Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it ideal for high-performance automotive windshields exposed to extreme temperature changes. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety by combining multiple glass layers with a plastic interlayer, preventing shattering and improving impact resistance in vehicle windshields.
Table of Comparison
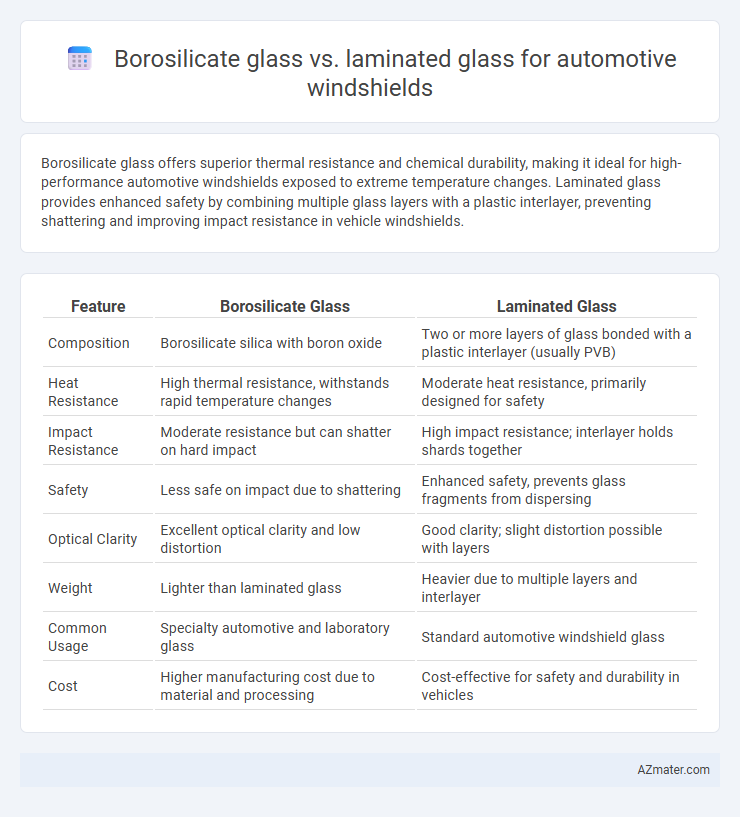
| Feature | Borosilicate Glass | Laminated Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Borosilicate silica with boron oxide | Two or more layers of glass bonded with a plastic interlayer (usually PVB) |
| Heat Resistance | High thermal resistance, withstands rapid temperature changes | Moderate heat resistance, primarily designed for safety |
| Impact Resistance | Moderate resistance but can shatter on hard impact | High impact resistance; interlayer holds shards together |
| Safety | Less safe on impact due to shattering | Enhanced safety, prevents glass fragments from dispersing |
| Optical Clarity | Excellent optical clarity and low distortion | Good clarity; slight distortion possible with layers |
| Weight | Lighter than laminated glass | Heavier due to multiple layers and interlayer |
| Common Usage | Specialty automotive and laboratory glass | Standard automotive windshield glass |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost due to material and processing | Cost-effective for safety and durability in vehicles |
Introduction to Automotive Windshield Materials
Automotive windshields primarily utilize laminated glass, composed of two layers of glass bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer for enhanced safety and impact resistance. Borosilicate glass, known for its thermal stability and chemical durability, is rarely used in automotive windshields due to its rigidity and higher cost. Laminated glass remains the industry standard by effectively combining shatter resistance and optical clarity to meet stringent safety regulations.
What is Borosilicate Glass?
Borosilicate glass is a type of glass known for its high resistance to thermal shock and chemical corrosion, making it ideal for automotive windshields requiring durability and safety. It contains silica and boron trioxide, which enhance its strength and prevent cracking under extreme temperature changes. Compared to laminated glass, borosilicate glass offers superior clarity and thermal stability, but laminated glass provides better impact resistance and shatterproof properties.
Laminated Glass: Structure and Composition
Laminated glass for automotive windshields consists of two or more layers of glass bonded together with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, enhancing impact resistance and occupant safety. The PVB layer absorbs energy during collisions, preventing shattering and reducing the risk of injury from glass shards. This multi-layered structure also improves sound insulation and UV protection compared to borosilicate glass, which is primarily known for its thermal resistance rather than impact performance.
Key Differences Between Borosilicate and Laminated Glass
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it less prone to cracking under temperature fluctuations in automotive applications, whereas laminated glass focuses on safety by combining two glass layers with a plastic interlayer to prevent shattering upon impact. Laminated glass provides superior impact resistance and sound insulation, commonly used for windshields to protect occupants during collisions, while borosilicate glass is more suited for specialized automotive parts requiring heat resistance. The key difference lies in borosilicate's robustness to heat and chemicals versus laminated glass's enhanced safety and impact absorption capabilities in automotive windshield applications.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical stability, making it highly durable under extreme temperature fluctuations commonly encountered in automotive environments. Laminated glass combines two layers of glass with an interlayer, providing enhanced impact resistance and preventing shattering, which significantly improves safety and structural integrity in windshields. While borosilicate glass excels in strength against thermal stress, laminated glass delivers better overall durability and occupant protection during collisions.
Safety Features for Vehicle Occupants
Borosilicate glass offers high thermal resistance and durability but lacks the shatterproof qualities essential for automotive windshields. Laminated glass, composed of two glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, enhances safety by preventing glass shards from dispersing upon impact, significantly reducing injury risks to vehicle occupants. Its ability to maintain windshield integrity during collisions minimizes ejection hazards and improves overall crash protection.
Thermal Performance and UV Protection
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal performance with high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for environments with rapid temperature changes in automotive windshields. Laminated glass, composed of two or more layers bonded with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer, provides excellent UV protection by filtering harmful ultraviolet rays, reducing interior fading and occupant exposure. While borosilicate glass enhances durability against temperature fluctuations, laminated glass ensures safety and UV blockage, critical for long-term vehicle use.
Cost Implications in Windshield Manufacturing
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and chemical durability but comes at a higher raw material cost compared to laminated glass, which primarily uses standard soda-lime glass layers with a polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer. Laminated glass manufacturing benefits from established large-scale production techniques and lower material expenses, making it more cost-effective for automotive windshields. The integration of laminated glass enhances safety features while maintaining affordability, positioning it as the preferred choice in automotive applications over the more expensive borosilicate alternatives.
Applications in Modern Automotive Design
Borosilicate glass exhibits superior thermal resistance and chemical durability, making it suitable for automotive components exposed to extreme temperature fluctuations, though it is less commonly used for windshields due to weight and cost considerations. Laminated glass, composed of two or more glass layers bonded with an interlayer like PVB, is the industry standard for automotive windshields, offering enhanced safety through impact resistance and preventing shattering. Modern automotive design increasingly integrates laminated glass with acoustic or UV-filtering interlayers to improve passenger comfort and safety while meeting stringent regulatory standards.
Which Glass is Best for Your Vehicle Windshield?
Borosilicate glass offers superior thermal resistance and durability, making it ideal for vehicles exposed to extreme temperature variations and requiring long-lasting performance. Laminated glass provides enhanced safety by holding shattered pieces together upon impact, reducing injury risk in collisions. For automotive windshields, laminated glass is generally preferred due to its safety benefits, while borosilicate glass suits specialty applications needing high heat and chemical resistance.
Infographic: Borosilicate glass vs Laminated glass for Automotive windshield
 azmater.com
azmater.com