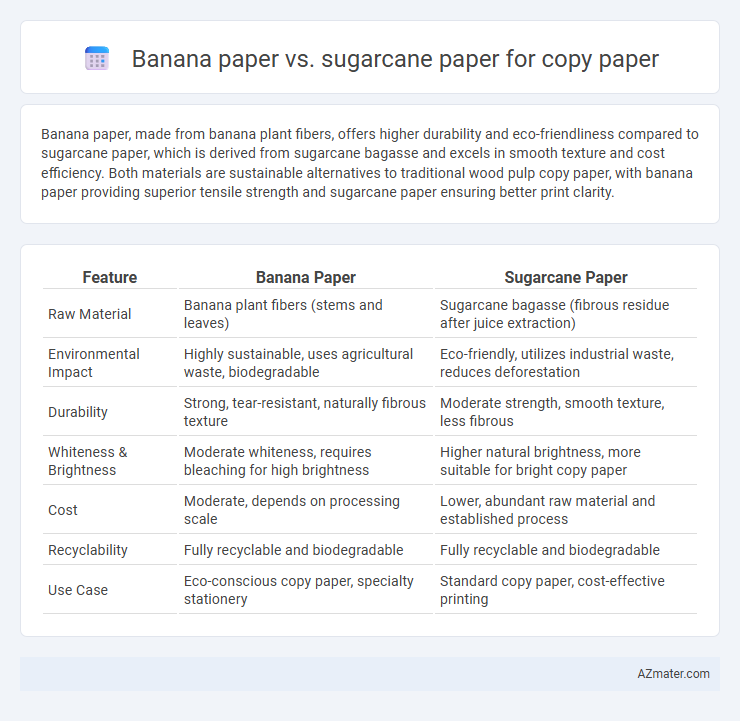
Banana paper, made from banana plant fibers, offers higher durability and eco-friendliness compared to sugarcane paper, which is derived from sugarcane bagasse and excels in smooth texture and cost efficiency. Both materials are sustainable alternatives to traditional wood pulp copy paper, with banana paper providing superior tensile strength and sugarcane paper ensuring better print clarity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Banana Paper | Sugarcane Paper |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Banana plant fibers (stems and leaves) | Sugarcane bagasse (fibrous residue after juice extraction) |
| Environmental Impact | Highly sustainable, uses agricultural waste, biodegradable | Eco-friendly, utilizes industrial waste, reduces deforestation |
| Durability | Strong, tear-resistant, naturally fibrous texture | Moderate strength, smooth texture, less fibrous |
| Whiteness & Brightness | Moderate whiteness, requires bleaching for high brightness | Higher natural brightness, more suitable for bright copy paper |
| Cost | Moderate, depends on processing scale | Lower, abundant raw material and established process |
| Recyclability | Fully recyclable and biodegradable | Fully recyclable and biodegradable |
| Use Case | Eco-conscious copy paper, specialty stationery | Standard copy paper, cost-effective printing |
Introduction: Exploring Eco-Friendly Copy Paper Alternatives
Banana paper and sugarcane paper emerge as innovative, sustainable alternatives to traditional wood-based copy paper, leveraging agricultural waste to reduce deforestation. Banana paper, made from banana plant fibers, offers durability and biodegradability, while sugarcane paper utilizes bagasse, a byproduct of sugar extraction, ensuring high fiber content and eco-efficiency. Both materials significantly lower carbon footprints and water consumption, aligning with growing demand for environmentally responsible office supplies.
Overview of Banana Paper Production
Banana paper production involves using the fibrous pseudostems of banana plants, which are typically agricultural waste, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood-based paper. The fibers are cleaned, boiled, and processed into pulp before being pressed into sheets, requiring less chemical treatment compared to wood pulp, which enhances its sustainability. This method not only reduces deforestation but also supports waste valorization in banana-growing regions, offering a renewable resource for copy paper manufacturing.
Overview of Sugarcane Paper Production
Sugarcane paper production utilizes bagasse, the fibrous byproduct left after extracting juice from sugarcane stalks, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional wood pulp paper. This process involves pulping bagasse fibers, bleaching, and pressing them into sheets, resulting in durable, smooth, and biodegradable copy paper. Compared to banana paper, sugarcane paper offers greater scalability and resource efficiency due to widespread sugarcane cultivation and the utilization of agricultural waste.
Environmental Impact: Banana Paper vs Sugarcane Paper
Banana paper, made from banana plant fibers, offers a sustainable alternative that reduces deforestation and repurposes agricultural waste, minimizing landfill contributions. Sugarcane paper, derived from bagasse--the fibrous residue of sugarcane processing--also promotes waste valorization and decreases reliance on wood pulp, resulting in lower carbon emissions and water consumption. Both papers significantly lower the environmental footprint compared to traditional wood-based copy paper, with sugarcane paper often exhibiting enhanced biodegradability and banana paper providing durable, eco-friendly qualities.
Paper Quality: Texture, Appearance, and Performance
Banana paper exhibits a distinctive fibrous texture and natural off-white appearance, offering high durability and resistance to tearing, making it ideal for premium copy paper applications. Sugarcane paper delivers a smoother surface with a consistent white shade and excellent print clarity, ensuring efficient performance in high-volume copying and printing tasks. Both papers provide eco-friendly alternatives, but banana paper's rougher texture favors artistic or specialty use, while sugarcane paper excels in standard office environments due to its superior smoothness and brightness.
Raw Material Availability and Sustainability
Banana paper is derived from agricultural waste like banana stems, offering a sustainable alternative by repurposing materials typically discarded, though its availability is region-specific to banana-growing areas. Sugarcane paper utilizes bagasse, the fibrous residue left after extracting juice, benefiting from the extensive global sugarcane cultivation that ensures a more consistent raw material supply. Both options reduce reliance on traditional wood pulp, but sugarcane paper generally provides a broader raw material availability and sustainability advantage due to the large-scale byproduct utilization in the sugar industry.
Manufacturing Process and Energy Consumption
Banana paper manufacturing utilizes agricultural waste from banana plants, primarily banana stalks, which undergo mechanical pulping and chemical retting, resulting in lower water and energy consumption compared to sugarcane paper. Sugarcane paper, often made from bagasse, involves intensive mechanical and chemical processes including high-temperature pulping and bleaching that demand substantial energy inputs. Energy consumption for banana paper production is typically 20-30% less than sugarcane paper, owing to its simpler processing steps and reduced chemical usage.
Cost Comparison: Banana Paper vs Sugarcane Paper
Banana paper tends to have higher production costs due to the manual extraction process of banana fibers, resulting in a slightly more expensive price per ream compared to sugarcane paper. Sugarcane paper benefits from the abundant availability of bagasse, a byproduct of sugar production, making it a more cost-effective option for bulk copy paper manufacturing. Overall, sugarcane paper offers better cost efficiency while banana paper provides enhanced durability and eco-friendliness, influencing pricing dynamics in different market segments.
Market Applications and Suitability for Copy Paper
Banana paper offers excellent durability and natural fiber strength suitable for high-quality copy paper, making it ideal for eco-conscious office environments seeking sustainable alternatives. Sugarcane paper provides superior whiteness and smooth texture, enhancing print clarity and is widely favored in mass-market copy paper production. Both materials align with increasing demand for environmentally friendly paper solutions, but sugarcane paper's cost-effectiveness and ease of processing position it as the more practical choice for large-scale copy paper applications.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Sustainable Copy Paper Option
Banana paper offers durability and eco-friendliness by utilizing agricultural waste, while sugarcane paper excels in softness and waste reduction with high post-consumer content. Both materials significantly reduce deforestation and water consumption compared to traditional wood-pulp paper. Choosing the best sustainable copy paper depends on prioritizing either strength and texture or maximum recycled content and environmental impact.
Infographic: Banana paper vs Sugarcane paper for Copy paper
 azmater.com
azmater.com