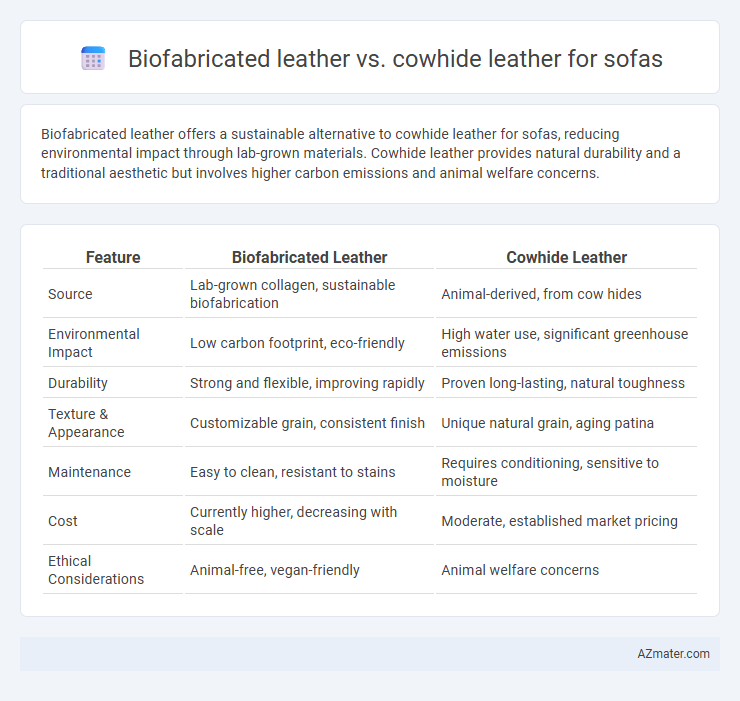
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative to cowhide leather for sofas, reducing environmental impact through lab-grown materials. Cowhide leather provides natural durability and a traditional aesthetic but involves higher carbon emissions and animal welfare concerns.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Cowhide Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown collagen, sustainable biofabrication | Animal-derived, from cow hides |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, eco-friendly | High water use, significant greenhouse emissions |
| Durability | Strong and flexible, improving rapidly | Proven long-lasting, natural toughness |
| Texture & Appearance | Customizable grain, consistent finish | Unique natural grain, aging patina |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, resistant to stains | Requires conditioning, sensitive to moisture |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing with scale | Moderate, established market pricing |
| Ethical Considerations | Animal-free, vegan-friendly | Animal welfare concerns |
Introduction to Biofabricated Leather and Cowhide Leather
Biofabricated leather is an innovative material created through cellular agriculture, growing collagen fibers in a lab to mimic traditional leather's texture and durability without animal involvement. Cowhide leather, derived from the tanned and treated hides of cattle, has been the conventional choice for sofas, known for its natural grain, durability, and breathability. Comparing these materials highlights biofabricated leather's sustainability and ethical advantages against cowhide leather's established luxury and performance characteristics.
Material Composition and Production Processes
Biofabricated leather is created using cultured animal cells or plant-based materials through biotechnological processes, resulting in a sustainable, cruelty-free alternative with a consistent texture and reduced environmental footprint. Cowhide leather is derived from animal hides, primarily cow skin, undergoing tanning and finishing treatments to enhance durability and appearance but involves resource-intensive livestock farming and chemical processing. The production of biofabricated leather emphasizes controlled lab environments and scalable bioengineering, while cowhide leather relies on traditional slaughterhouse supply chains and chemical tanning techniques.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated leather for sofas significantly reduces environmental impact by eliminating animal agriculture, decreasing greenhouse gas emissions, and minimizing water consumption compared to traditional cowhide leather. Cowhide leather production involves intensive resource use, including land, water, and chemicals for tanning, contributing to pollution and deforestation. Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative with lower carbon footprint and reduced ecological damage while maintaining durability and aesthetic appeal.
Durability and Lifespan
Biofabricated leather offers a durable alternative to traditional cowhide leather for sofas, exhibiting resistance to wear, stains, and UV damage. Cowhide leather has a proven lifespan, often lasting 10-15 years with proper care, characterized by natural strength and the capacity to develop a unique patina over time. Advances in biofabrication technologies aim to close the durability gap by mimicking the tensile strength and flexibility of cowhide, potentially extending the lifespan of biofabricated leather to rival or exceed that of conventional leather.
Comfort and Texture Differences
Biofabricated leather offers a softer, more supple texture compared to traditional cowhide leather, enhancing overall comfort for sofa seating. Its uniform surface reduces stiffness and breaks in more quickly, providing a consistently smooth feel. Cowhide leather, while durable and rich in natural grain, often requires a longer break-in period and can feel firmer initially, impacting immediate comfort.
Design Flexibility and Aesthetic Options
Biofabricated leather offers superior design flexibility and a broader range of aesthetic options compared to traditional cowhide leather for sofas. Its production process allows for customizable textures, colors, and finishes that can mimic or surpass natural leather's appearance while enabling innovative patterns and enhanced durability. Cowhide leather, while rich in natural grain and prestigious appeal, is limited by the inherent variability and color palette found in animal hides, restricting customization possibilities.
Cost Analysis and Market Pricing
Biofabricated leather for sofas typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced biotechnology processes and limited manufacturing scale, resulting in market prices that can be 2 to 3 times higher than traditional cowhide leather. Cowhide leather benefits from established supply chains and economies of scale, making it more cost-effective with average market prices ranging from $50 to $150 per square foot, compared to biofabricated leather's $120 to $300 per square foot. Market trends indicate a gradual price reduction in biofabricated leather as technological advancements increase production efficiency and scale.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Biofabricated leather for sofas offers low maintenance due to its resistance to stains, fading, and cracking, requiring only occasional gentle cleaning with a damp cloth. Cowhide leather demands more frequent conditioning and protection from direct sunlight and moisture to prevent drying, cracking, and discoloration. Choosing biofabricated leather reduces the need for specialized leather care products, making it a more practical option for homeowners seeking durability and ease of upkeep.
Ethical Considerations and Consumer Preferences
Biofabricated leather offers an ethical alternative to traditional cowhide leather by eliminating animal cruelty and reducing environmental impact through sustainable production methods. Consumers increasingly prefer biofabricated leather for its cruelty-free attributes, lower carbon footprint, and resistance to common ethical concerns associated with leather sourcing. This shift reflects a growing demand for eco-conscious and animal-friendly materials in sofa manufacturing.
Future Trends in Sofa Upholstery Materials
Biofabricated leather offers sustainable advantages with lower environmental impact and customizable properties, positioning it as a potential game-changer in future sofa upholstery trends. Cowhide leather remains valued for its durability, natural texture, and classic aesthetic but faces challenges due to ethical concerns and resource-intensive production. Innovations in biofabrication and increasing consumer demand for eco-friendly materials are driving the shift towards biofabricated leather in premium sofa designs.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Cowhide leather for Sofa
 azmater.com
azmater.com