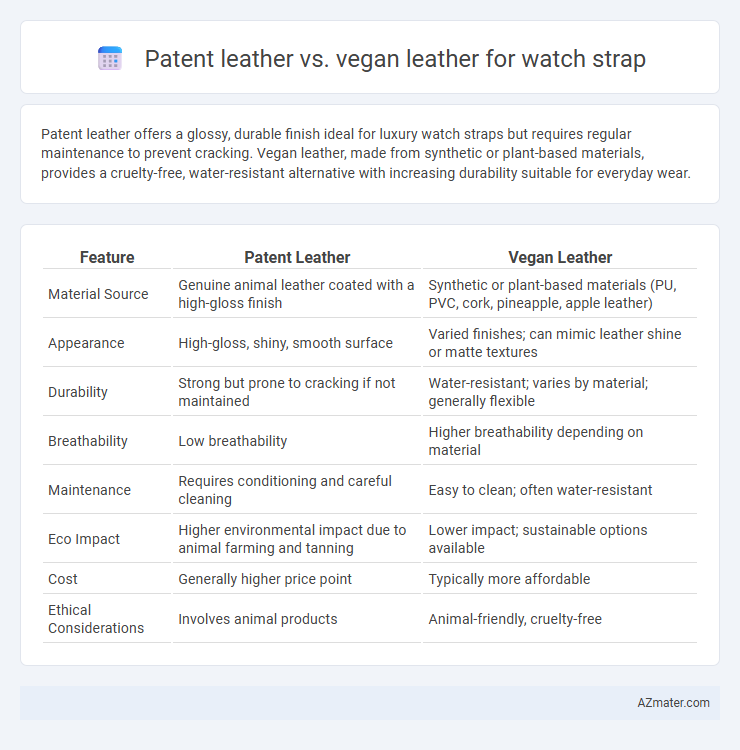
Patent leather offers a glossy, durable finish ideal for luxury watch straps but requires regular maintenance to prevent cracking. Vegan leather, made from synthetic or plant-based materials, provides a cruelty-free, water-resistant alternative with increasing durability suitable for everyday wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Patent Leather | Vegan Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Genuine animal leather coated with a high-gloss finish | Synthetic or plant-based materials (PU, PVC, cork, pineapple, apple leather) |
| Appearance | High-gloss, shiny, smooth surface | Varied finishes; can mimic leather shine or matte textures |
| Durability | Strong but prone to cracking if not maintained | Water-resistant; varies by material; generally flexible |
| Breathability | Low breathability | Higher breathability depending on material |
| Maintenance | Requires conditioning and careful cleaning | Easy to clean; often water-resistant |
| Eco Impact | Higher environmental impact due to animal farming and tanning | Lower impact; sustainable options available |
| Cost | Generally higher price point | Typically more affordable |
| Ethical Considerations | Involves animal products | Animal-friendly, cruelty-free |
Introduction to Patent Leather and Vegan Leather
Patent leather features a high-gloss finish created by applying a coating to natural animal leather, offering durability and a distinctive shiny appearance ideal for watch straps. Vegan leather, made from synthetic materials such as polyurethane or innovative plant-based alternatives, provides a cruelty-free and often more affordable option while mimicking the look and feel of genuine leather. Both materials cater to different consumer preferences for style, ethics, and maintenance in watch strap selection.
Material Composition and Production Processes
Patent leather watch straps are made from genuine leather coated with a high-gloss polyurethane or acrylic finish, providing durability and a polished appearance, while the tanning and finishing involve traditional leather processing followed by surface coating. Vegan leather straps use synthetic materials like polyurethane (PU) or thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU), or natural alternatives such as cork and pineapple leaves, created through chemical or bio-fabrication processes that avoid animal products. The production of patent leather involves animal hide treatment and solvent-based finishing, whereas vegan leather manufacturing often emphasizes sustainability with lower environmental impact and cruelty-free methods.
Aesthetic Differences: Shine, Texture, and Color
Patent leather watch straps exhibit a high-gloss shine with a smooth, almost glass-like texture that reflects light vividly, making them ideal for formal or dressy occasions. Vegan leather straps offer a more subdued, matte or semi-gloss finish, with textures ranging from smooth to slightly pebbled, providing versatility and a contemporary, casual aesthetic. Color options in patent leather tend to be classic and limited to rich blacks and browns, while vegan leather often comes in a broader spectrum, including vibrant hues and custom patterns, catering to diverse style preferences.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Patent leather watch straps offer superior durability due to their natural leather base combined with a glossy, protective coating that resists scratches and environmental wear, ensuring long-lasting quality. Vegan leather straps, while more environmentally friendly, generally lack the resilience of patent leather and may crack or peel over time when exposed to moisture and frequent bending. Choosing patent leather guarantees extended longevity and robust performance, making it ideal for daily wear, whereas vegan leather suits occasional use with a focus on ethical materials.
Comfort and Wearability Factors
Patent leather watch straps offer a glossy finish with durability, but tend to be less breathable and may cause discomfort during extended wear due to limited flexibility. Vegan leather straps, often made from polyurethane or plant-based materials, provide lightweight comfort, enhanced breathability, and greater flexibility, making them suitable for sensitive skin and all-day use. Wearability in vegan leather is typically superior for active lifestyles, while patent leather excels in formal settings where style takes precedence over prolonged comfort.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Patent leather watch straps, derived from animal hides coated with a glossy finish, often involve environmentally harmful tanning processes that emit toxic chemicals and consume significant water resources. Vegan leather watch straps, made from synthetic materials like polyurethane or innovative plant-based sources such as pineapple leaves and mushroom fibers, reduce reliance on animal agriculture and decrease greenhouse gas emissions. However, the sustainability of vegan leather varies depending on production methods, with plant-based alternatives offering a lower ecological footprint compared to traditional synthetic options.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Patent leather watch straps require regular cleaning with a damp cloth to maintain their glossy finish and prevent cracking, while avoiding prolonged exposure to water and direct sunlight. Vegan leather, often made from polyurethane or plant-based materials, demands gentle wiping and should be kept away from heat sources to prevent deformation and surface damage. Both materials benefit from occasional conditioning, but vegan leather typically requires less intensive upkeep due to its synthetic properties.
Price Range and Market Availability
Patent leather watch straps typically range from $50 to $200, reflecting the use of genuine leather coated with a glossy finish, and are widely available in luxury and mid-range markets. Vegan leather straps, made from synthetic or plant-based materials, offer a more affordable price range of $20 to $80, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and found commonly in mass-market and online retailers. Market availability of vegan leather is increasing rapidly due to growing demand for sustainable fashion alternatives, while patent leather remains preferred for its classic aesthetic and durability.
Ethical Considerations for Consumers
Patent leather watch straps, derived from animal hides, raise ethical concerns related to animal welfare and environmental impact due to the use of toxic chemicals in tanning processes. Vegan leather alternatives, made from synthetic materials or plant-based sources like pineapple leaves or cactus, offer cruelty-free options that reduce harm to animals and typically have a lower carbon footprint. Consumers prioritizing sustainability and animal rights often prefer vegan leather for its ethical advantages and increasing durability advancements.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Leather for Your Watch Strap
Patent leather offers a glossy, durable finish ideal for formal watch straps, while vegan leather provides an ethical and sustainable alternative with a variety of textures and colors. Consider factors like environmental impact, maintenance, and style preferences when selecting between natural and synthetic materials. Ultimately, choosing the right leather for your watch strap depends on balancing aesthetics, comfort, and personal values.
Infographic: Patent leather vs Vegan leather for Watch strap
 azmater.com
azmater.com