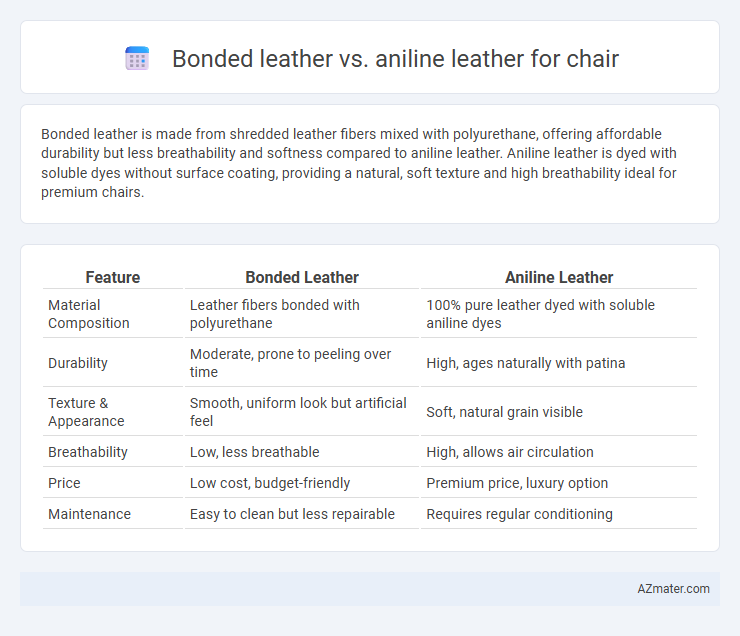
Bonded leather is made from shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, offering affordable durability but less breathability and softness compared to aniline leather. Aniline leather is dyed with soluble dyes without surface coating, providing a natural, soft texture and high breathability ideal for premium chairs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Bonded Leather | Aniline Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Leather fibers bonded with polyurethane | 100% pure leather dyed with soluble aniline dyes |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to peeling over time | High, ages naturally with patina |
| Texture & Appearance | Smooth, uniform look but artificial feel | Soft, natural grain visible |
| Breathability | Low, less breathable | High, allows air circulation |
| Price | Low cost, budget-friendly | Premium price, luxury option |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean but less repairable | Requires regular conditioning |
Overview of Bonded Leather and Aniline Leather
Bonded leather, composed of shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane or latex on a fabric backing, offers an affordable and eco-friendly option for chairs with a smooth finish and consistent texture. Aniline leather, crafted from high-quality, full-grain hides treated only with transparent dyes, provides a natural surface rich in visible grain and a soft, breathable feel ideal for premium, durable seating. While bonded leather emphasizes cost-effectiveness and uniform appearance, aniline leather prioritizes authenticity, softness, and aging character.
Key Differences Between Bonded and Aniline Leather
Bonded leather is made by combining shredded genuine leather fibers with polyurethane or latex on a fabric backing, resulting in a less durable and lower-cost material compared to aniline leather, which is made from full-grade leather with minimal processing and only a transparent dye, preserving the natural texture and breathability. Aniline leather exhibits superior softness, moisture absorption, and develops a unique patina over time, while bonded leather often lacks breathability and tends to peel or crack with prolonged use. The key difference lies in durability and aesthetic quality, making aniline leather ideal for high-end chairs requiring longevity and comfort, whereas bonded leather suits budget-conscious buyers prioritizing appearance over lifespan.
Durability: Bonded Leather vs Aniline Leather
Bonded leather, made from shredded leather fibers mixed with polyurethane, offers moderate durability but tends to crack and peel over time due to its synthetic composition. Aniline leather, crafted from top-grain leather dyed with transparent aniline dyes, boasts superior durability and natural aging, resisting wear and developing a rich patina with use. For chairs subjected to frequent use, aniline leather provides longer-lasting resilience compared to bonded leather's limited lifespan.
Comfort and Feel Comparison
Bonded leather offers a firmer, less breathable surface with a synthetic feel due to its composition of leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, making it less comfortable for prolonged seating. Aniline leather provides a soft, supple texture with natural breathability and flexibility, enhancing comfort by adapting to body temperature and movement. The higher quality and porous nature of aniline leather ensures a more luxurious and comfortable chair experience compared to bonded leather.
Appearance and Aesthetic Qualities
Bonded leather offers a uniform, smooth surface with consistent color and texture, often mimicking the appearance of genuine leather but with limited natural variation. Aniline leather showcases a rich, natural patina with visible grain patterns and slight imperfections, enhancing the chair's character and sophistication over time. The choice impacts the chair's aesthetic appeal, where bonded leather suits sleek, modern designs while aniline leather complements luxurious, classic interiors.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Bonded leather requires gentle cleaning with a damp cloth and mild soap, avoiding harsh chemicals to prevent peeling or cracking, while aniline leather demands more careful maintenance with specialized leather cleaners and conditioners to retain its natural look and softness. Bonded leather is less breathable and more prone to wear over time, making it less durable in high-use environments, whereas aniline leather, though more expensive, develops a desirable patina and resists drying out when properly maintained. For chair upholstery, choosing aniline leather offers longevity and a premium feel but requires routine care, whereas bonded leather provides a cost-effective, low-maintenance alternative with more frequent replacement needs.
Cost Differences and Budget Considerations
Bonded leather chairs are significantly more affordable than aniline leather, making them a popular choice for budget-conscious buyers seeking the leather aesthetic without high costs. Aniline leather, crafted from pure, natural leather dyed with soluble dyes, commands a higher price due to its premium quality and durability. When budgeting for chairs, bonded leather offers cost savings but may compromise on longevity and aging compared to the more expensive, luxurious aniline leather options.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Bonded leather is made from leather scraps bonded with polyurethane, resulting in lower durability and limited breathability, but it uses recycled materials, reducing waste. Aniline leather is dyed with soluble dyes without covering the surface, preserving its natural fibers and allowing for better biodegradability and a longer lifespan, making it more sustainable in the long term. Choosing aniline leather for chairs supports eco-friendliness through minimal chemical treatment and enhanced durability, whereas bonded leather offers a lower-cost, recycled alternative with shorter lifespan and environmental trade-offs.
Suitability for Different Chair Uses
Bonded leather offers budget-friendly durability ideal for occasional-use chairs in home offices or guest rooms, resisting spills and wear while providing a leather-like appearance. Aniline leather, valued for its softness and breathability, is best suited for high-end executive or lounge chairs where comfort and natural texture are priorities, though it requires careful maintenance. Choosing between the two depends on chair use frequency, desired aesthetics, and maintenance capacity, with bonded leather favoring practicality and aniline leather excelling in luxury and comfort.
Choosing the Right Leather for Your Chair
Bonded leather offers an affordable, durable option for chairs, composed of leather scraps fused with polyurethane, providing a consistent appearance but lower breathability and aging quality compared to genuine leather. Aniline leather, dyed with soluble dyes without a protective coating, showcases natural grain and wrinkles, offering a soft, luxurious feel ideal for high-end chairs but requiring more maintenance and care to prevent staining and fading. Selecting the right leather depends on budget, usage frequency, and desired aesthetic, with bonded leather suitable for cost-effective, easy-care solutions and aniline leather preferred for premium, natural elegance and comfort.
Infographic: Bonded leather vs Aniline leather for Chair
 azmater.com
azmater.com