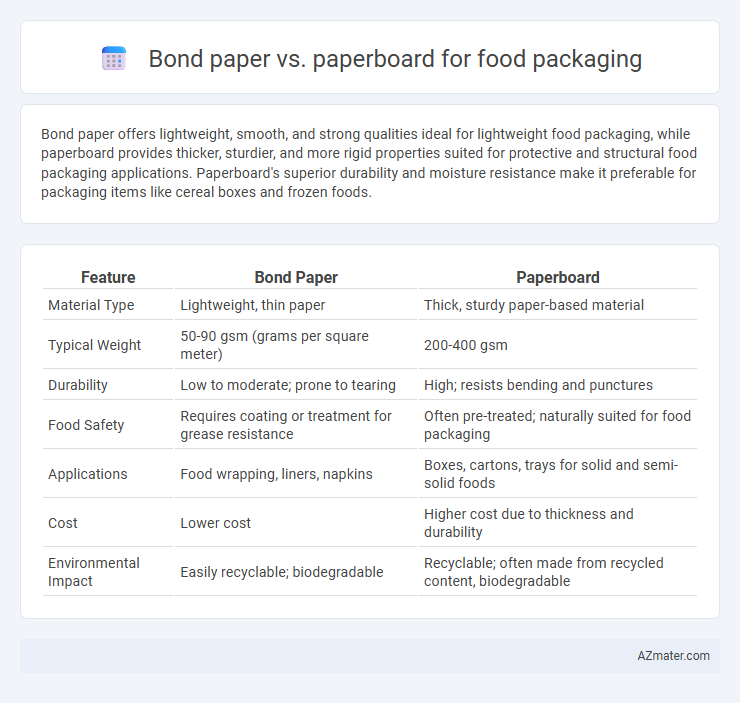
Bond paper offers lightweight, smooth, and strong qualities ideal for lightweight food packaging, while paperboard provides thicker, sturdier, and more rigid properties suited for protective and structural food packaging applications. Paperboard's superior durability and moisture resistance make it preferable for packaging items like cereal boxes and frozen foods.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bond Paper | Paperboard |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Lightweight, thin paper | Thick, sturdy paper-based material |
| Typical Weight | 50-90 gsm (grams per square meter) | 200-400 gsm |
| Durability | Low to moderate; prone to tearing | High; resists bending and punctures |
| Food Safety | Requires coating or treatment for grease resistance | Often pre-treated; naturally suited for food packaging |
| Applications | Food wrapping, liners, napkins | Boxes, cartons, trays for solid and semi-solid foods |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to thickness and durability |
| Environmental Impact | Easily recyclable; biodegradable | Recyclable; often made from recycled content, biodegradable |
Introduction to Food Packaging Materials
Bond paper and paperboard serve distinct roles in food packaging, with bond paper prized for its lightweight and smooth surface ideal for printed labels and lightweight wrapping. Paperboard offers enhanced durability and structural integrity, making it suitable for containers, cartons, and protective packaging requiring rigidity and strength. Selecting between these materials depends on factors such as product type, protection needs, and shelf appeal in food packaging applications.
Overview of Bond Paper
Bond paper is a durable, high-quality paper often used for printing and writing, characterized by its strength and smooth surface. It is made from chemical pulp and generally has a weight ranging from 50 to 100 gsm, making it thinner and more flexible compared to paperboard. In food packaging, bond paper is favored for wrappers and inner linings where lightweight and printability are crucial, whereas paperboard is typically used for structural packaging like boxes due to its rigidity and thickness.
Overview of Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick, durable material commonly used in food packaging due to its strength and ability to protect products from damage and contamination. It offers excellent printability and can be coated or laminated to enhance moisture resistance, making it ideal for packaging items like cereal boxes, frozen foods, and beverage carriers. Unlike bond paper, paperboard provides superior rigidity and structural support essential for maintaining product integrity during transportation and shelf display.
Key Properties of Bond Paper in Food Packaging
Bond paper in food packaging is valued for its high tensile strength, smooth surface, and superior printability, making it ideal for labels and lightweight pouches. Its porosity allows for adequate breathability, which is essential for packaging fresh produce and bakery items to maintain freshness. The paper's compatibility with food-safe coatings and inks ensures it meets safety standards without compromising the visual appeal or structural integrity of the packaging.
Key Properties of Paperboard in Food Packaging
Paperboard in food packaging is valued for its high stiffness, excellent moisture resistance, and superior durability compared to bond paper, enabling it to protect food products from physical damage and contamination effectively. Its thickness and multi-ply construction provide structural integrity for packaging applications like cereal boxes, frozen food containers, and takeaway cartons. The material's printability and barrier properties also enhance branding opportunities while maintaining food safety standards.
Food Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Bond paper offers a smooth surface ideal for printing and has moderate grease resistance, often requiring food-safe coatings to meet FDA regulations for direct food contact. Paperboard provides superior durability, thickness, and natural grease resistance, making it widely preferred for food packaging that demands compliance with FDA and EU food safety standards. Both materials must be certified free from harmful substances like BPA and phthalates to ensure compliance with regulatory guidelines and maintain food safety during storage and transportation.
Durability and Barrier Performance Comparison
Bond paper offers moderate durability and limited barrier performance, making it suitable for lightweight food packaging with low moisture sensitivity. Paperboard exhibits superior durability due to its thicker structure and provides enhanced barrier properties against grease, moisture, and oxygen, which is critical for preserving food freshness and extending shelf life. The choice between bond paper and paperboard depends on the required strength and barrier effectiveness for specific food packaging applications.
Cost Efficiency and Sustainability
Bond paper offers lower initial costs and easier recyclability, making it a cost-efficient choice for lightweight food packaging requiring moderate durability. Paperboard, though typically more expensive, provides superior strength and enhanced protection for heavier or moisture-sensitive foods, contributing to reduced product waste and longer shelf life. Both materials support sustainability goals through recyclability, but paperboard's higher fiber content often delivers better post-consumer reuse and compostability rates.
Typical Applications in the Food Industry
Bond paper is commonly used for food packaging applications such as bakery wraps, sandwich liners, and fast-food bags due to its lightweight, smooth surface, and printability. Paperboard is preferred for structural packaging like cereal boxes, frozen food cartons, and takeaway containers because of its rigidity, durability, and ability to protect contents during transport. The choice between bond paper and paperboard depends on the need for flexibility versus strength in food packaging solutions.
Choosing the Right Option: Bond Paper vs Paperboard
Bond paper offers a smooth finish and high print quality, making it ideal for lightweight, flexible food packaging such as labels and wrappers. Paperboard provides greater durability and rigidity, making it suitable for packaging heavier or more fragile food products like cereal boxes and frozen meals. Selecting between bond paper and paperboard depends on factors such as product weight, required durability, print quality, and cost efficiency for optimal food packaging performance.
Infographic: Bond paper vs Paperboard for Food packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com