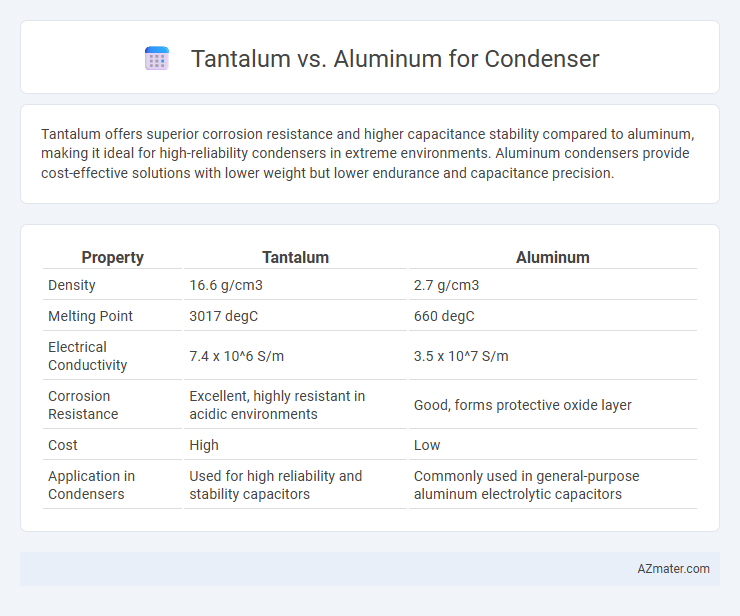
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and higher capacitance stability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for high-reliability condensers in extreme environments. Aluminum condensers provide cost-effective solutions with lower weight but lower endurance and capacitance precision.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Tantalum | Aluminum |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 16.6 g/cm3 | 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 3017 degC | 660 degC |
| Electrical Conductivity | 7.4 x 10^6 S/m | 3.5 x 10^7 S/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, highly resistant in acidic environments | Good, forms protective oxide layer |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Application in Condensers | Used for high reliability and stability capacitors | Commonly used in general-purpose aluminum electrolytic capacitors |
Introduction to Tantalum and Aluminum Condensers
Tantalum condensers feature a tantalum metal anode that offers superior capacitance stability and higher volumetric efficiency compared to aluminum condensers, making them ideal for compact electronic devices. Aluminum condensers use an aluminum foil anode and are widely favored for their lower cost and good performance in a broad voltage range, especially in power electronics. The key distinction lies in tantalum's higher reliability and better frequency response, while aluminum capacitors excel in applications requiring larger capacitance values and cost-effectiveness.
Material Properties: Tantalum vs Aluminum
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and higher melting point compared to aluminum, making it ideal for condensers operating under extreme temperatures and aggressive environments. Aluminum, while lightweight and cost-effective with excellent thermal conductivity, is prone to corrosion and lower mechanical strength than tantalum. The choice between tantalum and aluminum depends on the application's demands for durability, thermal performance, and environmental resistance.
Performance Efficiency Comparison
Tantalum capacitors exhibit superior performance efficiency in condensers due to their high volumetric capacitance and excellent frequency stability compared to aluminum capacitors, which typically have larger sizes for equivalent capacitance values. Tantalum's low equivalent series resistance (ESR) enhances energy efficiency and reduces power loss, making it ideal for high-frequency and ripple current applications. Aluminum capacitors often demonstrate lower cost but tend to have higher ESR and lower long-term reliability under thermal stress, limiting their performance in precision condenser applications.
Corrosion Resistance Analysis
Tantalum exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum in condenser applications, especially in acidic or chloride-rich environments due to its stable oxide layer that prevents metal degradation. While aluminum is lightweight and cost-effective, it is more prone to pitting and galvanic corrosion when exposed to aggressive media commonly found in condensers. The enhanced chemical inertness of tantalum ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance in harsh operating conditions.
Thermal Conductivity and Heat Transfer
Tantalum offers a thermal conductivity of approximately 57 W/m*K, which is significantly lower than aluminum's thermal conductivity of around 205 W/m*K, making aluminum more efficient for heat transfer applications in condensers. Aluminum's superior heat transfer capability enhances condenser performance by facilitating rapid dissipation of heat, reducing thermal resistance, and improving overall energy efficiency. While tantalum provides excellent corrosion resistance, aluminum remains the preferred choice for condensers where maximizing thermal conductivity and efficient heat transfer is critical.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Tantalum capacitors offer high reliability and stability but come at a significantly higher cost compared to aluminum capacitors, primarily due to the scarcity of tantalum ore and complex manufacturing processes. Aluminum capacitors benefit from abundant raw material availability and cost-effective production, making them the preferred choice for large-scale and budget-sensitive applications. Cost-sensitive projects with high volume demands typically opt for aluminum capacitors, whereas tantalum is chosen in performance-critical applications despite its premium price and limited supply.
Durability and Lifespan
Tantalum capacitors offer superior durability and lifespan compared to aluminum capacitors due to their robust oxide layer, which provides better resistance to corrosion and dielectric breakdown. Tantalum's stable oxide film enhances operational longevity under high temperature and stress conditions, making it ideal for critical applications. Aluminum capacitors, while cost-effective, tend to have shorter lifespans and are more prone to electrolyte drying and leakage, affecting long-term reliability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan in condenser applications, reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements, which enhances sustainability. Aluminum is abundant and lightweight, leading to lower energy consumption during manufacturing and easier recyclability, but its shorter durability can result in higher environmental costs over time. Choosing between tantalum and aluminum hinges on balancing immediate environmental benefits with long-term sustainability goals in condenser design.
Typical Applications in Industry
Tantalum is preferred in condenser applications requiring high corrosion resistance and stable conductivity, commonly used in aerospace, medical devices, and military electronics where durability under extreme conditions is critical. Aluminum condensers dominate in HVAC systems, automotive radiators, and large-scale industrial cooling due to their lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and excellent thermal conductivity. The choice between tantalum and aluminum hinges on application-specific needs for corrosion resistance, thermal performance, and budget constraints in industrial environments.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Condenser
Tantalum offers superior corrosion resistance and high-temperature stability compared to aluminum, making it ideal for condensers in harsh or demanding environments. Aluminum provides excellent thermal conductivity and lightweight properties, making it cost-effective and suitable for standard condenser applications. Selecting the right material depends on balancing factors such as operating temperature, corrosion exposure, budget constraints, and desired lifespan of the condenser.
Infographic: Tantalum vs Aluminum for Condenser
 azmater.com
azmater.com