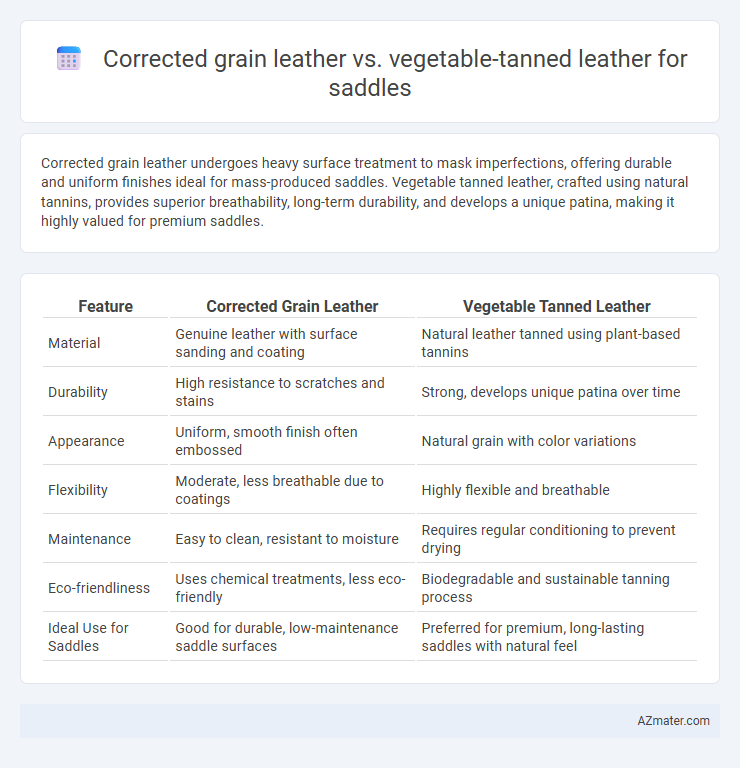
Corrected grain leather undergoes heavy surface treatment to mask imperfections, offering durable and uniform finishes ideal for mass-produced saddles. Vegetable tanned leather, crafted using natural tannins, provides superior breathability, long-term durability, and develops a unique patina, making it highly valued for premium saddles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrected Grain Leather | Vegetable Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Genuine leather with surface sanding and coating | Natural leather tanned using plant-based tannins |
| Durability | High resistance to scratches and stains | Strong, develops unique patina over time |
| Appearance | Uniform, smooth finish often embossed | Natural grain with color variations |
| Flexibility | Moderate, less breathable due to coatings | Highly flexible and breathable |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to moisture | Requires regular conditioning to prevent drying |
| Eco-friendliness | Uses chemical treatments, less eco-friendly | Biodegradable and sustainable tanning process |
| Ideal Use for Saddles | Good for durable, low-maintenance saddle surfaces | Preferred for premium, long-lasting saddles with natural feel |
Understanding Corrected Grain Leather
Corrected grain leather is created by sanding the surface of full-grain leather and applying an artificial grain layer, often coated with pigment to mask imperfections, resulting in a more uniform appearance and enhanced durability for saddles. Vegetable tanned leather, on the other hand, undergoes a natural tanning process using plant extracts, preserving the leather's original grain and offering a firm, moldable texture prized for traditional saddle craftsmanship. Understanding corrected grain leather helps saddle users prioritize ease of maintenance and consistent finish, whereas vegetable tanned leather appeals to those valuing natural aging and breathability.
What Is Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable tanned leather is a natural, eco-friendly leather tanning process that uses tannins and other ingredients found in vegetable matter like tree bark and leaves, resulting in a firm, durable, and biodegradable material ideal for saddles. Compared to corrected grain leather, which is chemically treated and embossed to hide imperfections, vegetable tanned leather maintains the hide's natural characteristics, offering superior breathability and a developing patina over time. This makes vegetable tanned leather saddles preferred for their longevity, comfort, and traditional craftsmanship.
Production Processes: Corrected Grain vs Vegetable Tanned
Corrected grain leather undergoes a mechanical buffing process to remove imperfections, followed by the application of synthetic pigments and coatings for a uniform appearance, ideal for saddle surfaces requiring durability and a consistent finish. Vegetable tanned leather is produced using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, resulting in a firm yet flexible material that develops a rich patina over time and offers excellent breathability for saddle comfort. The production of corrected grain leather prioritizes cosmetic refinement and resistance to wear, whereas vegetable tanning emphasizes natural treatment and long-term aging qualities.
Appearance and Surface Characteristics
Corrected grain leather features a uniform, smooth surface achieved through sanding and embossing, making it ideal for saddles requiring consistent texture and appearance. Vegetable tanned leather retains natural grain patterns and exhibits a more rugged, organic look with unique surface variations that deepen and develop a rich patina over time. The choice between these leathers impacts a saddle's aesthetic, with corrected grain offering a polished finish and vegetable tanned delivering a traditional, character-rich surface.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Corrected grain leather undergoes extensive buffing and coating processes to enhance surface uniformity, which improves resistance to scratches but may reduce breathability and natural texture compared to vegetable tanned leather. Vegetable tanned leather, processed using natural tannins from tree bark, offers superior durability through increased firmness and develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its longevity when properly maintained. For saddle use, vegetable tanned leather is preferred due to its strength, natural moisture resistance, and ability to mold to the rider's body, ensuring long-lasting performance without compromising comfort.
Comfort and Flexibility in Saddles
Corrected grain leather offers durability but tends to be stiffer, resulting in less initial comfort and flexibility compared to vegetable tanned leather. Vegetable tanned leather is prized for its natural pliability, molding to the rider's body over time to enhance comfort and flexibility in saddles. This makes vegetable tanned leather a preferred choice for riders seeking a saddle that adapts and softens with use, providing superior ergonomic support.
Aging and Patina Development
Corrected grain leather, treated with pigments and coatings, offers a uniform finish but ages with minimal patina development, often showing wear through surface abrasions rather than natural color shifts. Vegetable tanned leather, rich in tannins from natural plant extracts, develops a unique, deepening patina over time, enhancing character and aesthetic appeal on saddles through exposure to sunlight, moisture, and handling. This organic aging process in vegetable tanned leather results in a more pronounced texture and color variation, valued in premium saddle craftsmanship for its evolving beauty and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Corrected grain leather involves sanding and buffing the surface to remove imperfections, often coated with synthetic finishes, resulting in higher chemical use and reduced biodegradability compared to vegetable tanned leather. Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from tree bark, minimizing harmful chemicals and promoting biodegradability, which supports a more sustainable lifecycle for saddles. Choosing vegetable tanned leather reduces environmental impact by relying on renewable resources and fostering eco-friendly disposal.
Cost Differences: Which Is More Economical?
Corrected grain leather is generally more economical than vegetable tanned leather due to its lower production costs and use of synthetic finishes that speed up processing. Vegetable tanned leather involves a longer, more labor-intensive tanning process using natural tannins, making it pricier but more durable and eco-friendly. For saddles, corrected grain leather offers a budget-friendly option, while vegetable tanned leather provides long-term value despite the higher initial investment.
Choosing the Best Leather for Saddles
Corrected grain leather offers enhanced durability and a uniform appearance, making it a popular choice for saddles that require high resistance to wear and easier maintenance. Vegetable tanned leather provides natural breathability, moldability, and a classic aesthetic that improves with age, ideal for riders seeking comfort and traditional craftsmanship. Choosing the best leather for saddles depends on balancing the need for toughness and longevity with the desire for natural feel and patina development.
Infographic: Corrected grain leather vs Vegetable tanned leather for Saddle
 azmater.com
azmater.com