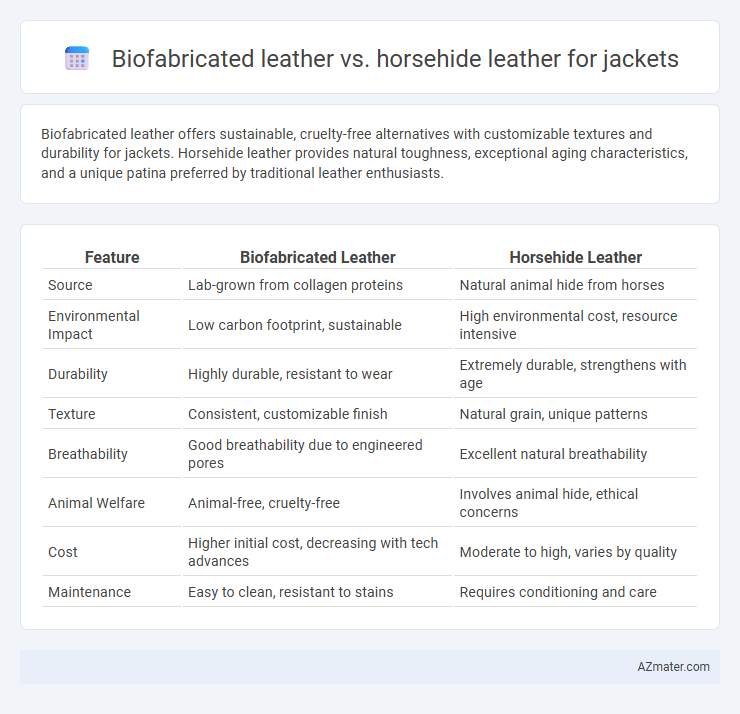
Biofabricated leather offers sustainable, cruelty-free alternatives with customizable textures and durability for jackets. Horsehide leather provides natural toughness, exceptional aging characteristics, and a unique patina preferred by traditional leather enthusiasts.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Horsehide Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown from collagen proteins | Natural animal hide from horses |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | High environmental cost, resource intensive |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to wear | Extremely durable, strengthens with age |
| Texture | Consistent, customizable finish | Natural grain, unique patterns |
| Breathability | Good breathability due to engineered pores | Excellent natural breathability |
| Animal Welfare | Animal-free, cruelty-free | Involves animal hide, ethical concerns |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, decreasing with tech advances | Moderate to high, varies by quality |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to stains | Requires conditioning and care |
Introduction to Biofabricated Leather and Horsehide Leather
Biofabricated leather is an innovative material created through cell culture techniques that mimic animal hide without the need for traditional livestock farming, offering sustainability and reduced environmental impact. Horsehide leather, known for its dense fiber structure and high durability, has been prized historically for jackets due to its toughness and natural resistance to stretching and abrasion. Comparing these materials highlights biofabricated leather's eco-friendly production and customizable properties against horsehide's established strength and classic aesthetic in durable outerwear.
Production Process: Biofabrication vs Traditional Tanning
Biofabricated leather is produced through a sustainable biofabrication process that cultivates animal cells in a controlled environment, eliminating the need for animal farming and reducing environmental impact. In contrast, traditional tanning of horsehide leather involves raising and slaughtering horses, followed by chemical-intensive tanning methods that can release harmful pollutants. The biofabrication process offers a cleaner, more ethical alternative by using biotechnology to replicate leather's texture and durability without harmful chemicals or animal cruelty.
Material Characteristics and Durability
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative with consistent texture and resistance to moisture, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional animal hides. Horsehide leather is prized for its toughness, natural grain, and ability to develop a rich patina over time, providing long-lasting durability for jackets. While horsehide excels in strength and aging quality, biofabricated leather often includes enhanced resistance to cracking and requires less maintenance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating animal farming, which cuts greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land degradation compared to traditional horsehide leather. Horsehide leather production contributes to deforestation, high methane emissions, and ethical concerns related to animal welfare. Sustainable biofabricated leather uses renewable resources and promotes a circular economy, making it a superior option for eco-conscious jacket manufacturing.
Texture, Appearance, and Aesthetic Appeal
Biofabricated leather offers a consistent, smooth texture that mimics natural leather but with improved durability and resistance to wear, while horsehide leather features a denser, grainier texture prized for its robustness and unique natural markings. The appearance of biofabricated leather is uniform and customizable in color and finish, providing a modern and sleek aesthetic, whereas horsehide leather develops a rich patina over time, enhancing its vintage and rugged charm. Both materials cater to different aesthetic appeals, with biofabricated leather appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking innovative design, and horsehide leather attracting enthusiasts of traditional craftsmanship and heritage style.
Comfort and Wearability in Jackets
Biofabricated leather offers superior breathability and flexibility compared to traditional horsehide leather, enhancing overall comfort in jackets. Horsehide leather is known for its durability and stiffness, providing excellent protection but requiring a break-in period that may reduce initial comfort. Jackets made from biofabricated leather tend to be lighter and more adaptive to body movement, improving wearability for extended periods.
Cost and Market Availability
Biofabricated leather jackets typically cost more due to advanced production technology and limited scale, often ranging from $300 to $600, whereas horsehide leather jackets usually cost between $150 and $400 depending on quality and tanning processes. Market availability of horsehide leather jackets is broader, benefiting from established supply chains and traditional demand, whereas biofabricated leather remains niche with limited brands and geographic reach. Consumers seeking sustainable alternatives may face higher prices and less accessibility with biofabricated leather despite growing interest and investment in biotechnology for fashion.
Ethical Considerations and Animal Welfare
Biofabricated leather offers a cruelty-free alternative to horsehide leather, eliminating the need to harm animals in the production process. Horsehide leather involves the use of animal skins, raising significant ethical concerns regarding animal welfare and treatment in the leather industry. Choosing biofabricated leather supports sustainable fashion practices that prioritize reducing animal suffering and environmental impact.
Maintenance and Longevity
Biofabricated leather offers superior resistance to water, stains, and UV damage, making it easier to maintain without the need for frequent conditioning or special cleaning products. Horsehide leather, known for its durability and natural aging, requires regular conditioning to prevent cracking and maintain flexibility, but can develop a unique patina that enhances its aesthetic over time. Longevity-wise, horsehide leather typically lasts decades with proper care, while biofabricated leather, though still developing, shows promising durability and consistent performance with less maintenance.
Choosing the Best Leather for Your Next Jacket
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional horsehide leather, making it ideal for environmentally conscious consumers seeking durable and supple material. Horsehide leather is renowned for its toughness, natural grain, and long-lasting wear, preferred by those valuing authenticity and heritage craftsmanship. Selecting the best leather depends on prioritizing eco-friendliness and innovation with biofabricated options or opting for classic strength and texture offered by horsehide for a premium jacket experience.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Horsehide leather for Jacket
 azmater.com
azmater.com