, utilizing hydrophilic coatings that control ink spread for sharp image quality. Blotting paper relies on its highly porous, fibrous structure to rapidly wick excess ink away via capillary action, preventing smudging but often causing uneven absorption and diffusion. The distinct ink absorption mechanisms highlight digital print paper's engineered control for clarity, while blotting paper emphasizes rapid ink removal through natural porosity.
Performance in Ink Drying Speed
Digital print paper features a smooth, coated surface that slows ink absorption, resulting in longer drying times compared to blotting paper. Blotting paper is highly porous and designed explicitly to absorb excess ink rapidly, significantly enhancing ink drying speed. This superior absorption capacity makes blotting paper ideal for preventing smudging and ensuring quick handling of freshly printed or handwritten documents.
Impact on Print Quality and Sharpness
Digital print paper offers a smooth, non-absorbent surface that preserves ink sharpness, producing crisp and vibrant images ideal for high-resolution prints. Blotting paper, highly absorbent by nature, quickly soaks up excess ink but can cause diffusion, leading to blurred edges and reduced print clarity. The choice between these papers significantly impacts print quality, with digital print paper ensuring better sharpness and color fidelity compared to the softness and potential ink spread of blotting paper.
Best Applications for Each Paper Type
Digital print paper excels in sharp image reproduction and precise ink absorption ideal for high-resolution printing, packaging, and professional photo prints. Blotting paper absorbs excess ink rapidly, preventing smudging and is best suited for calligraphy, fountain pen writing, and drying artwork. Choosing between them depends on whether the priority is detailed image clarity or quick ink drying and spill control.
Environmental Considerations and Sustainability
Digital print paper, designed for vibrant ink absorption and minimal bleed, typically features coatings that may limit biodegradability and recycling potential compared to blotting paper, which is uncoated and highly porous, allowing rapid ink absorption without synthetic additives. Blotting paper's natural fibers enable easier decomposition and lower environmental impact, making it a more sustainable option for ink absorption where durability and print quality are secondary. Choosing blotting paper supports eco-friendly practices by reducing chemical use and enhancing recyclability, whereas digital print paper often prioritizes performance at the expense of complete environmental sustainability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Paper for Ink Absorption
Digital print paper offers smooth surfaces with moderate ink absorption suited for crisp, detailed printing, whereas blotting paper excels in rapid ink absorption, preventing smudging and bleeding. For precision printing and vibrant color retention, digital print paper is optimal, while blotting paper is ideal for drying excess ink in handwritten or calligraphy work. Selecting the right paper depends on ink type and intended use, prioritizing either controlled absorption for print clarity or fast drying for preventing ink spread.
Infographic: Digital print paper vs Blotting paper for Ink absorption
 azmater.com
azmater.com