Coated paper offers a smoother finish and higher print quality with vibrant colors, ideal for premium newspapers and inserts. Newsprint paper is lightweight, cost-effective, and designed for high-speed printing, making it the standard choice for daily newspapers.
Table of Comparison
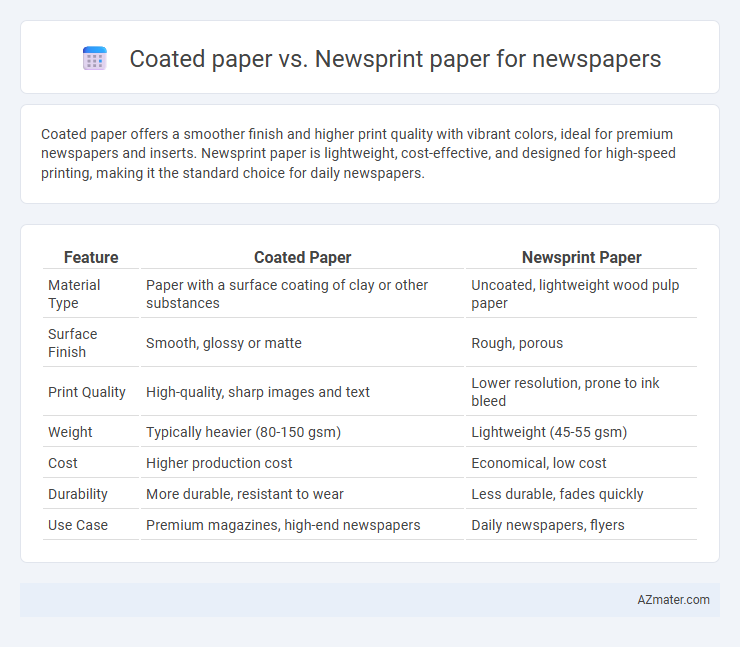
| Feature | Coated Paper | Newsprint Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Paper with a surface coating of clay or other substances | Uncoated, lightweight wood pulp paper |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, glossy or matte | Rough, porous |
| Print Quality | High-quality, sharp images and text | Lower resolution, prone to ink bleed |
| Weight | Typically heavier (80-150 gsm) | Lightweight (45-55 gsm) |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Economical, low cost |
| Durability | More durable, resistant to wear | Less durable, fades quickly |
| Use Case | Premium magazines, high-end newspapers | Daily newspapers, flyers |
Introduction to Newspaper Paper Types
Newspaper paper primarily consists of newsprint and coated paper, each serving distinct purposes based on print quality and cost. Newsprint is an inexpensive, lightweight, and uncoated paper ideal for high-speed printing and mass distribution, offering good legibility but less vibrant color reproduction. Coated paper, featuring a smooth, clay or polymer outer layer, enhances image sharpness and color saturation, making it suitable for premium inserts or magazines within newspapers.
What is Coated Paper?
Coated paper features a surface layer of clay or other substances that enhances brightness, smoothness, and print quality, making it ideal for high-resolution images and vibrant colors in newspapers. Unlike newsprint paper, which is uncoated and more porous, coated paper offers superior ink holdout and reduces ink absorption, resulting in sharper text and graphics. This type of paper is commonly used for premium newspapers and magazines that demand enhanced visual appeal and durability.
What is Newsprint Paper?
Newsprint paper is a lightweight, inexpensive paper primarily used for printing newspapers, characterized by its low brightness and high absorbency. Unlike coated paper, newsprint has an uncoated surface that allows for quick drying of ink, making it ideal for high-speed printing presses in newspaper production. Its composition typically includes a mix of recycled fibers and groundwood pulp, offering an economical option that balances print quality with rapid, large-scale distribution.
Printing Quality: Coated vs Newsprint Paper
Coated paper offers a smoother surface that enhances ink absorption and produces sharper, more vibrant images, making it ideal for high-quality newspaper printing. Newsprint paper, being more porous and uncoated, results in lower resolution and duller prints but is highly cost-effective for mass circulation. The choice between coated and newsprint paper significantly impacts the visual clarity and color accuracy of newspaper content.
Image and Color Reproduction Comparison
Coated paper offers superior image clarity and vibrant color reproduction for newspapers due to its smooth, sealed surface that prevents ink absorption and allows sharper, more detailed prints. Newsprint paper, being porous and uncoated, tends to produce duller colors with lower contrast and can lead to ink bleed, resulting in less crisp images. For high-quality color-intensive newspaper content, coated paper significantly enhances visual appeal compared to the traditional newsprint option.
Cost Differences Between Coated and Newsprint
Newsprint paper is significantly more cost-effective for newspaper production due to its lower manufacturing expenses and higher recyclability. Coated paper involves additional processing steps and materials, such as clay or polymers, which increase its price compared to newsprint. The price difference often leads publishers to prefer newsprint when cost savings are essential, especially for high-volume circulation.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Coated paper, often used for glossy newspaper inserts, requires more chemical processing and energy-intensive production, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to newsprint paper. Newsprint paper is typically made from recycled fibers and is more biodegradable, making it a more sustainable option for mass-circulation newspapers. Choosing newsprint supports reduced deforestation and lower greenhouse gas emissions due to its reliance on recycled materials and simpler manufacturing processes.
Reader Experience and Handling
Coated paper offers a smoother surface and richer color reproduction, enhancing the visual appeal and readability of newspapers, especially for image-heavy content. Newsprint paper, being lighter and more absorbent, provides a quicker drying time and is easier to handle in large volumes, making it ideal for fast distribution and daily use. While coated paper improves tactile quality and reduces ink bleed, newsprint's lightweight nature supports cost-effective production and easier recycling, influencing overall reader satisfaction and handling efficiency.
Durability and Lifespan in Circulation
Coated paper offers superior durability and longer lifespan in newspaper circulation due to its protective surface layer, which resists moisture, smudging, and wear during handling. Newsprint paper, being uncoated and made from lower-quality pulp, absorbs ink easily but is more prone to tearing, yellowing, and deterioration over time. This makes coated paper preferable for high-value or collectible newspapers requiring extended durability, while newsprint remains cost-effective for short-term, mass-distributed editions.
Choosing the Right Paper for Your Newspaper
Coated paper offers vibrant color reproduction and sharp images, making it ideal for high-quality newspapers with photo-rich content, while newsprint paper is more cost-effective and suitable for large-scale, daily publications focused on text. Selecting the right paper involves balancing print quality, budget constraints, and target audience preferences to achieve optimal readability and impact. Consider factors such as ink absorption, durability, and environmental impact to ensure the newspaper meets both operational and sustainability goals.
Infographic: Coated paper vs Newsprint paper for Newspaper
 azmater.com
azmater.com