Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m*K, outperforming phenolic foam's typical 0.020 W/m*K in energy-efficient construction. Its lightweight, hydrophobic properties enhance durability and moisture resistance compared to phenolic foam, making it ideal for high-performance building envelopes.
Table of Comparison
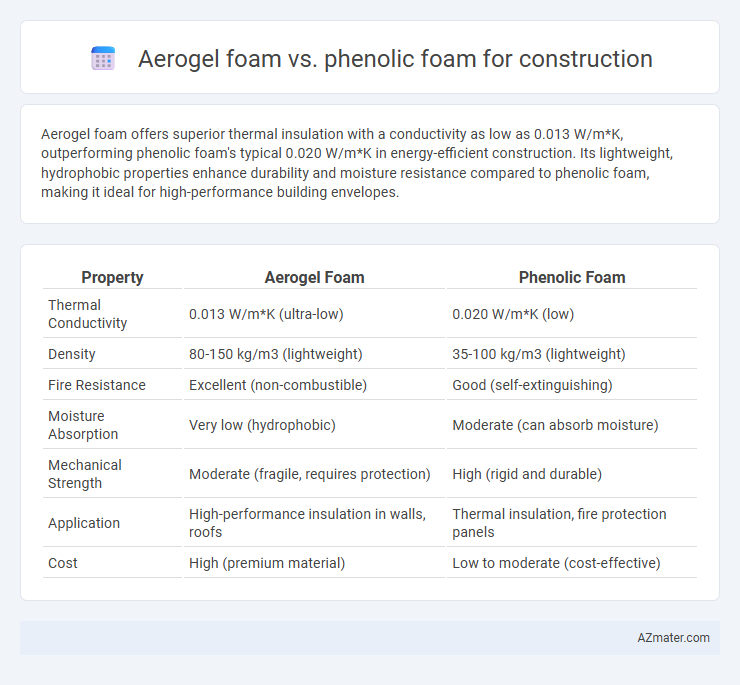
| Property | Aerogel Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.013 W/m*K (ultra-low) | 0.020 W/m*K (low) |
| Density | 80-150 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 35-100 kg/m3 (lightweight) |
| Fire Resistance | Excellent (non-combustible) | Good (self-extinguishing) |
| Moisture Absorption | Very low (hydrophobic) | Moderate (can absorb moisture) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate (fragile, requires protection) | High (rigid and durable) |
| Application | High-performance insulation in walls, roofs | Thermal insulation, fire protection panels |
| Cost | High (premium material) | Low to moderate (cost-effective) |
Introduction to Insulation Foams in Construction
Aerogel foam and phenolic foam are advanced insulation materials widely used in construction to enhance thermal performance and energy efficiency. Aerogel foam is distinguished by its ultra-low thermal conductivity, lightweight properties, and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring high-performance insulation in limited spaces. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and rigidity, making it a preferred choice for structural insulation panels and fire-rated assemblies in commercial and industrial buildings.
What is Aerogel Foam?
Aerogel foam is an ultra-light, highly porous material known for its exceptional thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient construction. Its silica-based structure provides low thermal conductivity, superior fire resistance, and excellent moisture control compared to traditional insulating materials. Phenolic foam, while also offering good fire resistance and thermal insulation, typically has higher density and lower flexibility than aerogel foam, affecting installation and performance in building applications.
What is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material made from phenol-formaldehyde resins, known for its excellent fire resistance, low smoke emission, and thermal insulation properties. It offers superior dimensional stability and moisture resistance compared to other foams, making it ideal for building envelopes, roof insulation, and wall panels in construction. This foam's closed-cell structure provides a high R-value per inch, enhancing energy efficiency in residential and commercial buildings.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Aerogel foam exhibits superior thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m*K, significantly outperforming phenolic foam, which typically ranges from 0.020 to 0.030 W/m*K. The ultralight structure of aerogel minimizes heat transfer through conduction, convection, and radiation, enhancing energy efficiency in building envelopes. Phenolic foam offers good fire resistance and compressive strength but cannot match the extreme thermal performance and thinner application profiles provided by aerogel foam in advanced construction projects.
Fire Resistance and Safety Analysis
Aerogel foam offers superior fire resistance compared to phenolic foam due to its low thermal conductivity and excellent insulation properties that prevent heat transfer during high-temperature exposure. Phenolic foam, while also fire-resistant and self-extinguishing, exhibits higher smoke density and toxicity under combustion, raising safety concerns in enclosed spaces. Safety analysis favors aerogel foam for critical applications requiring enhanced fire protection and minimal smoke generation in construction environments.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Aerogel foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to phenolic foam, due to its hydrophobic properties and ultra-low water absorption, making it ideal for damp or humid construction environments. Phenolic foam, while providing decent thermal insulation, tends to absorb more moisture, which can compromise its structural integrity and insulation performance over time. The durability of aerogel foam surpasses phenolic foam as it maintains its insulation capabilities and physical stability even under prolonged exposure to moisture and varying temperatures.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with minimal thickness, significantly reducing energy consumption and associated CO2 emissions in buildings. Phenolic foam provides good fire resistance and low smoke density but can have higher embodied energy due to its chemical composition. Aerogel's recyclable properties and lower environmental footprint make it a more sustainable choice compared to phenolic foam in eco-conscious construction projects.
Cost Effectiveness and Budget Considerations
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a higher R-value per inch compared to phenolic foam, often reducing overall energy consumption and long-term operational costs in construction projects. Phenolic foam, while less expensive upfront, provides decent fire resistance and moisture performance but may require thicker layers to match aerogel's insulation efficiency, impacting space and materials budget. Choosing between aerogel and phenolic foam depends on balancing initial material costs against lifecycle savings and project-specific insulation requirements.
Installation Process and Practicality
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation and is lightweight, making installation easier in tight spaces, but it requires careful handling due to its fragility. Phenolic foam provides good fire resistance and rigidity, facilitating straightforward cutting and fitting during installation while offering robust structural support. Practicality considerations favor phenolic foam for large-scale projects due to cost-effectiveness and durability, whereas aerogel foam is ideal for specialized applications needing high-performance insulation.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Foam for Construction
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with extremely low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for high-performance construction projects requiring maximum energy efficiency. Phenolic foam provides cost-effective fire resistance and good mechanical strength, suitable for standard insulation needs with stringent fire safety codes. Selecting the best foam depends on balancing performance requirements, budget constraints, and specific application demands within the construction environment.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Phenolic foam for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com