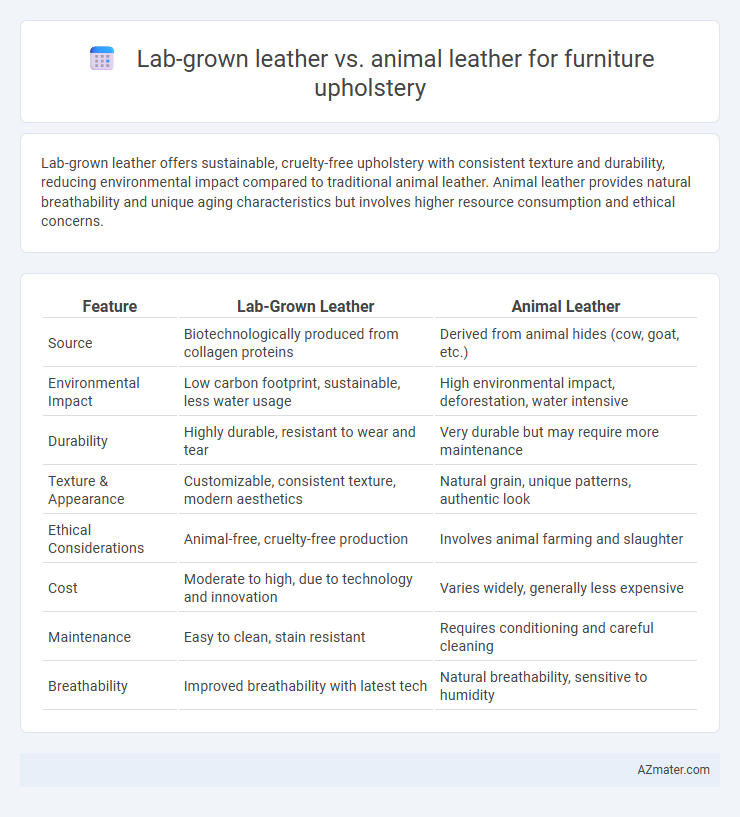
Lab-grown leather offers sustainable, cruelty-free upholstery with consistent texture and durability, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather. Animal leather provides natural breathability and unique aging characteristics but involves higher resource consumption and ethical concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lab-Grown Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Biotechnologically produced from collagen proteins | Derived from animal hides (cow, goat, etc.) |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable, less water usage | High environmental impact, deforestation, water intensive |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear and tear | Very durable but may require more maintenance |
| Texture & Appearance | Customizable, consistent texture, modern aesthetics | Natural grain, unique patterns, authentic look |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free, cruelty-free production | Involves animal farming and slaughter |
| Cost | Moderate to high, due to technology and innovation | Varies widely, generally less expensive |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, stain resistant | Requires conditioning and careful cleaning |
| Breathability | Improved breathability with latest tech | Natural breathability, sensitive to humidity |
Introduction to Lab-Grown and Animal Leather
Lab-grown leather is produced through biotechnology, utilizing collagen proteins to create a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather sourced from cattle hides. This innovative material mimics the texture, durability, and aesthetic qualities of conventional leather while significantly reducing environmental impact, including water usage and greenhouse gas emissions. Animal leather remains prized for its natural grain patterns and strength but involves ethical concerns and higher resource consumption inherent in livestock farming.
How Lab-Grown Leather is Made
Lab-grown leather for furniture upholstery is produced through a biofabrication process that cultivates animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need for traditional livestock farming. This method involves extracting collagen-producing cells, which are then grown on a scaffold to form durable, flexible leather-like material that mimics the texture and strength of animal leather. Lab-grown leather offers a sustainable alternative by reducing environmental impact, water usage, and greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional leather production.
Traditional Animal Leather Production Process
Traditional animal leather production for furniture upholstery involves a complex process beginning with raw hides sourced from livestock such as cattle. These hides undergo stages including curing, soaking, tanning with chromium or vegetable-based agents, and finishing to enhance durability and aesthetic appeal. The extensive use of chemicals and substantial water consumption in this process raises environmental concerns, driving interest toward sustainable alternatives like lab-grown leather.
Environmental Impact: Lab-Grown vs Animal Leather
Lab-grown leather significantly reduces environmental impact by minimizing land use, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional animal leather. Animal leather production contributes to deforestation, methane release, and chemical pollution from tanning processes. Sustainable furniture upholstery benefits from lab-grown leather's lower carbon footprint and decreased reliance on livestock farming.
Durability and Performance in Furniture Upholstery
Lab-grown leather offers consistent durability and resistance to wear, ideal for high-traffic furniture upholstery, while animal leather provides natural strength and the ability to develop a unique patina over time. Lab-grown leather often features enhanced stain resistance and UV protection, improving long-term performance and maintenance ease compared to traditional animal leather. Performance-wise, animal leather typically excels in breathability and flexibility, contributing to prolonged comfort, whereas lab-grown options can be engineered for specific use-cases, including increased water resistance and scratch-proof surfaces.
Aesthetic Differences: Texture and Appearance
Lab-grown leather offers a more uniform texture and consistent coloration compared to the natural variations found in animal leather, resulting in a sleek, modern aesthetic for furniture upholstery. Animal leather displays unique grain patterns and natural imperfections that convey a rich, authentic character sought after in classic and luxury designs. The subtle sheen of lab-grown leather contrasts with the deeper, more complex patina developed by animal leather over time, influencing long-term visual appeal.
Cost Comparison and Market Availability
Lab-grown leather for furniture upholstery generally commands higher upfront costs than traditional animal leather due to advanced manufacturing techniques and limited mass production. Animal leather remains more widely available and cost-effective, supported by established supply chains and economies of scale in the furniture industry. Market availability of lab-grown leather is expanding but remains niche, often targeting premium or sustainable product segments.
Ethical Considerations and Animal Welfare
Lab-grown leather significantly reduces animal cruelty by eliminating the need for livestock farming and slaughter, addressing major ethical concerns tied to traditional animal leather production. The process uses cultured cells to create durable and sustainable leather alternatives, minimizing environmental impact and promoting animal welfare. Ethical considerations include reducing biodiversity loss and greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional leather, enhancing sustainability in furniture upholstery choices.
Consumer Preferences and Industry Adoption
Lab-grown leather is gaining traction in furniture upholstery due to its sustainability, consistent quality, and ethical appeal, attracting eco-conscious consumers seeking cruelty-free alternatives. Traditional animal leather remains preferred for its natural durability, patina development, and luxury perception, maintaining strong demand among customers valuing authenticity and classic aesthetics. Industry adoption reflects a gradual shift, with manufacturers increasingly integrating lab-grown leather to meet evolving market preferences while preserving animal leather's established presence for premium product lines.
Future Trends in Leather for Furniture Upholstery
Lab-grown leather for furniture upholstery is poised to disrupt the industry with its sustainable production methods, lower environmental footprint, and consistent quality control, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and designers. Advances in biotechnology and material science are enhancing the durability, texture, and aesthetic versatility of lab-grown leather, making it increasingly competitive with traditional animal leather. Future trends indicate a growing preference for lab-grown leather due to regulatory pressures on animal welfare and the demand for innovative, cruelty-free materials in interior design.
Infographic: Lab-grown leather vs Animal leather for Furniture upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com