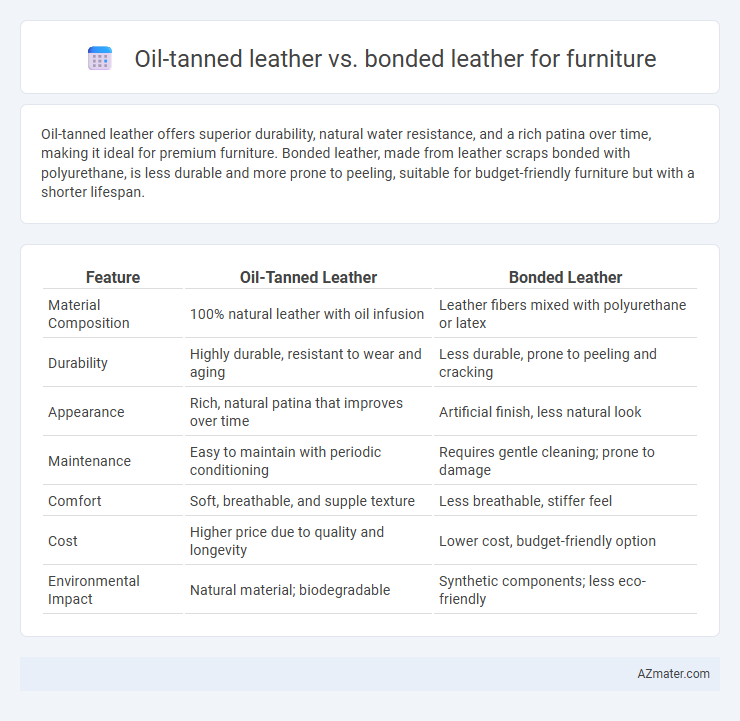
Oil-tanned leather offers superior durability, natural water resistance, and a rich patina over time, making it ideal for premium furniture. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, is less durable and more prone to peeling, suitable for budget-friendly furniture but with a shorter lifespan.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Oil-Tanned Leather | Bonded Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | 100% natural leather with oil infusion | Leather fibers mixed with polyurethane or latex |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear and aging | Less durable, prone to peeling and cracking |
| Appearance | Rich, natural patina that improves over time | Artificial finish, less natural look |
| Maintenance | Easy to maintain with periodic conditioning | Requires gentle cleaning; prone to damage |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, and supple texture | Less breathable, stiffer feel |
| Cost | Higher price due to quality and longevity | Lower cost, budget-friendly option |
| Environmental Impact | Natural material; biodegradable | Synthetic components; less eco-friendly |
Introduction to Oil-Tanned and Bonded Leather
Oil-tanned leather is crafted from full-grain or top-grain hides treated with oils and waxes, enhancing durability, water resistance, and a rich, natural patina over time. Bonded leather, made by blending shredded leather fibers with polyurethane or latex onto a fabric backing, offers a more affordable and uniform appearance but lacks the strength and breathability of genuine leather. Choosing between oil-tanned and bonded leather depends on desired durability, aesthetic appeal, and budget considerations for furniture upholstery.
What is Oil-Tanned Leather?
Oil-tanned leather is a durable, high-quality material treated with natural oils and waxes during the tanning process, enhancing its water resistance and flexibility. This type of leather retains a rich texture and develops a unique patina over time, making it ideal for furniture that combines longevity with aesthetic appeal. Unlike bonded leather, which is made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, oil-tanned leather offers superior breathability and natural authenticity for premium furniture upholstery.
What is Bonded Leather?
Bonded leather is a material made by recycling leather scraps and fibers mixed with a polyurethane or latex backing, designed to resemble genuine leather at a lower cost. It lacks the durability and natural texture of oil-tanned leather, making it more prone to cracking and peeling over time. While bonded leather offers an affordable alternative for furniture upholstery, oil-tanned leather provides superior strength, breathability, and aging characteristics.
Appearance and Texture Differences
Oil-tanned leather features a rich, natural patina with a buttery smooth texture that enhances over time, offering a luxurious, durable finish ideal for premium furniture. Bonded leather, composed of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, has a uniform, synthetic appearance and a smoother, less porous surface that can feel less supple and more plastic-like. The appearance of oil-tanned leather is characterized by unique grain patterns and color variations, while bonded leather tends to look more artificial and consistent, lacking the depth and character of full-grain materials.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Oil-tanned leather offers superior durability and longevity for furniture due to its dense fiber structure and natural oils that enhance resistance to wear, scratches, and moisture. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, tends to deteriorate more quickly, showing peeling and cracking within a few years of use. For long-lasting furniture investment, oil-tanned leather outperforms bonded leather by maintaining its appearance and structural integrity over decades.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Oil-tanned leather requires minimal maintenance, benefiting from natural oils that enhance durability and water resistance, making it easy to clean with a damp cloth and occasional application of leather conditioner. Bonded leather demands more frequent care since it is made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane; it is prone to peeling and cracking, requiring cautious use of mild cleaners and conditioners specifically designed for coated surfaces. Proper maintenance of oil-tanned leather significantly extends its lifespan, whereas bonded leather typically needs replacement sooner due to its lower durability and susceptibility to wear.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Oil-tanned leather uses natural oils and minimal chemical processing, offering enhanced durability and biodegradability compared to bonded leather, which is composed of shredded leather scraps bonded with synthetic adhesives, leading to reduced recyclability and higher environmental impact. The production of oil-tanned leather tends to consume fewer synthetic materials and generates less hazardous waste, while bonded leather's reliance on polyurethane or vinyl backing contributes to microplastic pollution and complicates end-of-life disposal. Choosing oil-tanned leather supports sustainable practices by extending furniture lifespan and minimizing synthetic waste, making it a more eco-friendly option for furniture upholstery.
Cost Comparison: Oil-Tanned vs Bonded Leather
Oil-tanned leather typically costs significantly more than bonded leather due to its durability, premium quality, and natural tanning process that enhances texture and longevity. Bonded leather, made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane or latex, offers a budget-friendly alternative but sacrifices durability and aging quality, leading to faster wear and potential peeling. Investing in oil-tanned leather furniture delivers better long-term value despite the higher upfront cost, while bonded leather suits short-term or low-cost furnishing needs.
Best Uses for Each Leather Type in Furniture
Oil-tanned leather is ideal for high-quality furniture requiring durability, water resistance, and a rich patina that improves with age, making it perfect for luxury sofas and chairs in high-traffic living spaces. Bonded leather suits budget-conscious buyers seeking the look of genuine leather in low-use areas such as decorative chairs or accent pieces, as it combines leather scraps and polyurethane for an affordable, less durable surface. Choosing oil-tanned leather ensures long-term value and comfort in frequently used furniture, whereas bonded leather is best reserved for aesthetic appeal in light-use furniture to maintain cost-efficiency.
Which Leather is Right for Your Furniture?
Oil-tanned leather offers superior durability, water resistance, and a rich, natural patina that improves with age, making it ideal for high-traffic furniture pieces requiring long-lasting quality. Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers bonded with polyurethane, provides a more affordable option with a consistent appearance but tends to wear out faster and lacks the unique character of genuine leather. Choosing the right leather depends on your budget, furniture usage, and preference for authenticity or cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Oil-tanned leather vs Bonded leather for Furniture
 azmater.com
azmater.com