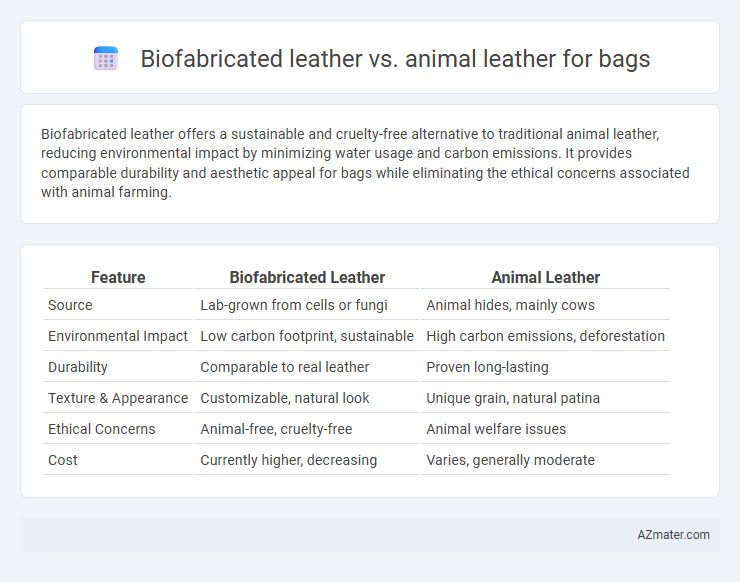
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather, reducing environmental impact by minimizing water usage and carbon emissions. It provides comparable durability and aesthetic appeal for bags while eliminating the ethical concerns associated with animal farming.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Biofabricated Leather | Animal Leather |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Lab-grown from cells or fungi | Animal hides, mainly cows |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, sustainable | High carbon emissions, deforestation |
| Durability | Comparable to real leather | Proven long-lasting |
| Texture & Appearance | Customizable, natural look | Unique grain, natural patina |
| Ethical Concerns | Animal-free, cruelty-free | Animal welfare issues |
| Cost | Currently higher, decreasing | Varies, generally moderate |
Introduction to Biofabricated and Animal Leather
Biofabricated leather, created through lab-grown collagen fibers, offers a sustainable and cruelty-free alternative to traditional animal leather derived from cowhides. This innovative material replicates the texture and durability of animal leather while reducing environmental impact by minimizing water usage, greenhouse gas emissions, and land consumption. Consumers seeking eco-friendly bags benefit from biofabricated leather's ethical production processes and potential for customization without sacrificing quality or aesthetic appeal.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Biofabricated leather is created using cultured animal cells or plant-based materials, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional animal leather, which is derived from the tanned hides of cows or other animals. The manufacturing process of biofabricated leather involves cell culture techniques or bioengineering methods that reduce environmental impact by minimizing water usage and chemical treatments compared to the conventional tanning process. Animal leather production requires intensive resource consumption, including water, chemicals like chromium, and long curing times, while biofabricated alternatives aim to replicate leather's durability and texture through innovative, eco-friendly approaches.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Biofabricated leather significantly reduces environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather by minimizing greenhouse gas emissions, water usage, and land consumption. Animal leather production involves extensive resource-intensive processes, including livestock farming that contributes to deforestation and methane emissions. Sustainable biofabricated leather offers a low-carbon alternative with biodegradable properties, promoting eco-friendly bag manufacturing.
Durability and Longevity
Biofabricated leather offers exceptional durability comparable to high-quality animal leather, as it is engineered to resist wear, tear, and environmental factors. Unlike traditional animal leather, biofabricated leather maintains its structural integrity without the natural oils that can deteriorate over time, enhancing its longevity. Both materials can withstand daily use, but biofabricated leather's resistance to cracking and fading often results in a longer lifespan for bags.
Aesthetic Qualities and Customization
Biofabricated leather offers a sleek, uniform texture with consistent color options that enhance modern bag designs, while animal leather displays natural grain variations, imparting a unique, organic aesthetic valued in luxury craftsmanship. Customization in biofabricated leather can be precisely controlled at the molecular level, enabling innovative patterns, colors, and finishes that traditional animal leather cannot easily replicate. Both materials support high-quality craftsmanship, but biofabricated leather allows for greater experimental design flexibility without compromising durability or feel.
Ethical Considerations
Biofabricated leather offers a sustainable alternative to animal leather by reducing the ethical concerns related to animal cruelty and slaughter in the fashion industry. It eliminates the need for raising and killing livestock, thereby addressing issues of animal welfare and environmental degradation from traditional leather production. Consumers seeking cruelty-free and eco-friendly bags increasingly prefer biofabricated leather due to its minimal ethical impact and lower carbon footprint.
Cost Analysis: Biofabricated vs Animal Leather
Biofabricated leather for bags typically incurs higher production costs due to advanced biotechnology and sustainable materials, contrasting with animal leather's established supply chains and economies of scale. While animal leather benefits from lower upfront costs and widespread availability, biofabricated alternatives offer potential long-term savings through scalable lab-grown processes and reduced environmental compliance expenses. Cost analysis reveals a shifting landscape where increasing demand and technological improvements are expected to narrow the price gap between biofabricated and animal leather in the bag industry.
Consumer Perceptions and Market Trends
Biofabricated leather, made from lab-grown collagen and plant-based materials, is gaining traction among eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives to traditional animal leather, which is often criticized for its environmental impact and ethical concerns. Market trends indicate a rising demand for cruelty-free, biodegradable bags with biofabricated leather appealing to younger demographics and luxury brands aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. Consumer perceptions highlight biofabricated leather as innovative and socially responsible, while animal leather remains valued for its durability and premium status but faces increasing scrutiny.
Regulatory and Certification Standards
Biofabricated leather for bags adheres to emerging regulatory frameworks emphasizing sustainability and non-toxic production, with certifications such as OEKO-TEX and Cradle to Cradle ensuring environmental safety and material traceability. Animal leather complies with traditional standards like the Leather Working Group (LWG) certification, which focuses on water use, chemical management, and sustainable tanning processes to reduce ecological impact. Both materials are increasingly subject to stringent environmental and health regulations, reflecting growing consumer demand for transparency and ethical sourcing in the fashion industry.
Future Outlook for Leather in Bag Production
Biofabricated leather showcases significant potential to revolutionize bag production by offering sustainable, cruelty-free alternatives that reduce environmental impact compared to traditional animal leather. Advances in biotechnology enable scalable manufacturing with customizable properties tailored for durability and aesthetics, meeting contemporary consumer demands for ethical fashion. The future of leather in bag production is poised for a paradigm shift as biofabricated materials gain market acceptance and regulatory support, fostering innovation and sustainability in the fashion industry.
Infographic: Biofabricated leather vs Animal leather for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com