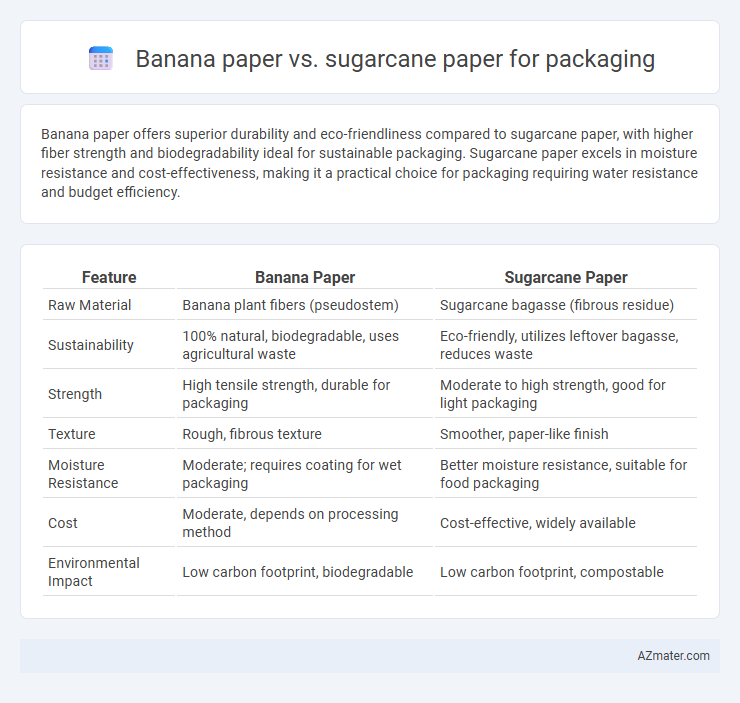
Banana paper offers superior durability and eco-friendliness compared to sugarcane paper, with higher fiber strength and biodegradability ideal for sustainable packaging. Sugarcane paper excels in moisture resistance and cost-effectiveness, making it a practical choice for packaging requiring water resistance and budget efficiency.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Paper | Sugarcane Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Banana plant fibers (pseudostem) | Sugarcane bagasse (fibrous residue) |
| Sustainability | 100% natural, biodegradable, uses agricultural waste | Eco-friendly, utilizes leftover bagasse, reduces waste |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable for packaging | Moderate to high strength, good for light packaging |
| Texture | Rough, fibrous texture | Smoother, paper-like finish |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate; requires coating for wet packaging | Better moisture resistance, suitable for food packaging |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on processing method | Cost-effective, widely available |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | Low carbon footprint, compostable |
Introduction to Sustainable Packaging Materials
Banana paper and sugarcane paper are innovative sustainable packaging materials derived from agricultural waste, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional wood-based paper. Banana paper, made from banana plant fibers, boasts strong durability and biodegradability, while sugarcane paper, produced from bagasse, provides excellent moisture resistance and compostability. Both materials significantly reduce deforestation and carbon emissions, supporting circular economy goals in sustainable packaging.
What is Banana Paper?
Banana paper is an eco-friendly packaging material made from the fibers of banana plant trunks, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional paper by utilizing agricultural waste. It features natural durability, biodegradability, and a unique texture suitable for various packaging applications. Compared to sugarcane paper, banana paper provides comparable strength while reducing reliance on food crops and minimizing environmental impact.
What is Sugarcane Paper?
Sugarcane paper is an eco-friendly packaging material made from bagasse, the fibrous residue left after extracting juice from sugarcane stalks, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional wood-based paper. Its production reduces agricultural waste and lowers carbon emissions, making it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious brands. Compared to banana paper, sugarcane paper provides comparable durability and printability, enhancing brand presentation while supporting circular economy principles.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Banana paper and sugarcane paper both offer sustainable packaging alternatives, but banana paper uses agricultural waste from banana plants, reducing landfill waste and promoting resource efficiency with low water consumption during production. Sugarcane paper leverages bagasse, a byproduct of sugar extraction, minimizing deforestation and lowering greenhouse gas emissions due to its fast-growing crop cycle and renewable nature. Both materials significantly reduce plastic pollution and carbon footprints compared to conventional paper, yet banana paper tends to have a slightly smaller environmental impact due to its utilization of non-food plant waste.
Material Properties and Strength
Banana paper exhibits high tensile strength and natural fiber durability, making it resistant to tearing and suitable for eco-friendly packaging that requires flexibility and resilience. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse, offers excellent stiffness and moisture resistance, enhancing its ability to protect contents while maintaining biodegradability. Both materials provide sustainable alternatives to traditional paper, with banana paper excelling in toughness and sugarcane paper in structural rigidity for packaging applications.
Cost and Production Scalability
Banana paper offers a cost-effective alternative due to its use of agricultural waste, reducing raw material expenses, but production scalability remains limited by seasonal fiber availability. Sugarcane paper benefits from abundant agro-industrial byproducts, enabling higher production scalability and more consistent supply chains, which often translates to lower long-term costs. While banana paper targets niche, eco-conscious markets, sugarcane paper's scalability and competitive pricing make it a stronger candidate for mass packaging applications.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Banana paper and sugarcane paper both offer high biodegradability, decomposing naturally within weeks to months under composting conditions, making them eco-friendly packaging options. Banana paper, derived from banana plant fibers, tends to have a slightly faster degradation rate due to its loose fiber structure, while sugarcane paper, made from bagasse, provides durability alongside compostability. Both materials support multiple end-of-life options including composting, recycling where facilities exist, and safe landfill disposal, significantly reducing environmental impact compared to conventional plastic packaging.
Usability in Packaging Applications
Banana paper offers excellent durability and moisture resistance, making it suitable for eco-friendly packaging of lightweight products, while sugarcane paper excels in strength and printability, ideal for high-quality packaging and branding. Both materials provide biodegradable and sustainable alternatives to conventional paper, but sugarcane paper's smooth texture enhances graphic clarity and packaging aesthetics. Usability in packaging depends on product requirements, with banana paper favored for flexible applications and sugarcane paper preferred for rigid or premium packaging solutions.
Market Adoption and Industry Trends
Banana paper and sugarcane paper are gaining traction in the sustainable packaging market due to their eco-friendly properties and biodegradability. Sugarcane paper, derived from agricultural waste like bagasse, sees higher adoption in large-scale packaging industries because of its cost-effectiveness and established supply chains. Banana paper, made from banana stem fibers, appeals to niche markets emphasizing zero-waste and artisanal products, reflecting a growing trend toward diversification in sustainable packaging solutions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Eco-Friendly Paper
Banana paper offers superior durability and biodegradability due to its strong fiber composition, making it ideal for sturdy packaging needs. Sugarcane paper excels in cost-effectiveness and sustainability by utilizing agricultural waste, providing a versatile option for eco-friendly packaging. Selecting the right paper depends on balancing durability requirements and environmental impact, with both materials significantly reducing reliance on traditional wood-based paper.
Infographic: Banana paper vs Sugarcane paper for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com