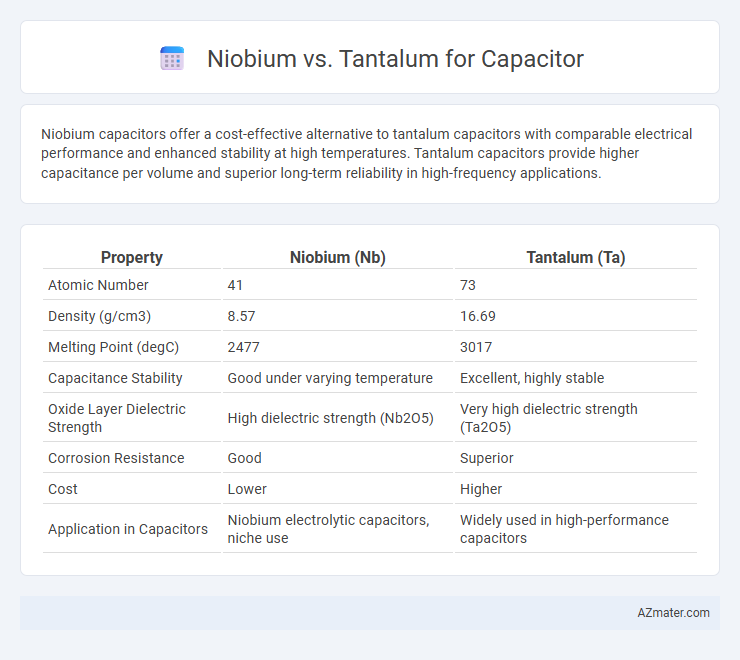
Niobium capacitors offer a cost-effective alternative to tantalum capacitors with comparable electrical performance and enhanced stability at high temperatures. Tantalum capacitors provide higher capacitance per volume and superior long-term reliability in high-frequency applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Niobium (Nb) | Tantalum (Ta) |
|---|---|---|
| Atomic Number | 41 | 73 |
| Density (g/cm3) | 8.57 | 16.69 |
| Melting Point (degC) | 2477 | 3017 |
| Capacitance Stability | Good under varying temperature | Excellent, highly stable |
| Oxide Layer Dielectric Strength | High dielectric strength (Nb2O5) | Very high dielectric strength (Ta2O5) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good | Superior |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Application in Capacitors | Niobium electrolytic capacitors, niche use | Widely used in high-performance capacitors |
Introduction to Niobium and Tantalum Capacitors
Niobium and tantalum capacitors are essential components in electronic circuits, valued for their high capacitance and reliability. Niobium capacitors leverage niobium pentoxide as the dielectric, offering cost-effective alternatives with lower toxicity compared to tantalum capacitors that use tantalum pentoxide dielectrics. Both types excel in stability and volumetric efficiency, with specific benefits depending on the application requirements such as frequency response and temperature tolerance.
Material Properties: Niobium vs Tantalum
Niobium capacitors offer higher volumetric efficiency and excellent corrosion resistance compared to tantalum counterparts, primarily due to niobium's stable oxide layer aiding dielectric strength. Tantalum provides superior capacitance per volume and reliable performance under high-temperature conditions, attributed to its dense oxide film formation. Both materials exhibit high melting points--niobium at 2,468degC and tantalum at 3,017degC--ensuring thermal stability in advanced capacitor applications.
Electrical Performance Comparison
Niobium capacitors exhibit lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) and improved leakage current stability compared to tantalum capacitors, enhancing overall efficiency in high-frequency applications. Tantalum capacitors offer higher volumetric capacitance and superior thermal stability, making them preferable for environments with elevated temperature conditions. Both materials provide excellent capacitance retention, but niobium shows better performance in pulse current handling and long-term reliability under high-stress electrical loads.
Reliability and Lifespan Factors
Niobium capacitors offer enhanced reliability and longer lifespan due to their stable oxide layer, which resists degradation under high temperature and voltage stress better than tantalum. Tantalum capacitors, while widely used, are more prone to dielectric breakdown and failure under surge current conditions, impacting long-term durability. The intrinsic material properties of niobium contribute to improved leakage current characteristics and lower ESR, making niobium capacitors more suitable for high-reliability applications.
Safety and Failure Modes
Niobium capacitors offer enhanced safety due to their lower risk of short circuits caused by self-healing oxide layers, while tantalum capacitors are more prone to catastrophic failures if subjected to voltage spikes or overheating. The failure mode of tantalum capacitors often involves thermal runaway and ignition, making them less reliable in high-stress environments. Niobium capacitors exhibit better thermal stability and reduced failure rates, making them preferable for applications prioritizing safety and long-term reliability.
Cost and Market Availability
Niobium capacitors offer a cost advantage over tantalum capacitors due to lower raw material prices and more abundant supply, making them more budget-friendly for large-scale applications. The market availability of niobium is higher with fewer supply chain disruptions compared to tantalum, whose limited deposits and geopolitical risks can lead to price volatility and sourcing challenges. Consequently, niobium capacitors are increasingly favored in industries seeking a reliable, economically viable alternative to tantalum without compromising performance.
Applications and Industry Usage
Niobium capacitors are favored in aerospace and military applications due to their superior volumetric efficiency and reliability under extreme conditions. Tantalum capacitors dominate consumer electronics and telecommunications industries, offering high capacitance in compact sizes with stable electrical performance. Both materials are critical in automotive electronics and medical devices, where durability and consistent capacitance are essential.
Environmental and Ethical Considerations
Niobium and tantalum, both critical metals used in capacitors, differ significantly in environmental and ethical impacts. Niobium is mainly sourced from stable mining regions like Brazil and Canada, resulting in lower risks of conflict minerals and more regulated extraction practices, while tantalum often comes from conflict-affected areas such as the Democratic Republic of Congo, raising concerns about human rights abuses and unethical labor conditions. The lower environmental footprint of niobium mining, combined with its greater availability and recyclability, makes it a more sustainable and ethically responsible choice for capacitor manufacturing.
Advancements and Future Trends
Niobium and tantalum capacitors have seen significant advancements in dielectric materials and electrode technology, enhancing their energy density and reliability for high-performance electronics. Emerging trends emphasize the development of niobium capacitors due to their cost-effectiveness and improved temperature stability, making them suitable for automotive and aerospace applications. Future research focuses on nano-structured anodes and hybrid capacitor systems to optimize capacitance, reduce equivalent series resistance (ESR), and extend operational lifespan.
Choosing the Right Capacitor: Niobium or Tantalum
Choosing the right capacitor between niobium and tantalum depends on application-specific requirements like voltage rating, capacitance stability, and cost efficiency. Niobium capacitors offer a lower-cost alternative with comparable performance for high-capacitance, low-voltage applications, while tantalum capacitors excel in high-reliability, high-temperature environments requiring stable capacitance and low ESR. Evaluating factors such as equivalent series resistance (ESR), ripple current tolerance, and environmental conditions ensures optimal performance and longevity in electronic circuits.
Infographic: Niobium vs Tantalum for Capacitor
 azmater.com
azmater.com