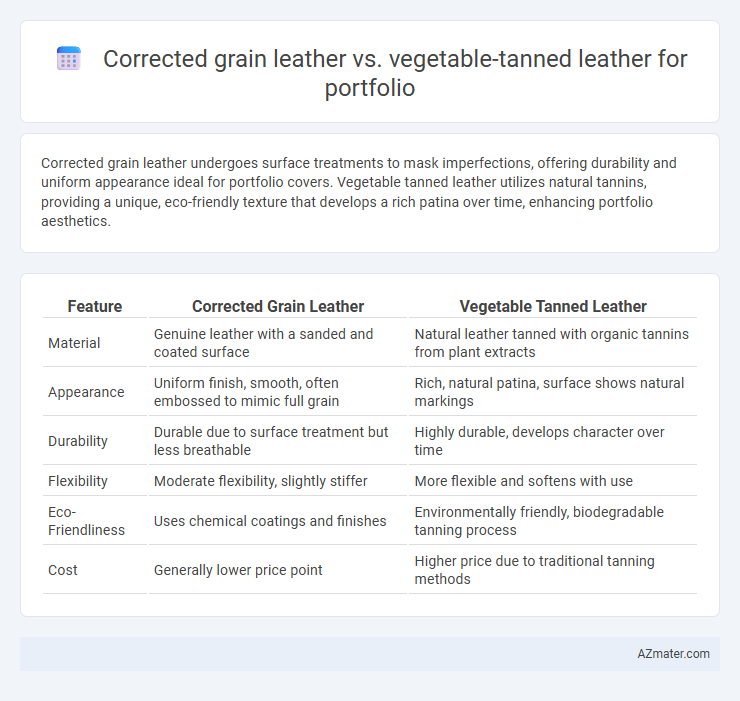
Corrected grain leather undergoes surface treatments to mask imperfections, offering durability and uniform appearance ideal for portfolio covers. Vegetable tanned leather utilizes natural tannins, providing a unique, eco-friendly texture that develops a rich patina over time, enhancing portfolio aesthetics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Corrected Grain Leather | Vegetable Tanned Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Genuine leather with a sanded and coated surface | Natural leather tanned with organic tannins from plant extracts |
| Appearance | Uniform finish, smooth, often embossed to mimic full grain | Rich, natural patina, surface shows natural markings |
| Durability | Durable due to surface treatment but less breathable | Highly durable, develops character over time |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, slightly stiffer | More flexible and softens with use |
| Eco-Friendliness | Uses chemical coatings and finishes | Environmentally friendly, biodegradable tanning process |
| Cost | Generally lower price point | Higher price due to traditional tanning methods |
Introduction: Understanding Leather Types for Portfolios
Corrected grain leather features a smooth, uniform surface achieved through sanding and embossing, making it highly durable and resistant to scratches, ideal for portfolios requiring a polished appearance. Vegetable tanned leather undergoes a natural tanning process using plant extracts, resulting in a firm texture and rich patina that develops uniquely over time, offering a classic and organic aesthetic for portfolios. Both leather types ensure quality and longevity but cater to different style preferences and usage demands in portfolio design.
What is Corrected Grain Leather?
Corrected grain leather is a type of leather that has been sanded and buffed to remove imperfections, then coated with a synthetic finish to achieve a uniform appearance, making it more durable and easier to maintain than natural grain leather. Unlike vegetable tanned leather, which retains its natural surface and develops a unique patina over time due to tannins extracted from plant material, corrected grain leather prioritizes consistency and resistance to stains and scratches. This makes corrected grain leather an ideal choice for portfolio covers requiring a polished look and long-lasting durability.
What is Vegetable Tanned Leather?
Vegetable tanned leather is crafted using natural tannins extracted from tree bark, leaves, and other plant materials, resulting in a durable and environmentally friendly material. Unlike corrected grain leather, which is coated and embossed to mask imperfections, vegetable tanned leather retains its natural surface, offering unique patina and breathability over time. This type of leather is favored for high-quality portfolios due to its strength, aesthetic appeal, and aging characteristics.
Durability: Corrected Grain vs Vegetable Tanned Leather
Corrected grain leather, treated with surface coatings to hide imperfections, offers enhanced durability and resistance to stains and scratches compared to vegetable tanned leather, which is untreated and ages naturally over time. Vegetable tanned leather develops a unique patina, increasing its aesthetic value but making it more susceptible to wear and environmental damage. For portfolio use where longevity and consistent appearance are crucial, corrected grain leather provides a more durable and low-maintenance option.
Appearance and Texture Comparison
Corrected grain leather features a uniform appearance with a smooth, often embossed surface that conceals natural imperfections, making it ideal for consistent texture in portfolios. Vegetable tanned leather showcases a rich, natural patina that develops over time, offering a unique, textured surface with visible grain and slight variations that enhance character and authenticity. While corrected grain leather emphasizes a polished, flawless look, vegetable tanned leather provides a more organic, tactile experience valued for its natural aesthetics.
Aging and Patina Development
Corrected grain leather features a surface coating that limits natural aging and patina development, resulting in a more uniform but less dynamic finish over time. Vegetable tanned leather undergoes a chemical-free tanning process that enhances its ability to develop rich, unique patinas with deep color variations as it ages. The evolving character and texture of vegetable tanned leather make it ideal for portfolios seeking a distinctive vintage aesthetic with visible signs of wear and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Corrected grain leather involves heavy processing with synthetic chemicals and pigments, leading to higher environmental pollution and reduced biodegradability compared to vegetable tanned leather. Vegetable tanned leather uses natural tannins from plant materials, making it more sustainable and biodegradable, with a lower carbon footprint and minimal chemical waste. Brands prioritizing eco-friendly practices often prefer vegetable tanned leather for its renewable resources and reduced toxic impact on ecosystems.
Cost Considerations for Portfolios
Corrected grain leather often presents a more budget-friendly option for portfolios due to its lower production costs and ability to mask imperfections with surface coatings. Vegetable tanned leather, while typically more expensive, offers greater durability and develops a rich patina over time, enhancing the portfolio's aesthetic and value. For cost-conscious buyers, corrected grain leather balances affordability with appearance, whereas vegetable tanned leather suits those prioritizing long-term quality and investment.
Best Use Cases: Which Leather Suits Your Portfolio?
Corrected grain leather offers enhanced durability and uniform appearance ideal for sleek, professional portfolios used daily in corporate environments, while vegetable tanned leather boasts natural patina development and eco-friendly tanning, making it perfect for artisanal portfolios with a rustic, unique aesthetic. Corrected grain leather resists stains and scratches, supporting portfolios that undergo frequent handling, whereas vegetable tanned leather suits portfolios prioritized for craftsmanship and aging beauty. Selecting between these leathers depends on portfolio needs: functional longevity favors corrected grain, while organic texture and sustainability align with vegetable tanned leather.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Leather for Portfolios
Corrected grain leather offers enhanced durability and a consistent, polished appearance ideal for portfolios requiring a professional look. Vegetable tanned leather provides a natural finish that develops a unique patina over time, appealing to those who value authenticity and aging character. Selecting the right leather depends on balancing durability and aesthetic preferences to match the portfolio's purpose and user lifestyle.
Infographic: Corrected grain leather vs Vegetable tanned leather for Portfolio
 azmater.com
azmater.com