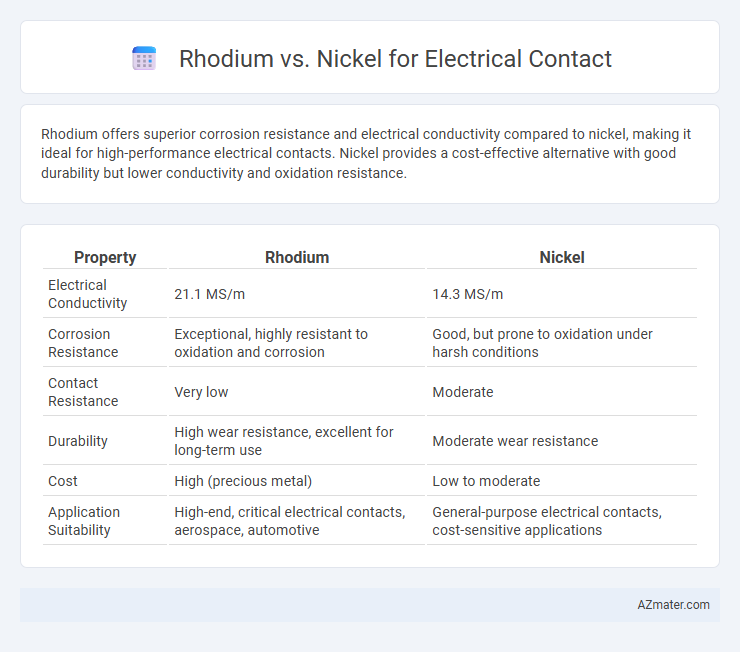
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to nickel, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts. Nickel provides a cost-effective alternative with good durability but lower conductivity and oxidation resistance.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Rhodium | Nickel |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | 21.1 MS/m | 14.3 MS/m |
| Corrosion Resistance | Exceptional, highly resistant to oxidation and corrosion | Good, but prone to oxidation under harsh conditions |
| Contact Resistance | Very low | Moderate |
| Durability | High wear resistance, excellent for long-term use | Moderate wear resistance |
| Cost | High (precious metal) | Low to moderate |
| Application Suitability | High-end, critical electrical contacts, aerospace, automotive | General-purpose electrical contacts, cost-sensitive applications |
Introduction to Rhodium and Nickel in Electrical Contacts
Rhodium and nickel are widely used metals in electrical contacts due to their excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. Rhodium offers superior hardness, oxidation resistance, and low contact resistance, making it ideal for high-reliability applications such as automotive and aerospace connectors. Nickel provides good electrical conductivity and mechanical strength at a lower cost, commonly used in general-purpose electrical contacts and terminals.
Key Properties of Rhodium and Nickel
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and hardness, making it ideal for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments and high wear conditions. Nickel provides excellent conductivity and solderability with moderate corrosion resistance, often used in cost-sensitive applications requiring reliable electrical performance. Rhodium's higher melting point and better resistance to oxidation contribute to longer contact lifespan compared to nickel in demanding electrical systems.
Conductivity Comparison: Rhodium vs Nickel
Rhodium exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to nickel, making it a preferred choice for high-performance electrical contacts requiring minimal resistive loss. Nickel's conductivity is significantly lower, approximately 14.3% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), whereas rhodium offers conductivity closer to 20% IACS, enhancing signal integrity and reducing power dissipation. The higher conductivity of rhodium ensures better efficiency and longevity in electrical contact applications where reliable current flow is critical.
Corrosion and Oxidation Resistance
Rhodium offers superior corrosion and oxidation resistance compared to nickel, making it ideal for electrical contacts exposed to harsh environments. Its noble metal properties prevent the formation of oxides that can degrade conductivity over time, ensuring stable performance and longevity. Nickel, while cost-effective, is more prone to oxidation and corrosion, which can increase contact resistance and reduce electrical reliability.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Rhodium offers superior mechanical strength and excellent resistance to wear and corrosion, making it highly durable for electrical contacts in harsh environments. Nickel provides good mechanical strength and corrosion resistance but tends to have lower hardness compared to rhodium, which can lead to faster wear under high friction conditions. The enhanced durability of rhodium results in longer contact life and more reliable electrical performance in demanding applications.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity compared to nickel, but its significantly higher cost limits widespread use in electrical contacts. Nickel is more abundant and affordable, making it a practical choice for many industrial applications despite slightly lower performance. Availability of rhodium is constrained by limited mining sources, whereas nickel benefits from extensive global reserves and established supply chains.
Application Suitability: Rhodium vs Nickel
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance electrical contacts in aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications industries. Nickel, while more cost-effective, provides robust wear resistance and moderate conductivity, better suited for general-purpose applications with less stringent electrical demands. Choosing between rhodium and nickel depends on the criticality of conductivity and durability requirements in specific electrical contact applications.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Rhodium offers superior lifespan compared to nickel in electrical contacts due to its exceptional corrosion resistance and hardness, reducing wear and oxidation over time. Nickel contacts, while cost-effective, require more frequent maintenance and cleaning to prevent deterioration and ensure reliable conductivity. Rhodium's minimal maintenance needs make it ideal for high-reliability applications where long-term performance is critical.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and durability compared to nickel, reducing the frequency of replacements and minimizing environmental waste from discarded contacts. Nickel plating can pose allergy risks and release harmful nickel ions during wear or disposal, raising concerns about human health and environmental pollution. Choosing rhodium for electrical contacts supports safer handling and reduces toxic metal leaching, aligning with stricter environmental regulations and sustainability goals.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Metal for Electrical Contacts
Rhodium offers superior corrosion resistance and maintains excellent conductivity under high-temperature conditions, making it ideal for critical electrical contacts requiring long-term reliability. Nickel provides robust mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness but may suffer from oxidation and higher resistance over time in harsh environments. Selecting between rhodium and nickel depends on balancing performance needs with budget constraints and operating conditions to ensure optimal electrical contact durability and efficiency.
Infographic: Rhodium vs Nickel for Electrical Contact
 azmater.com
azmater.com