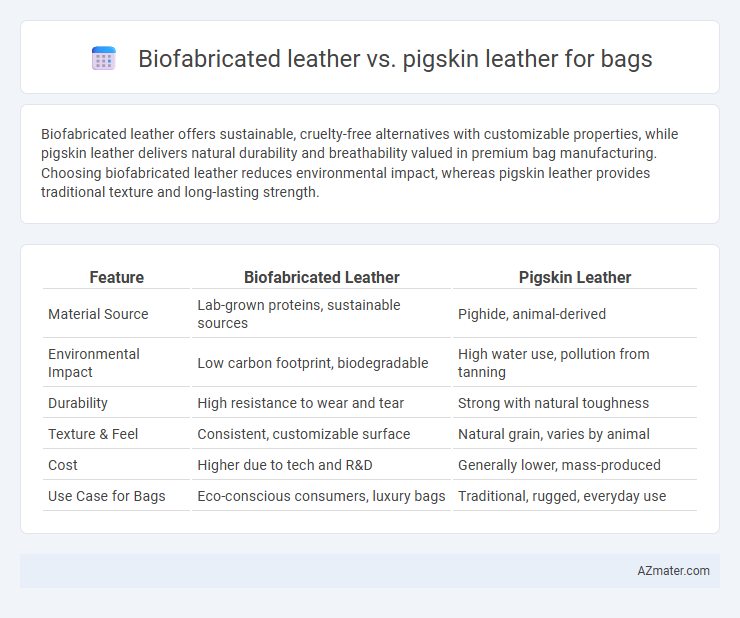
Biofabricated leather offers sustainable, cruelty-free alternatives with customizable properties, while pigskin leather delivers natural durability and breathability valued in premium bag manufacturing. Choosing biofabricated leather reduces environmental impact, whereas pigskin leather provides traditional texture and long-lasting strength.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Pigskin Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Lab-grown proteins, sustainable sources | Pighide, animal-derived |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable | High water use, pollution from tanning |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and tear | Strong with natural toughness |
| Texture & Feel | Consistent, customizable surface | Natural grain, varies by animal |
| Cost | Higher due to tech and R&D | Generally lower, mass-produced |
| Use Case for Bags | Eco-conscious consumers, luxury bags | Traditional, rugged, everyday use |
Introduction: The Evolution of Leather in Bag Manufacturing
Biofabricated leather, crafted from cultured cells and plant-based materials, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional pigskin leather in bag manufacturing. Pigskin leather, valued for its durability and natural grain, remains popular but faces environmental and ethical challenges. Innovation in biofabrication combines advanced biotechnology and material science, driving a shift towards eco-friendly, cruelty-free leather goods.
What Is Biofabricated Leather?
Biofabricated leather is an innovative material created through cellular agriculture by growing collagen fibers from animal cells without raising livestock, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional leather. Unlike pigskin leather, which is derived from the epidermis of pigs and involves conventional tanning processes, biofabricated leather minimizes environmental impact by reducing water usage, carbon emissions, and deforestation. This cutting-edge material maintains the durability and aesthetic qualities of natural leather, making it ideal for eco-conscious consumers seeking high-quality bags.
Understanding Pigskin Leather: Origins and Properties
Pigskin leather, derived from the skin of domestic pigs, boasts a unique grain texture and durability ideal for bag manufacturing. Its natural breathability and resistance to abrasion make it a preferred material in traditional leather goods, offering a distinctive balance between toughness and flexibility. Understanding pigskin leather's origins and inherent properties highlights its role as a benchmark in comparing innovative alternatives like biofabricated leather in the evolving bag industry.
Sustainability: Biofabricated Leather vs Pigskin Leather
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating animal farming, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, and conserving water compared to pigskin leather, which relies on resource-intensive livestock production. Unlike pigskin leather, which involves chemical tanning processes that contribute to pollution, biofabricated leather is often produced using biodegradable materials with fewer toxic substances. Sustainable sourcing and lower carbon footprints position biofabricated leather as a more eco-friendly alternative for bags in the fashion industry.
Durability Comparison: Biofabricated vs Pigskin Leather Bags
Biofabricated leather offers high durability with enhanced resistance to wear and environmental damage, making it suitable for long-lasting bag use. Pigskin leather is traditionally known for its toughness and natural flexibility, providing excellent abrasion resistance and a strong grain structure. When comparing durability, biofabricated leather is engineered for consistency and sustainability, while pigskin leather delivers proven resilience through natural fiber composition and years of practical application in bag manufacturing.
Ethical Considerations in Leather Production
Biofabricated leather offers a more ethical alternative to pigskin leather by eliminating the need for animal slaughter and reducing the environmental impact associated with traditional livestock farming. The production of biofabricated leather minimizes greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water consumption, addressing key concerns in sustainable fashion. In contrast, pigskin leather involves ethical challenges related to animal welfare, including intensive farming practices and the ethical implications of using animal hides for consumer goods.
Aesthetic Qualities: Surface Texture and Color Options
Biofabricated leather offers a smooth, uniform surface texture with customizable color options, allowing for vibrant and consistent finishes ideal for modern bag designs. Pigskin leather features a naturally textured grain that provides a rich, authentic look with subtle variations, typically available in traditional earthy tones. The choice between biofabricated and pigskin leather impacts aesthetic appeal, with biofabricated materials emphasizing sleek aesthetics and pigskin showcasing organic character.
Cost and Accessibility for Consumers
Biofabricated leather offers a premium price point due to advanced production technologies and limited scalability, making it less accessible for average consumers compared to pigskin leather. Pigskin leather remains cost-effective and widely available through established supply chains, supporting affordable pricing for bags. The growing demand for sustainable alternatives may gradually reduce biofabricated leather costs, but pigskin leather currently dominates consumer accessibility and budget considerations.
Environmental Impact and Carbon Footprint
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing lab-grown collagen proteins, eliminating the need for animal farming, which is a major source of methane emissions and deforestation. Pigskin leather production involves high water consumption, toxic chemical tanning processes, and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to a larger carbon footprint compared to biofabricated alternatives. Choosing biofabricated leather for bags supports sustainability by lowering resource use and minimizing pollution throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Future Trends: The Rise of Biofabricated Leather in Fashion
Biofabricated leather, derived from sustainable materials like fungi and microbes, offers a revolutionary alternative to traditional pigskin leather by reducing environmental impact and ethical concerns. Innovations in biofabrication technology are enabling scalable production, making biofabricated leather increasingly viable for high-quality bag manufacturing. Market demand for eco-friendly, cruelty-free fashion drives major brands to adopt biofabricated leather, signaling a significant shift toward sustainable luxury in future trends.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Pigskin leather for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com