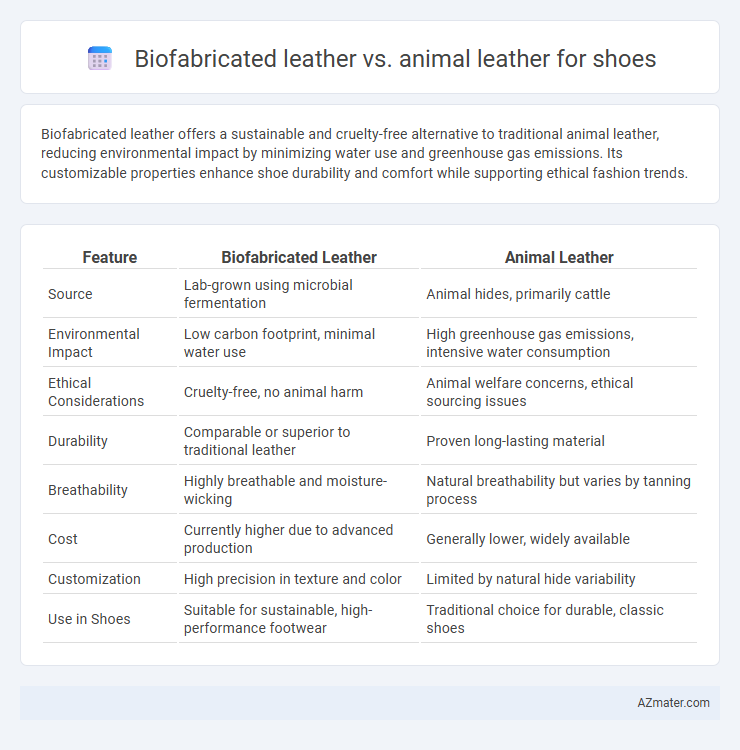
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather, reducing environmental impact by minimizing water use and greenhouse gas emissions. Its customizable properties enhance shoe durability and comfort while supporting ethical fashion trends.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown using microbial fermentation | Animal hides, primarily cattle |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, minimal water use | High greenhouse gas emissions, intensive water consumption |
| Ethical Considerations | Cruelty-free, no animal harm | Animal welfare concerns, ethical sourcing issues |
| Durability | Comparable or superior to traditional leather | Proven long-lasting material |
| Breathability | Highly breathable and moisture-wicking | Natural breathability but varies by tanning process |
| Cost | Currently higher due to advanced production | Generally lower, widely available |
| Customization | High precision in texture and color | Limited by natural hide variability |
| Use in Shoes | Suitable for sustainable, high-performance footwear | Traditional choice for durable, classic shoes |
Introduction to Biofabricated vs Animal Leather
Biofabricated leather is created through innovative biotechnology that cultivates collagen fibers in a lab, offering a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather derived from bovine hides. Unlike conventional leather, which involves extensive water use, chemical processing, and environmental impact, biofabricated leather reduces ecological footprints and ethical concerns. This cutting-edge material mimics the texture, durability, and aesthetic qualities of animal leather while supporting circular economy principles in the footwear industry.
Material Composition and Production Methods
Biofabricated leather is created using cultured animal cells or plant-based fibers, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather derived from bovine hides. The production of biofabricated leather involves biotechnological processes such as cell cultivation and tissue engineering, reducing environmental impact and eliminating the need for animal slaughter. In contrast, animal leather production includes activities like tanning and chemical treatment, which often result in significant water usage and pollution.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact compared to animal leather by lowering greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, and land use. Traditional animal leather production contributes to deforestation and methane emissions, whereas biofabricated leather utilizes sustainable cell cultures and renewable materials, minimizing resource depletion. Life cycle assessments reveal that biofabricated leather can cut carbon footprints by up to 80%, making it a more eco-friendly option for shoe manufacturing.
Durability and Performance in Shoes
Biofabricated leather exhibits impressive durability, often matching or surpassing animal leather in resistance to wear, water, and environmental stress, making it highly suitable for high-performance shoe applications. Unlike animal leather, which naturally offers excellent breathability and flexibility, biofabricated leather can be engineered to enhance specific attributes like tensile strength and abrasion resistance, optimizing shoe longevity and comfort. The sustainable production of biofabricated leather also ensures consistent quality and minimizes defects common in natural hides, contributing to more reliable performance in footwear.
Aesthetic and Sensory Qualities
Biofabricated leather offers a consistent texture and customizable appearance, allowing for unique finishes and vibrant colors that enhance shoe design aesthetics. Unlike traditional animal leather, which develops a natural patina and varies in grain and softness, biofabricated options maintain uniformity and can be engineered for specific tactile sensations such as smoothness or flexibility. Sensory qualities in biofabricated leather prioritize comfort through breathability and lightweight structure, while animal leather provides a rich, organic feel that many consumers associate with luxury and authenticity.
Ethical and Animal Welfare Considerations
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather by eliminating the need for animal slaughter, significantly reducing ethical concerns regarding animal welfare. This innovation supports cruelty-free fashion by utilizing cultured cells or plant-based materials, minimizing environmental impact while maintaining durability required for high-quality shoes. Consumer demand for ethical products continues to drive the growth of biofabricated leather, highlighting its role in promoting animal rights and responsible sourcing in the footwear industry.
Cost and Market Availability
Biofabricated leather for shoes offers a promising alternative with production costs currently higher than traditional animal leather due to advanced biotechnological processes and limited manufacturing scale. Animal leather remains more cost-effective and widely available in global markets, benefiting from established supply chains and mass production. However, biofabricated leather's market availability is expanding as startups and major brands invest in sustainable material innovations.
Consumer Perceptions and Trends
Biofabricated leather garners increasing consumer interest due to its ethical appeal, sustainability, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather. Market trends indicate a growing preference among environmentally conscious buyers for cruelty-free alternatives, with biofabricated leather noted for comparable durability and aesthetics. Consumer surveys reveal heightened willingness to pay premium prices for biofabricated leather shoes, driven by awareness of animal welfare and carbon footprint concerns.
Technological Innovations Shaping the Industry
Biofabricated leather utilizes advanced biotechnology and cellular agriculture to produce sustainable, cruelty-free materials that mimic the durability and texture of traditional animal leather. Innovations such as lab-grown collagen fibers and 3D bioprinting enable precise control over material properties, reducing environmental impact and waste compared to conventional leather tanning. These technological advancements are transforming the shoe industry by offering scalable, eco-friendly alternatives that maintain high performance and aesthetic appeal.
Future Prospects for Sustainable Footwear
Biofabricated leather, created through lab-grown collagen and microbial fermentation, offers a scalable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional animal leather, significantly reducing environmental impact and ethical concerns. Innovations in biofabrication are enhancing durability and texture, making it increasingly viable for high-performance footwear applications. The sustainable footwear market is projected to grow exponentially as consumer demand shifts towards cruelty-free and low-carbon materials, positioning biofabricated leather as a key player in the future of sustainable shoe manufacturing.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Animal leather for Shoe
 azmater.com
azmater.com