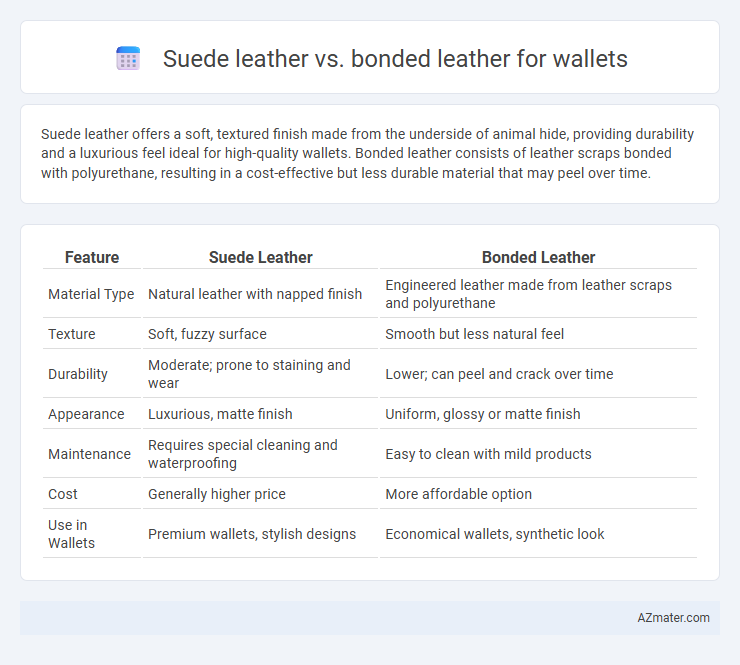
Suede leather offers a soft, textured finish made from the underside of animal hide, providing durability and a luxurious feel ideal for high-quality wallets. Bonded leather consists of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, resulting in a cost-effective but less durable material that may peel over time.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Suede Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural leather with napped finish | Engineered leather made from leather scraps and polyurethane |
| Texture | Soft, fuzzy surface | Smooth but less natural feel |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to staining and wear | Lower; can peel and crack over time |
| Appearance | Luxurious, matte finish | Uniform, glossy or matte finish |
| Maintenance | Requires special cleaning and waterproofing | Easy to clean with mild products |
| Cost | Generally higher price | More affordable option |
| Use in Wallets | Premium wallets, stylish designs | Economical wallets, synthetic look |
Introduction to Suede Leather and Bonded Leather
Suede leather is crafted from the underside of animal hide, featuring a soft, napped finish that provides a luxurious texture and breathability ideal for wallets requiring a supple feel. Bonded leather is manufactured by binding shredded leather scraps with polyurethane or latex onto a fiber sheet, resulting in a cost-effective material with a consistent appearance but less durability. When choosing between the two, suede offers natural softness and aging qualities, whereas bonded leather excels in affordability and uniformity.
What is Suede Leather?
Suede leather is a type of leather made from the underside of animal hide, offering a soft, napped finish distinct from the smooth surface of bonded leather. Unlike bonded leather, which is manufactured by bonding leather scraps with polyurethane or latex onto a fiber backing, suede is valued for its natural texture and breathability, making it a premium choice for wallets that require durability and aesthetic appeal. The porous surface of suede leather provides a unique tactile experience but may require more care to prevent staining and water damage compared to bonded leather alternatives.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made from shredded leather scraps mixed with a polyurethane or latex binder, then pressed onto a fiber backing to create a leather-like surface. Unlike suede leather, which is derived from the underside of animal hides offering a soft, napped texture, bonded leather is less durable and prone to peeling over time. For wallets, bonded leather provides a more affordable option but lacks the longevity and premium feel associated with genuine suede.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Suede leather wallets showcase a soft, velvety texture with a matte finish, providing a luxurious and plush feel that enhances grip and aesthetic appeal. Bonded leather wallets feature a more uniform, smooth surface derived from compressed leather fibers, often coated to mimic genuine leather but lacking the natural grain and softness of suede. The tactile experience of suede is rich and inviting, whereas bonded leather offers a firmer, synthetic touch that may wear faster and show signs of peeling over time.
Durability and Longevity
Suede leather offers a soft texture and moderate durability, with natural fibers prone to wear and moisture damage over time, making it less ideal for high-impact use in wallets. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps and polyurethane, provides a more uniform appearance but generally lacks the longevity of genuine leather due to the layered construction that can peel and crack. For wallet durability and longevity, genuine suede may outlast bonded leather if properly cared for, but bonded leather wallets often degrade faster under daily wear conditions.
Comfort and Feel in Daily Use
Suede leather offers a soft, velvety texture that enhances comfort and provides a luxurious feel during daily use, making it ideal for wallets that prioritize tactile experience. Bonded leather, created from shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane or latex, tends to feel stiffer and less breathable, which can reduce comfort over extended periods. The natural breathability and flexibility of suede leather result in a wallet that adapts better to hand contours, whereas bonded leather may feel rigid and less comfortable to hold for long durations.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Suede leather wallets demand gentle maintenance, including regular brushing with a suede brush to remove dirt and avoid water exposure to prevent stains. Bonded leather wallets require less intensive care, needing only occasional wiping with a damp cloth and conditioning to maintain flexibility. Proper upkeep of suede prolongs its softness, while bonded leather benefits from minimal maintenance to prevent cracking and peeling.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Suede leather, derived from the underside of animal hides, typically involves more intensive animal farming, contributing to higher carbon emissions and water usage compared to bonded leather, which is made by pulverizing leather scraps and bonding them with polyurethane or latex. Bonded leather offers a recycling advantage by utilizing leather waste, reducing landfill impact, but it often includes synthetic materials that are less biodegradable and may release microplastics over time. Choosing sustainably sourced suede with certified animal welfare practices or bonded leather with lower synthetic content can mitigate environmental impact and promote more sustainable wallet production.
Price Difference and Value for Money
Suede leather wallets generally cost more than bonded leather due to the premium quality and durability of the material, which offers a soft texture and long-lasting wear. Bonded leather, made from scraps and leather fibers bonded with polyurethane, is significantly cheaper but lacks the durability and luxurious feel of suede. For value for money, suede leather provides superior longevity and aesthetic appeal, making it a better investment despite the higher initial price.
Which Leather is Best for Wallets?
Suede leather offers a soft, textured finish with natural durability, making it ideal for wallets that require a luxurious feel and long-lasting wear. Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, provides a more affordable option but lacks the strength and breathability of genuine suede. For wallets needing premium quality, resilience, and elegant aesthetics, suede leather is generally the best choice.
Infographic: Suede leather vs Bonded leather for Wallet
 azmater.com
azmater.com