Nubuck leather offers a soft, velvety texture with high durability, ideal for stylish and comfortable boots. Vegetable tanned leather provides a firm, natural finish that develops a rich patina over time, ensuring longevity and a classic look for rugged footwear.
Table of Comparison
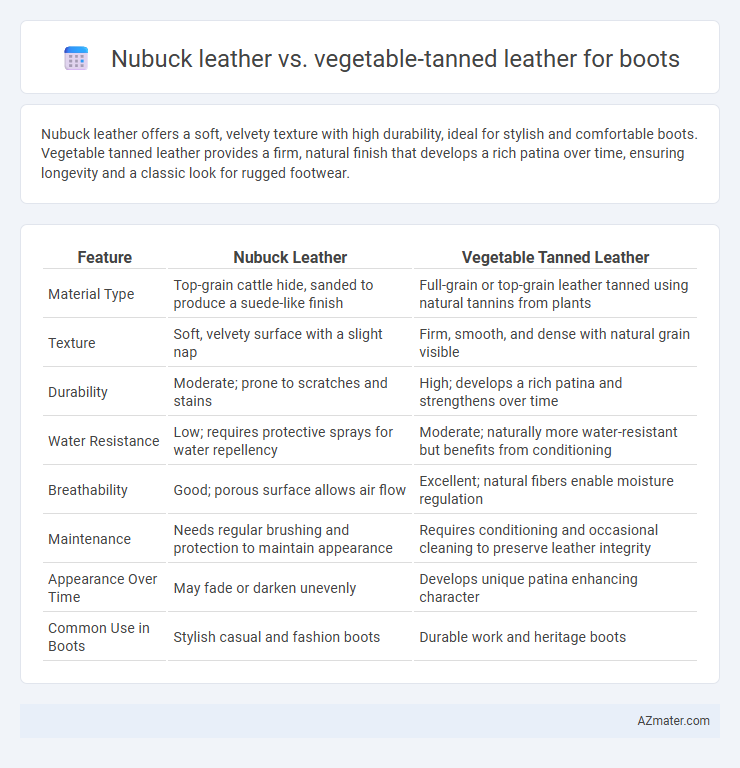
| Feature | Nubuck Leather | Vegetable Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Top-grain cattle hide, sanded to produce a suede-like finish | Full-grain or top-grain leather tanned using natural tannins from plants |
| Texture | Soft, velvety surface with a slight nap | Firm, smooth, and dense with natural grain visible |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to scratches and stains | High; develops a rich patina and strengthens over time |
| Water Resistance | Low; requires protective sprays for water repellency | Moderate; naturally more water-resistant but benefits from conditioning |
| Breathability | Good; porous surface allows air flow | Excellent; natural fibers enable moisture regulation |
| Maintenance | Needs regular brushing and protection to maintain appearance | Requires conditioning and occasional cleaning to preserve leather integrity |
| Appearance Over Time | May fade or darken unevenly | Develops unique patina enhancing character |
| Common Use in Boots | Stylish casual and fashion boots | Durable work and heritage boots |
Introduction to Nubuck Leather and Vegetable Tanned Leather
Nubuck leather is a top-grain cattle hide that has been sanded or buffed on the grain side to produce a soft, velvety surface ideal for premium boots, offering durability combined with a luxurious texture. Vegetable tanned leather undergoes a natural tanning process using tannins from tree bark and plant extracts, resulting in a firm, flexible material known for its eco-friendly production and the ability to develop a rich patina over time. Both leathers are prized in boot-making for their unique qualities, with Nubuck emphasizing softness and aesthetics, while vegetable tanned leather highlights natural tanning and durability.
Origins and Production Processes
Nubuck leather originates from the outer side of a hide, carefully sanded to create a soft, velvety surface, and is typically produced using chrome tanning methods that enhance durability and resistance to water. Vegetable tanned leather, rooted in ancient traditions, is crafted by soaking hides in natural tannins derived from tree bark and plant extracts, resulting in a firmer, more rigid material that ages with a rich patina over time. Both processes influence the boot's texture, color, and longevity, with nubuck offering a plush finish and vegetable tanned leather emphasizing a more natural, eco-friendly approach.
Texture and Appearance Differences
Nubuck leather features a soft, velvety texture created by sanding the outer grain, resulting in a matte, slightly fuzzy appearance that enhances with wear, while vegetable tanned leather showcases a firm, smooth surface with natural markings and a rich patina that deepens in color over time. Nubuck's delicate finish offers a more casual, suede-like look, whereas vegetable tanned leather exudes a classic, rugged aesthetic with visible grain patterns and a polished sheen. Each leather type develops unique aging characteristics, with nubuck becoming more supple and textured, and vegetable tanned leather gaining depth and character through exposure to sunlight and natural oils.
Durability and Longevity Compared
Nubuck leather, with its sanded surface, offers a soft texture but tends to be less durable and more susceptible to stains and abrasion compared to vegetable tanned leather. Vegetable tanned leather undergoes a natural tanning process using plant extracts, resulting in a tougher, more rigid material that develops a rich patina over time, enhancing longevity. For boots requiring long-term durability and resistance to wear, vegetable tanned leather is generally preferred due to its robustness and ability to age gracefully.
Water Resistance and Weather Performance
Nubuck leather, characterized by its sanded surface, offers moderate water resistance but requires frequent treatment with waterproofing agents to maintain durability in wet conditions. Vegetable tanned leather, treated with natural tannins, provides superior weather performance due to its dense fiber structure, which enhances water resistance and ages well with exposure. For boots subjected to varying weather, vegetable tanned leather is preferable for long-term resilience and protection against moisture.
Comfort and Wear Experience
Nubuck leather offers a soft, velvety texture due to its buffed grain surface, providing immediate comfort and a flexible fit ideal for boots worn over extended periods. Vegetable tanned leather, known for its firmness and natural aging process, molds gradually to the foot, enhancing wear experience through personalized support and durability. Choosing between nubuck and vegetable tanned leather depends on the desired balance of initial comfort versus long-term molding and toughness in boot wear.
Color Options and Patina Development
Nubuck leather offers a soft, velvety texture with a muted matte finish, typically available in a wide range of rich, uniform colors that maintain their tone over time. Vegetable tanned leather boasts a natural, warm hue that deepens and develops a distinctive patina, showcasing variations in shade and character as the boots age. While nubuck's color remains relatively stable with subtle wear, vegetable tanned leather evolves dramatically, enhancing the boot's uniqueness and aesthetic appeal through exposure to sunlight and oils.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Nubuck leather requires regular gentle brushing with a suede brush to remove dirt and maintain its soft texture, along with periodic application of a water and stain repellent spray to protect against moisture. Vegetable tanned leather demands conditioning with natural oils or specialized leather conditioners to prevent drying and cracking while developing a rich patina with use. Both types should be stored in a cool, dry place and kept away from direct sunlight to preserve their durability and appearance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nubuck leather, typically made from the outer side of a hide and sanded for a soft texture, involves chrome tanning processes that can release harmful chemicals, raising environmental concerns. Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from plant sources, offering a more eco-friendly and biodegradable alternative with less chemical pollution. For sustainable boots, vegetable tanned leather is preferred due to its reduced ecological footprint and compatibility with ethical leather processing practices.
Which Leather is Best for Boots?
Nubuck leather offers a soft, velvety texture with excellent breathability, making it ideal for boots requiring a stylish yet durable finish. Vegetable tanned leather provides superior rigidity, natural water resistance, and develops a unique patina over time, enhancing longevity and character in boots. For boots prioritizing durability and aging beauty, vegetable tanned leather is best, whereas Nubuck suits those seeking comfort and refined aesthetics.
Infographic: Nubuck leather vs Vegetable tanned leather for Boot
 azmater.com
azmater.com