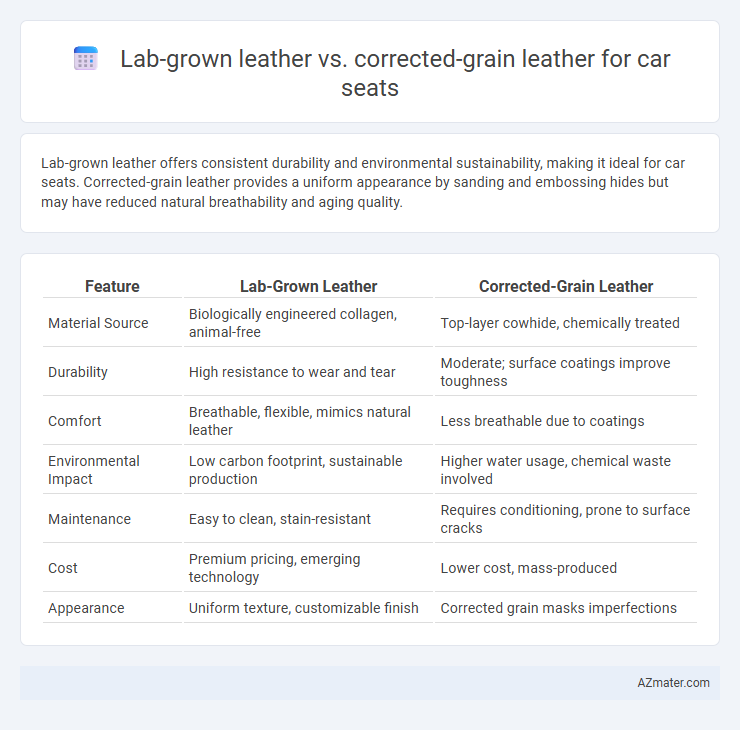
Lab-grown leather offers consistent durability and environmental sustainability, making it ideal for car seats. Corrected-grain leather provides a uniform appearance by sanding and embossing hides but may have reduced natural breathability and aging quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lab-Grown Leather | Corrected-Grain Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Biologically engineered collagen, animal-free | Top-layer cowhide, chemically treated |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Moderate; surface coatings improve toughness |
| Comfort | Breathable, flexible, mimics natural leather | Less breathable due to coatings |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable production | Higher water usage, chemical waste involved |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain-resistant | Requires conditioning, prone to surface cracks |
| Cost | Premium pricing, emerging technology | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Appearance | Uniform texture, customizable finish | Corrected grain masks imperfections |
Introduction: Lab-Grown Leather vs Corrected-Grain Leather
Lab-grown leather offers a sustainable alternative to traditional car seat materials by using cultured cells to produce genuine leather without animal cruelty, while corrected-grain leather is made from lower-quality hides that undergo surface sanding and reprocessing to achieve a uniform appearance. Lab-grown leather provides enhanced durability, breathability, and eco-friendly benefits, whereas corrected-grain leather often features artificial coatings that can reduce its natural texture and longevity. Choosing between these materials impacts factors such as environmental footprint, tactile comfort, and long-term maintenance in automotive interiors.
Material Origins and Manufacturing Processes
Lab-grown leather for car seats is produced through biofabrication, using cultured animal cells to create a sustainable and animal-free alternative with reduced environmental impact. Corrected-grain leather originates from bovine hides, undergoing extensive processing including buffing and coating to eliminate surface imperfections and enhance durability. Manufacturing lab-grown leather involves cutting-edge biotechnological methods, while corrected-grain leather relies on traditional tanneries employing chemical treatments and mechanical refinements to achieve its finish.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lab-grown leather significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating the need for animal farming, cutting greenhouse gas emissions by up to 80% compared to traditional corrected-grain leather production. It requires less water and land resources, offering a more sustainable alternative while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal for car seats. Corrected-grain leather, though durable, involves intensive chemical treatments and livestock farming, contributing to deforestation, high water consumption, and pollution, making it less eco-friendly in comparison.
Durability and Longevity for Car Seats
Lab-grown leather offers consistent durability due to its controlled manufacturing process, resisting wear and tear commonly experienced in car seats. Corrected-grain leather undergoes surface sanding and coating, which enhances scratch resistance but may degrade faster under prolonged exposure to UV rays and friction. For car seat longevity, lab-grown leather maintains structural integrity and color retention more effectively than corrected-grain leather over extended use.
Comfort and User Experience
Lab-grown leather for car seats offers enhanced breathability and consistent texture, improving overall comfort during long drives. Corrected-grain leather, treated to remove imperfections, provides a durable surface but may retain a stiffer feel, affecting seating softness. User experience with lab-grown leather often benefits from its eco-friendly production and customizable cushioning properties, while corrected-grain leather emphasizes traditional luxury and resistance to wear.
Aesthetic Appeal and Customization Options
Lab-grown leather offers a consistent texture and color with high aesthetic appeal, allowing for unique finishes and precise customization in car seat design. Corrected-grain leather features a surface treated to remove imperfections, providing a smooth and uniform appearance but with less variability than lab-grown leather. Customization in lab-grown leather extends to patterns, embossing, and colors, whereas corrected-grain leather customization is generally limited to dyeing and surface treatments.
Cost and Market Availability
Lab-grown leather for car seats typically incurs higher manufacturing costs due to advanced biotechnology processes, limiting its market availability primarily to luxury and prototype vehicles. Corrected-grain leather, processed to improve surface imperfections, offers a more cost-effective option with widespread availability across mainstream automotive brands. Market adoption favors corrected-grain leather largely for its balance of durability, aesthetic appeal, and affordability in mass production.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Lab-grown leather offers easier maintenance and cleaning due to its uniform surface that resists stains and requires only mild soap and water for routine care. Corrected-grain leather, treated to remove imperfections, demands more frequent conditioning to prevent dryness and cracking, and specialized leather cleaners to preserve its finish. Both materials benefit from immediate stain treatment, but lab-grown leather generally sustains its appearance longer with minimal upkeep in automotive environments.
Performance in Different Climate Conditions
Lab-grown leather offers superior breathability and consistent texture, enhancing comfort in both hot and humid climates by reducing heat retention and moisture buildup in car seats. Corrected-grain leather, with its dense grain and protective coatings, provides greater durability and resistance to UV damage, making it well-suited for extreme temperature fluctuations and prolonged sun exposure. Performance in cold climates favors lab-grown leather's flexibility, while corrected-grain leather maintains structural integrity under heavy wear, balancing comfort and longevity depending on environmental stressors.
Future Trends in Automotive Upholstery Materials
Lab-grown leather offers sustainable and customizable options for car seat upholstery, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional corrected-grain leather, which remains valued for its durability and premium feel. Innovations in biofabrication techniques and nanotechnology are driving the adoption of lab-grown leather, enabling enhanced breathability, stain resistance, and texture control tailored to automotive requirements. Market trends indicate a growing shift towards eco-friendly materials, with manufacturers increasingly integrating lab-grown leather to meet consumer demand for luxury, performance, and sustainability in automotive interiors.
Infographic: Lab-grown leather vs Corrected-grain leather for Car seat
 azmater.com
azmater.com