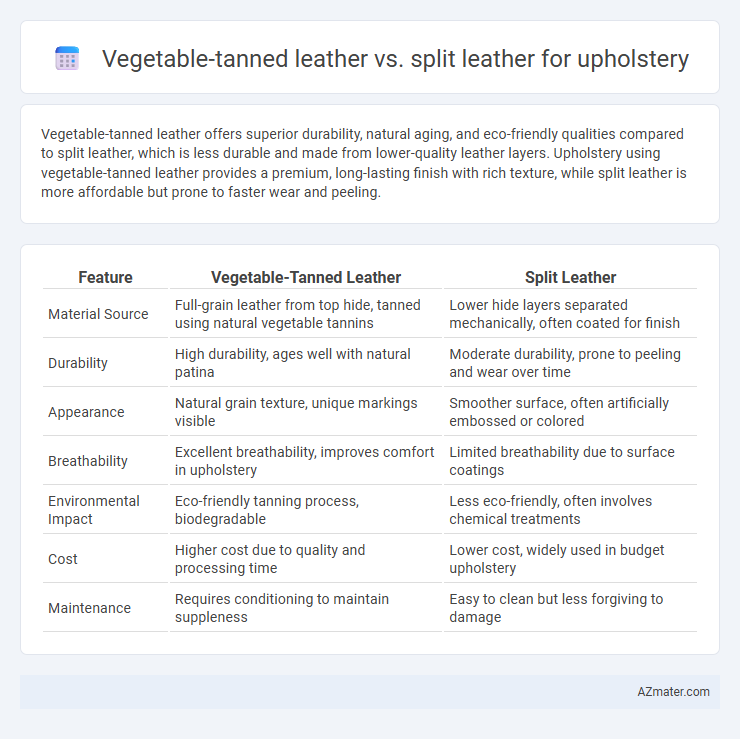
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability, natural aging, and eco-friendly qualities compared to split leather, which is less durable and made from lower-quality leather layers. Upholstery using vegetable-tanned leather provides a premium, long-lasting finish with rich texture, while split leather is more affordable but prone to faster wear and peeling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Vegetable-Tanned Leather | Split Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Full-grain leather from top hide, tanned using natural vegetable tannins | Lower hide layers separated mechanically, often coated for finish |
| Durability | High durability, ages well with natural patina | Moderate durability, prone to peeling and wear over time |
| Appearance | Natural grain texture, unique markings visible | Smoother surface, often artificially embossed or colored |
| Breathability | Excellent breathability, improves comfort in upholstery | Limited breathability due to surface coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly tanning process, biodegradable | Less eco-friendly, often involves chemical treatments |
| Cost | Higher cost due to quality and processing time | Lower cost, widely used in budget upholstery |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning to maintain suppleness | Easy to clean but less forgiving to damage |
Introduction to Leather Types in Upholstery
Vegetable-tanned leather, known for its natural and eco-friendly tanning process using plant-based tannins, offers durability and develops a rich patina over time, making it ideal for high-quality upholstery. Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layer of animal hides, provides a more affordable option but typically lacks the strength and aesthetic appeal of top-grain leather used in upholstery. Understanding these leather types helps in selecting materials that balance cost, durability, and appearance for furniture applications.
What is Vegetable-Tanned Leather?
Vegetable-tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant sources, resulting in a durable and eco-friendly material ideal for upholstery. This type of leather develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its aesthetic appeal and longevity compared to split leather, which is made from the lower layers of the hide and treated with chemicals. Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior breathability and strength, making it a preferred choice for high-quality furniture upholstery.
Understanding Split Leather
Split leather is created by separating the fibrous layers of the hide, leaving a lower-quality, less durable material compared to full-grain or vegetable-tanned leather. Unlike vegetable-tanned leather, which is processed using natural tannins and retains the hide's original grain, split leather typically undergoes heavy finishing or coating to mimic the appearance of higher-grade leather. Its porous structure absorbs moisture and stains more easily, making it less ideal for high-traffic upholstery applications that require longevity and resilience.
Production Processes Compared
Vegetable-tanned leather undergoes a natural tanning process using plant-derived tannins, which can take several weeks and imparts durability, firmness, and an environmentally friendly profile ideal for high-quality upholstery. Split leather is produced from the lower layers of a hide, separated mechanically, then often treated with synthetic chemicals and finishes to mimic grain leather, resulting in a more affordable, less durable material. The intricate vegetable tanning method preserves the leather's natural texture and breathability, whereas split leather's production emphasizes cost efficiency and mass production with less emphasis on longevity.
Durability and Longevity
Vegetable-tanned leather offers superior durability and ages gracefully, developing a rich patina over time, making it ideal for long-lasting upholstery. Split leather, derived from the fibrous lower layers of the hide, is less durable and more prone to wear, often requiring synthetic coatings to improve longevity. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather ensures enhanced resistance to tears and stains, providing upholstery that maintains its structural integrity and aesthetic appeal for years.
Aesthetic Differences
Vegetable-tanned leather features a rich, natural patina that deepens over time, offering a warm and luxurious aesthetic ideal for high-end upholstery. Split leather generally has a more uniform texture with a less pronounced grain, resulting in a smoother but less distinctive appearance. The color depth and organic imperfections in vegetable-tanned leather create a visually dynamic surface, while split leather's consistent finish provides a more practical, budget-friendly option.
Environmental Impact
Vegetable-tanned leather is more environmentally friendly for upholstery due to its natural tanning process using plant-based tannins, which reduces harmful chemical runoff and lowers pollution levels. Split leather, derived from the lower layers of a hide and often bonded with synthetic materials, involves chemical treatments that contribute to higher environmental toxicity and waste. Choosing vegetable-tanned leather helps minimize ecological damage and supports sustainable leather production practices.
Comfort and Feel in Upholstery Applications
Vegetable-tanned leather offers a supple, natural feel that becomes more comfortable with age, making it ideal for upholstery requiring softness and durability. Split leather, derived from the lower layer of the hide, tends to be less flexible and often requires a synthetic coating, resulting in a stiffer, less breathable surface. Comfort in upholstery largely depends on the leather's breathability and pliability, where vegetable-tanned leather outperforms split leather by providing enhanced softness and a luxurious touch.
Cost Comparison
Vegetable-tanned leather for upholstery typically commands a higher price due to its natural tanning process using plant-based materials, which enhances durability and develops a unique patina over time. Split leather, derived from the fibrous part of the hide separated from the top grain, is more affordable but lacks the strength and aging quality of vegetable-tanned leather. Budget-conscious buyers often choose split leather for cost savings, while those seeking long-term investment prefer vegetable-tanned leather despite its premium cost.
Choosing the Right Leather for Upholstery
Vegetable-tanned leather offers durability, a rich patina, and breathability, making it ideal for high-quality upholstery that ages beautifully over time. Split leather, often coated with finishes to mimic top grain leather, provides a more affordable option but lacks the natural texture and longevity of vegetable-tanned leather. Choosing the right leather depends on balancing budget preferences with desired durability, appearance, and maintenance needs in upholstery.
Infographic: Vegetable-tanned leather vs Split leather for Upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com