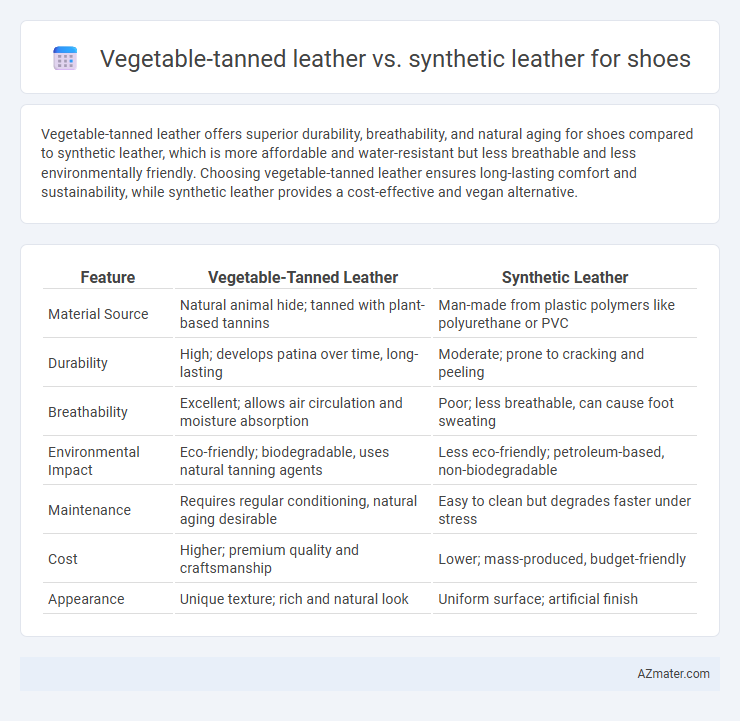
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability, breathability, and natural aging for shoes compared to synthetic leather, which is more affordable and water-resistant but less breathable and less environmentally friendly. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures long-lasting comfort and sustainability, while synthetic leather provides a cost-effective and vegan alternative.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Synthetic Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Natural animal hide; tanned with plant-based tannins | Man-made from plastic polymers like polyurethane or PVC |
| Durability | High; develops patina over time, long-lasting | Moderate; prone to cracking and peeling |
| Breathability | Excellent; allows air circulation and moisture absorption | Poor; less breathable, can cause foot sweating |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; biodegradable, uses natural tanning agents | Less eco-friendly; petroleum-based, non-biodegradable |
| Maintenance | Requires regular conditioning, natural aging desirable | Easy to clean but degrades faster under stress |
| Cost | Higher; premium quality and craftsmanship | Lower; mass-produced, budget-friendly |
| Appearance | Unique texture; rich and natural look | Uniform surface; artificial finish |
Overview: Vegetable-Tanned Leather vs Synthetic Leather
Vegetable-tanned leather, crafted using natural tannins from plant sources, offers durability, breathability, and the ability to develop a unique patina over time, making it ideal for premium footwear. Synthetic leather, typically made from polyurethane or PVC, provides a cost-effective, water-resistant alternative with consistent texture and lower environmental impact during production. Choosing between vegetable-tanned and synthetic leather depends on factors such as sustainability preferences, durability requirements, and aesthetic appeal for shoe manufacturing.
Material Composition and Sources
Vegetable-tanned leather is derived from natural animal hides treated with tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, providing a biodegradable and durable option for high-quality shoes. Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane (PU) or polyvinyl chloride (PVC), uses petroleum-based polymers designed to mimic the texture and appearance of natural leather but lacks the organic origins and breathability of vegetable-tanned leather. The material composition difference significantly impacts sustainability, with vegetable-tanned leather sourced from renewable natural inputs, while synthetic leather depends largely on non-renewable fossil fuels.
Production Processes and Environmental Impact
Vegetable-tanned leather for shoes is produced using natural tannins from plant sources like bark and leaves, resulting in fewer harmful chemicals and a biodegradable product. Synthetic leather, often made from polyurethane or PVC, involves petroleum-based processes with higher greenhouse gas emissions and non-biodegradable waste. The environmental impact of vegetable-tanned leather is lower due to its renewable resources and traditional methods, whereas synthetic leather contributes significantly to pollution and resource depletion.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability and ages gracefully, developing a unique patina over time that enhances its longevity. Synthetic leather, while often more resistant to water and stains, tends to crack and peel with prolonged use, reducing its lifespan. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures a longer-lasting, more robust shoe that maintains structural integrity better than synthetic alternatives.
Comfort and Feel for Footwear
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior breathability and molds naturally to the foot, providing enhanced comfort and a personalized fit over time. In contrast, synthetic leather tends to lack the same level of moisture absorption and flexibility, often resulting in less ventilation and a stiffer feel during extended wear. The natural fibers in vegetable-tanned leather also contribute to temperature regulation, making it a preferred choice for footwear aimed at long-term comfort.
Aesthetics: Texture, Color, and Aging
Vegetable-tanned leather boasts a rich, natural texture with unique grain patterns that deepen and develop a distinctive patina over time, enhancing shoe aesthetics. Its colors are typically warm and earthy, evolving gracefully through exposure to sunlight and wear, resulting in a personalized vintage look. Synthetic leather offers uniform texture and color consistency but lacks the aging charm and depth of character found in vegetable-tanned leather, often appearing flat and less dynamic over time.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior breathability and moisture management compared to synthetic leather, allowing air to circulate naturally and helping to wick away sweat from the foot. This material's porous structure reduces moisture buildup, preventing odor and enhancing overall foot comfort during extended wear. Synthetic leather, often less permeable, traps heat and moisture, increasing the risk of discomfort and skin irritation in shoe applications.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Vegetable-tanned leather requires regular conditioning with natural oils or leather balms to maintain its flexibility and prevent drying or cracking, and it benefits from occasional polishing to enhance its rich patina. Synthetic leather demands less maintenance, typically needing only occasional cleaning with a damp cloth and mild soap to remove dirt, but it may degrade faster under harsh conditions or prolonged exposure to heat and sunlight. Proper storage away from moisture and extreme temperatures prolongs the lifespan of both materials, with vegetable-tanned leather benefiting from breathable storage solutions to avoid mold and mildew.
Cost Efficiency and Value for Money
Vegetable-tanned leather shoes typically have a higher upfront cost due to the labor-intensive tanning process and premium raw materials, but they offer superior durability and develop a unique patina over time, enhancing long-term value and aesthetic appeal. Synthetic leather shoes are more affordable initially and resistant to water and stains, making them cost-efficient for budget-conscious consumers seeking easy maintenance and ethical alternatives. Considering overall lifespan and aging characteristics, vegetable-tanned leather provides greater value for money through prolonged wear, while synthetic options excel in lower initial investment and consistent appearance.
Sustainability and Ethical Considerations
Vegetable-tanned leather, derived from natural tannins in plant materials, offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic leather, which is typically made from petrochemical-based plastics contributing to microplastic pollution. The production of vegetable-tanned leather often supports ethical labor practices and reduces harmful chemical use compared to synthetic leather manufacturing processes that can involve toxic solvents and high energy consumption. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather for shoes aligns with sustainable fashion principles by promoting durability, biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact over synthetic alternatives.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Synthetic leather for Shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com