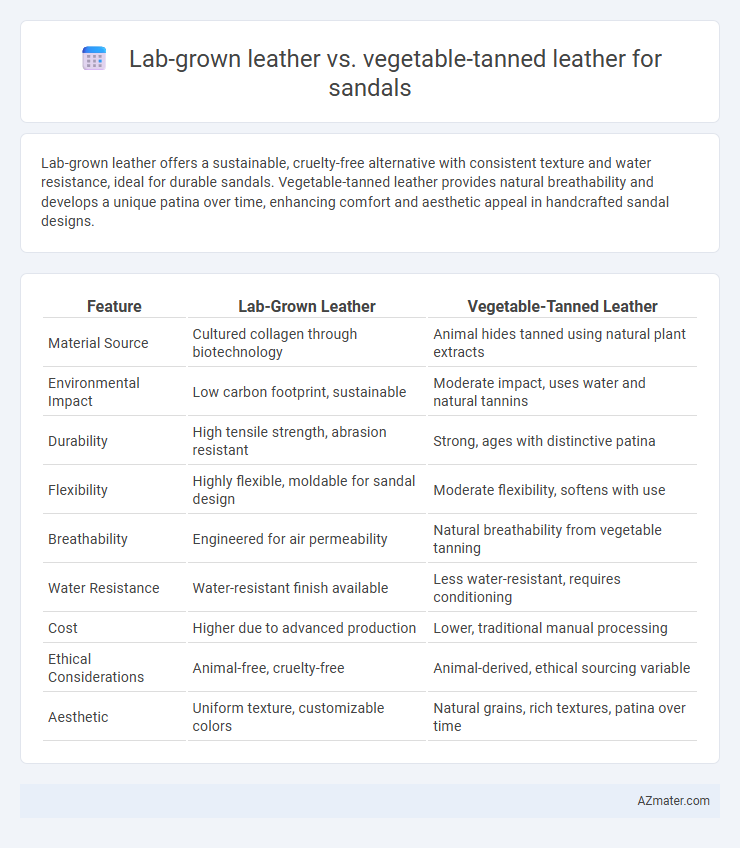
Lab-grown leather offers a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative with consistent texture and water resistance, ideal for durable sandals. Vegetable-tanned leather provides natural breathability and develops a unique patina over time, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal in handcrafted sandal designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lab-Grown Leather | Vegetable-Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Cultured collagen through biotechnology | Animal hides tanned using natural plant extracts |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | Moderate impact, uses water and natural tannins |
| Durability | High tensile strength, abrasion resistant | Strong, ages with distinctive patina |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, moldable for sandal design | Moderate flexibility, softens with use |
| Breathability | Engineered for air permeability | Natural breathability from vegetable tanning |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant finish available | Less water-resistant, requires conditioning |
| Cost | Higher due to advanced production | Lower, traditional manual processing |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free, cruelty-free | Animal-derived, ethical sourcing variable |
| Aesthetic | Uniform texture, customizable colors | Natural grains, rich textures, patina over time |
Introduction: Lab-Grown Leather vs. Vegetable-Tanned Leather for Sandals
Lab-grown leather offers a sustainable alternative to traditional vegetable-tanned leather by using cultured animal cells to create material with similar durability and flexibility, ideal for sandals. Vegetable-tanned leather, produced through natural tannins extracted from tree bark and plants, provides a biodegradable and eco-friendly option known for its rich texture and unique patina over time. Both materials emphasize sustainability, but lab-grown leather advances innovation with reduced environmental impact compared to the resource-intensive tanning process.
Understanding Lab-Grown Leather: What Is It?
Lab-grown leather is an innovative material created through cellular agriculture by cultivating animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need for animal slaughter. This biofabricated leather mimics the texture, durability, and breathability of traditional leather but with significantly lower environmental impact and resource consumption. Its use in sandals offers sustainable alternatives by providing cruelty-free, customizable, and eco-friendly footwear options.
The Process of Vegetable Tanning Explained
Vegetable tanning transforms raw animal hides into durable leather by immersing them in tannin-rich plant extracts, such as bark, leaves, and fruits, over several weeks, resulting in a natural, eco-friendly material ideal for sandals. This slow, chemical-free method preserves the hide's strength and breathability while developing a rich patina with use, enhancing the aesthetic and longevity of vegetable-tanned leather footwear. In contrast to lab-grown leather, vegetable-tanned leather relies on traditional techniques that emphasize environmental sustainability and artisanal craftsmanship in sandal production.
Sustainability Comparison: Environmental Impact
Lab-grown leather significantly reduces water consumption and carbon emissions compared to vegetable-tanned leather, which relies on large quantities of water and natural tannins extracted from tree bark and leaves. The cultivation process of lab-grown leather minimizes deforestation and chemical use, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional vegetable tanning that involves lengthy soaking and tanning cycles releasing effluents. Lab-grown leather's scalable production with controlled resource inputs promotes lower environmental degradation, making it a preferable eco-friendly choice for sustainable sandal manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity in Sandal Applications
Lab-grown leather offers consistent durability due to its controlled production process, resisting wear and tear effectively in sandal applications. Vegetable-tanned leather, known for developing a rich patina over time, provides long-lasting strength but may require regular maintenance to sustain its longevity. Both materials deliver robust performance, with lab-grown leather excelling in uniform durability and vegetable-tanned leather offering durability enhanced by natural aging characteristics.
Comfort and Wearability: How Each Leather Performs
Lab-grown leather offers consistent softness and flexibility, enhancing sandal comfort through its engineered uniform texture and breathability. Vegetable-tanned leather provides natural durability and molds to the foot over time, improving wearability by developing a personalized fit and unique patina. Both materials excel in comfort and wearability, but lab-grown leather delivers immediate softness while vegetable-tanned leather improves with age and use.
Ethical Considerations: Animal Welfare and Beyond
Lab-grown leather offers a cruelty-free alternative by eliminating the need for animal hides, significantly reducing animal suffering compared to vegetable-tanned leather derived from animal skins. Vegetable-tanned leather, while often marketed as eco-friendly and chemically natural, still involves animal agriculture with ethical concerns related to livestock welfare and environmental impact. Beyond animal welfare, lab-grown leather reduces reliance on land and water resources, lowering the carbon footprint and supporting sustainable fashion choices for sandals.
Aesthetic Differences: Look and Feel for Sandal Design
Lab-grown leather offers a consistent and smooth texture with a uniform color ideal for sleek, modern sandal designs, while vegetable-tanned leather exhibits rich, natural variations and develops a distinctive patina over time, enhancing its vintage appeal. Lab-grown leather tends to have a polished finish that feels supple yet synthetic, contrasting with the warm, firm, and slightly textured feel of vegetable-tanned leather, which softens with wear. Designers prioritize lab-grown leather for precise, contemporary aesthetics whereas vegetable-tanned leather is favored for rustic, artisanal sandals with character and durability.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Market Trends
Lab-grown leather for sandals typically incurs higher production costs but offers scalability and eco-friendly advantages that attract premium market segments. Vegetable-tanned leather features lower upfront costs due to traditional methods, making it more affordable and widely accessible in mass-market footwear. Market trends reveal increasing consumer willingness to invest in lab-grown leather sandals for sustainability, despite the higher price point, while vegetable-tanned leather remains a cost-effective choice favored for classic and artisanal designs.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Sandals: Final Thoughts
Lab-grown leather offers consistent durability and eco-friendly benefits, making it an ideal choice for sustainable sandals, while vegetable-tanned leather provides natural aesthetics and develops a unique patina with wear. Consider factors such as environmental impact, desired texture, and longevity when selecting between these materials. Choosing the right leather for your sandals ultimately depends on balancing sustainability goals with the traditional craftsmanship and appearance you prefer.
Infographic: Lab-grown leather vs Vegetable-tanned leather for Sandal
 azmater.com
azmater.com