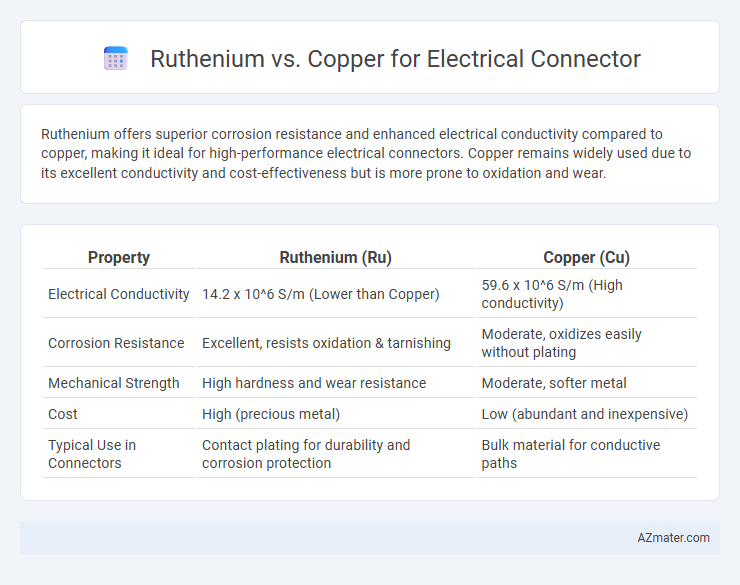
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and enhanced electrical conductivity compared to copper, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors. Copper remains widely used due to its excellent conductivity and cost-effectiveness but is more prone to oxidation and wear.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ruthenium (Ru) | Copper (Cu) |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 14.2 x 10^6 S/m (Lower than Copper) | 59.6 x 10^6 S/m (High conductivity) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists oxidation & tarnishing | Moderate, oxidizes easily without plating |
| Mechanical Strength | High hardness and wear resistance | Moderate, softer metal |
| Cost | High (precious metal) | Low (abundant and inexpensive) |
| Typical Use in Connectors | Contact plating for durability and corrosion protection | Bulk material for conductive paths |
Introduction to Electrical Connector Materials
Ruthenium and copper are prominent materials utilized in electrical connectors due to their conductive properties and durability. Ruthenium, a rare platinum-group metal, offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance, high-reliability connectors. Copper provides cost-effective conductivity with high electrical and thermal performance but requires protective coatings to prevent oxidation in harsh environments.
Key Properties of Ruthenium and Copper
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and higher hardness compared to copper, enhancing durability and longevity in electrical connectors exposed to harsh environments. Copper excels in electrical conductivity, providing excellent current carrying capacity and low resistance, which is critical for efficient signal transmission. Ruthenium's ability to maintain stable contact resistance under mechanical stress makes it ideal for high-reliability applications, while copper remains the preferred choice for cost-effective, high-conductivity needs.
Electrical Conductivity Comparison
Ruthenium offers excellent corrosion resistance and durability in electrical connectors but exhibits lower electrical conductivity than copper, which is among the highest conductors with approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m. Copper's superior conductivity ensures minimal electrical resistance and efficient current flow, making it the preferred choice for high-performance electrical connections. Ruthenium, often used as a plating material, enhances connector lifespan and reliability despite its lower conductivity compared to pure copper.
Corrosion Resistance: Ruthenium vs Copper
Ruthenium exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to copper, maintaining conductivity and structural integrity in harsh environments such as high humidity and acidic conditions. Copper tends to oxidize and form surface corrosion layers that degrade electrical performance over time, necessitating protective coatings or frequent maintenance. The robust corrosion resistance of ruthenium significantly enhances the longevity and reliability of electrical connectors in demanding applications.
Mechanical Durability and Wear
Ruthenium offers superior mechanical durability and wear resistance compared to copper, making it ideal for electrical connectors subjected to frequent mating cycles. Ruthenium's hardness reduces surface deformation and contact resistance over time, whereas copper tends to deform easily under mechanical stress, leading to increased wear and potential signal loss. This enhanced longevity of ruthenium-coated connectors significantly improves reliability in high-performance electronic applications.
Cost and Availability Considerations
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability for electrical connectors but comes at a significantly higher cost due to its scarcity and limited mining sources compared to copper. Copper remains the most cost-effective and widely available option, benefiting from extensive global production and established recycling processes. The choice between ruthenium and copper depends on balancing budget constraints with performance requirements in connector applications.
Applications in Modern Electronics
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and stable conductivity compared to copper, making it ideal for high-reliability electrical connectors in aerospace and telecommunications. Copper, known for its excellent electrical conductivity and cost-effectiveness, remains prevalent in consumer electronics and power distribution systems. Ruthenium coatings on copper contacts enhance durability and performance in microelectronic connectors used in smartphones and advanced computing devices.
Environmental and Safety Impacts
Ruthenium offers greater corrosion resistance and longer lifespan in electrical connectors, reducing environmental waste compared to copper, which tends to oxidize and degrade more quickly. Copper mining and refining involve significant environmental pollutants and energy consumption, whereas ruthenium, a rare platinum-group metal, requires less frequent replacement, mitigating overall environmental damage despite its extraction challenges. Both metals demand careful handling, but copper's higher toxicity and potential for soil and water contamination pose greater safety risks during manufacture and disposal.
Industry Trends and Preferences
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and longer lifespan compared to copper, making it increasingly preferred in high-reliability electrical connectors within the aerospace and automotive industries. Industry trends show a rising demand for ruthenium-plated connectors due to their enhanced conductivity and durability under extreme conditions, despite higher material costs. Copper remains dominant in cost-sensitive applications, but shifts toward ruthenium coatings grow as manufacturers prioritize performance and longevity in advanced electronics.
Choosing the Best Material for Your Connector
Ruthenium offers superior corrosion resistance and enhances electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance electrical connectors exposed to harsh environments. Copper remains a cost-effective choice with excellent conductivity but is more prone to oxidation and wear over time. Selecting Ruthenium-plated connectors ensures longer durability and stable signal transmission, while copper connectors suit budget-sensitive applications with moderate performance requirements.
Infographic: Ruthenium vs Copper for Electrical Connector
 azmater.com
azmater.com