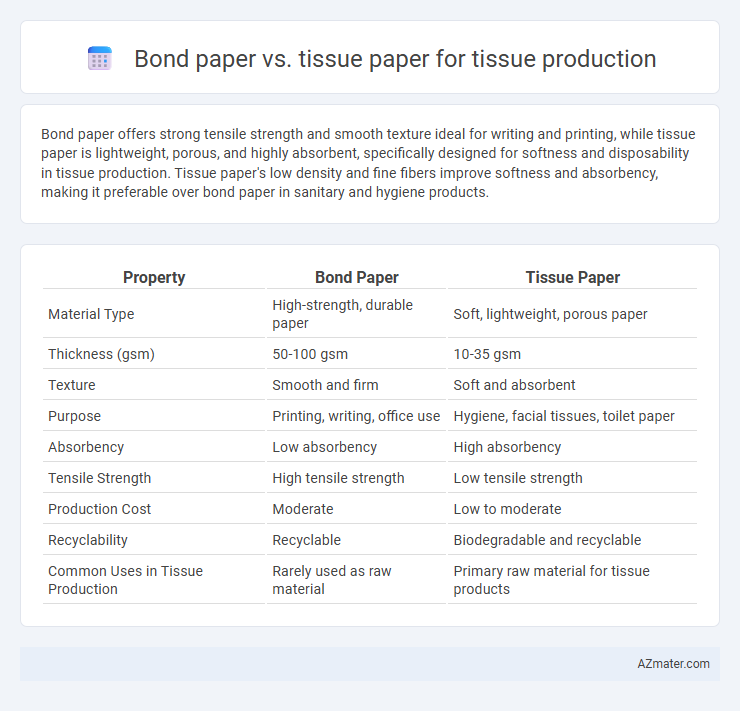
Bond paper offers strong tensile strength and smooth texture ideal for writing and printing, while tissue paper is lightweight, porous, and highly absorbent, specifically designed for softness and disposability in tissue production. Tissue paper's low density and fine fibers improve softness and absorbency, making it preferable over bond paper in sanitary and hygiene products.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Bond Paper | Tissue Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High-strength, durable paper | Soft, lightweight, porous paper |
| Thickness (gsm) | 50-100 gsm | 10-35 gsm |
| Texture | Smooth and firm | Soft and absorbent |
| Purpose | Printing, writing, office use | Hygiene, facial tissues, toilet paper |
| Absorbency | Low absorbency | High absorbency |
| Tensile Strength | High tensile strength | Low tensile strength |
| Production Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate |
| Recyclability | Recyclable | Biodegradable and recyclable |
| Common Uses in Tissue Production | Rarely used as raw material | Primary raw material for tissue products |
Introduction to Bond Paper and Tissue Paper
Bond paper, characterized by its high durability, smooth texture, and acid-free composition, is often used for printing important documents and stationery but is less effective for tissue production due to its thickness and rigidity. Tissue paper, made from lightweight, soft cellulose fibers, is specifically designed for absorbency, softness, and disposability, making it ideal for products such as facial tissues, toilet paper, and napkins. Understanding the fundamental differences in fiber composition, strength, and texture is crucial for selecting the appropriate material in tissue production processes.
Key Differences Between Bond Paper and Tissue Paper
Bond paper is a strong, durable type of paper typically used for printing and writing, characterized by its high tensile strength and smooth surface, while tissue paper is lightweight, soft, and highly absorbent, designed primarily for hygiene and cleaning purposes. Bond paper is generally thicker and less porous, making it suitable for applications that require durability, whereas tissue paper's thin, fibrous structure allows for easy tearing and rapid absorption. The manufacturing processes differ significantly: bond paper involves pulping and pressing wood fibers into dense sheets, whereas tissue paper production utilizes a more delicate approach, focusing on softness and flexibility to meet consumer comfort needs.
Raw Material Composition
Bond paper primarily consists of high-quality wood pulp fibers with a significant amount of chemical pulp, providing strength and durability, whereas tissue paper is made from a blend of recycled fibers and virgin pulp, often including eucalyptus or other hardwoods for softness and absorbency. The raw material composition of tissue paper emphasizes shorter fibers to enhance softness and pliability, contrasting with the longer, stronger fibers found in bond paper. This fundamental difference in fiber type and processing directly affects the texture, thickness, and end-use suitability of each paper type in tissue production.
Production Processes Compared
Bond paper production involves a high-quality, durable fabrication process using wood pulp fibers, chemical treatments, and a calendering machine to achieve a smooth, strong finish suitable for printing and writing. Tissue paper production requires a gentler approach, combining recycled or virgin fibers with water in a thin slurry, followed by a delicate drying process on a moving mesh or felt to create a soft, absorbent texture ideal for hygiene and packaging. The key difference lies in bonding and calendaring intensity; bond paper undergoes extensive pressing and sizing, while tissue paper prioritizes lightweight, porous structure through minimal pressing and specialized drying techniques.
Physical Properties and Strength
Bond paper exhibits higher tensile strength and durability due to its tightly bonded fibers, making it less prone to tearing, while tissue paper is characterized by its lightweight, softness, and lower basis weight, prioritizing flexibility and absorbency over mechanical strength. The physical properties of bond paper include a denser fiber network and greater stiffness, contributing to its enhanced load-bearing capacity, whereas tissue paper possesses a porous structure with loose fibers, resulting in superior softness but reduced tensile strength. Choosing between bond paper and tissue paper for tissue production depends on the desired balance between strength and softness, with bond paper offering robustness and tissue paper providing gentle texture for delicate applications.
Cost Implications in Tissue Production
Bond paper typically incurs higher raw material and manufacturing costs compared to tissue paper due to its denser composition and higher weight per square meter. Tissue paper production involves lower energy consumption and uses less pulp, leading to reduced operational expenses and more cost-effective large-scale manufacturing. Selecting tissue paper over bond paper can significantly minimize cost implications in tissue production without compromising functional efficiency for disposable applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Bond paper production typically involves higher energy consumption and chemical use compared to tissue paper, resulting in a larger carbon footprint. Tissue paper production often incorporates recycled fibers and biodegradable materials, enhancing its environmental sustainability. Choosing tissue paper over bond paper can significantly reduce deforestation and landfill waste due to its renewable sourcing and compostability.
End-Product Quality and Performance
Bond paper offers superior tensile strength and durability, making it less prone to tearing during tissue production, which enhances the end-product's structural integrity. Tissue paper, characterized by its softness and high absorbency, is optimized for consumer comfort and efficiency in applications like facial and toilet tissues. The choice between bond and tissue paper directly influences the final product's balance of softness, strength, and absorbency, critical factors in tissue quality and user satisfaction.
Applications in Tissue Manufacturing
Bond paper generally serves as a high-strength base material in tissue manufacturing, providing durability and structural support for products like facial tissues and paper towels. Tissue paper, characterized by its softness and absorbency, is primarily used in producing hygiene products such as toilet paper, napkins, and medical tissues. The choice between bond paper and tissue paper depends on the desired balance between strength and softness, influencing the final application in consumer tissue products.
Conclusion: Optimal Choice for Tissue Production
Tissue paper is the optimal choice for tissue production due to its softness, absorbency, and biodegradability, which align with consumer preferences and environmental standards. Bond paper lacks the necessary pliability and moisture absorption properties, making it less suitable for tissue products like facial and toilet paper. Selecting tissue paper enhances product quality and sustainability in the tissue manufacturing industry.
Infographic: Bond paper vs Tissue paper for Tissue production
 azmater.com
azmater.com