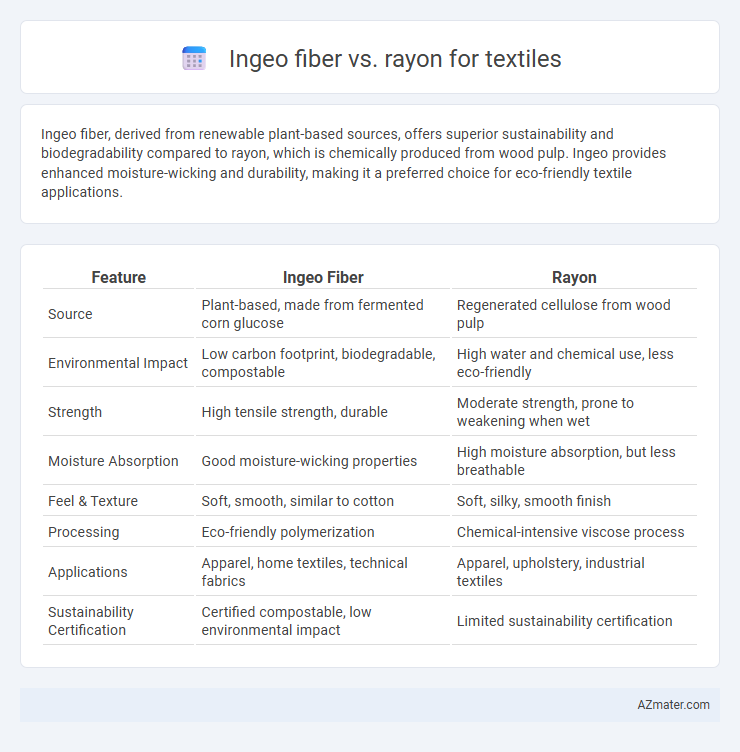
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior sustainability and biodegradability compared to rayon, which is chemically produced from wood pulp. Ingeo provides enhanced moisture-wicking and durability, making it a preferred choice for eco-friendly textile applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ingeo Fiber | Rayon |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Plant-based, made from fermented corn glucose | Regenerated cellulose from wood pulp |
| Environmental Impact | Low carbon footprint, biodegradable, compostable | High water and chemical use, less eco-friendly |
| Strength | High tensile strength, durable | Moderate strength, prone to weakening when wet |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture-wicking properties | High moisture absorption, but less breathable |
| Feel & Texture | Soft, smooth, similar to cotton | Soft, silky, smooth finish |
| Processing | Eco-friendly polymerization | Chemical-intensive viscose process |
| Applications | Apparel, home textiles, technical fabrics | Apparel, upholstery, industrial textiles |
| Sustainability Certification | Certified compostable, low environmental impact | Limited sustainability certification |
Introduction to Ingeo Fiber and Rayon
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials such as corn, offers a sustainable alternative to traditional rayon, which is made from chemically processed wood pulp. Ingeo fiber boasts biodegradability and a lower carbon footprint compared to rayon, which involves intensive chemical treatments during production. Both fibers provide softness and breathability for textile applications, but Ingeo's eco-friendly attributes position it as a preferred choice for environmentally conscious manufacturers.
Fiber Origins: Ingeo vs Rayon
Ingeo fiber is derived from renewable plant-based materials, primarily corn starch, through a patented fermentation process producing polylactic acid (PLA), offering a sustainable alternative to conventional fibers. Rayon originates from cellulose extracted mostly from wood pulp, involving chemical-intensive processes like viscose or lyocell production, which impact environmental footprints differently. The key distinction lies in Ingeo's bio-based, closed-loop manufacturing that reduces resource use and emissions, while rayon's origin depends on deforestation and chemical usage, influencing its ecological sustainability.
Production Processes Compared
Ingeo fiber is produced through a fermentation process that converts plant-based sugars, primarily from corn, into a biopolymer called polylactic acid (PLA), which is then spun into fibers using industrial-scale extrusion techniques. Rayon production involves chemically processing cellulose from wood pulp or cotton linters through the viscose process, which uses hazardous chemicals like carbon disulfide and sodium hydroxide, raising environmental concerns. Compared to rayon, Ingeo fiber's production is more sustainable and eco-friendly, relying on renewable resources with lower carbon emissions and minimal toxic byproducts, making it a preferable choice for environmentally conscious textile manufacturing.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources through a low-impact fermentation process, offers a significantly lower carbon footprint and reduced water usage compared to rayon, which relies heavily on chemically intensive wood pulp processing. The biodegradability of Ingeo further enhances its environmental credentials, making it a more sustainable option within the textile industry. Rayon production often involves toxic chemicals like carbon disulfide, posing environmental and health risks, whereas Ingeo presents a safer and more eco-friendly alternative.
Physical Properties and Performance
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources, offers higher tensile strength and better moisture-wicking properties compared to Rayon, which is a regenerated cellulose fiber prone to weaker durability and lower resistance to abrasion. Ingeo exhibits enhanced dimensional stability and elasticity, making it more resistant to wrinkles and deformation under stress, whereas Rayon tends to lose shape and strength when wet. The superior UV resistance and biodegradability of Ingeo fiber also contribute to longer-lasting textiles with reduced environmental impact compared to traditional Rayon fabrics.
Comfort and Wearability
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based sources, offers superior moisture-wicking and breathability compared to Rayon, enhancing comfort during extended wear. Rayon, derived from regenerated cellulose, feels soft but tends to retain moisture, which can reduce wearability in hot or humid conditions. The natural biodegradability and lightweight texture of Ingeo fiber also contribute to a more comfortable and eco-friendly textile choice over Rayon.
Textile Applications and Versatility
Ingeo fiber, made from renewable plant-based materials, offers excellent moisture management and breathability, making it ideal for activewear and sustainable fashion textiles. Rayon, derived from cellulose, provides a soft, silky texture with high absorbency, suited for drapery and delicate apparel applications. Both fibers demonstrate versatility, but Ingeo's eco-friendly production and durability give it a competitive edge in performance-driven textile markets.
Cost Analysis: Ingeo Fiber vs Rayon
Ingeo fiber offers a cost advantage over rayon due to its renewable corn-based origin, which reduces dependency on petroleum and results in lower raw material price volatility. While rayon production involves energy-intensive chemical processes that raise manufacturing costs and environmental compliance expenses, Ingeo fiber's eco-friendly production methods contribute to more stable and potentially lower overall expenses. Textile manufacturers seeking sustainable yet cost-effective materials often find Ingeo fiber more financially appealing compared to traditional rayon costs.
Market Trends and Consumer Preferences
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based sources like corn, is gaining market traction due to its biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional Rayon, which is produced from chemically processed wood pulp. Consumer preferences are shifting towards sustainable and eco-friendly textiles, driving demand for Ingeo fibers in apparel and home textiles markets. Market trends indicate growing investment in bio-based fabrics, with Ingeo positioned as a preferred alternative for brands targeting environmentally conscious consumers.
Future Prospects in Textile Industry
Ingeo fiber, derived from renewable plant-based materials, offers superior sustainability compared to traditional Rayon, which relies on chemically intensive processes from wood pulp. The textile industry increasingly values Ingeo for its lower carbon footprint, biodegradability, and compatibility with circular economy principles. Future prospects highlight Ingeo's potential to replace Rayon in mainstream applications, driven by growing consumer demand for eco-friendly fibers and stricter environmental regulations.
Infographic: Ingeo fiber vs Rayon for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com