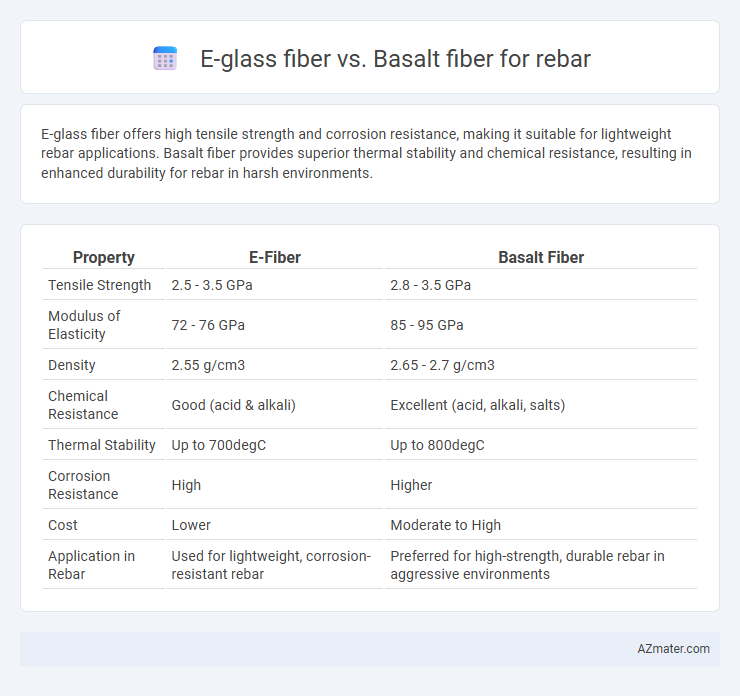
E-glass fiber offers high tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for lightweight rebar applications. Basalt fiber provides superior thermal stability and chemical resistance, resulting in enhanced durability for rebar in harsh environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | E-Fiber | Basalt Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 2.5 - 3.5 GPa | 2.8 - 3.5 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 72 - 76 GPa | 85 - 95 GPa |
| Density | 2.55 g/cm3 | 2.65 - 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Chemical Resistance | Good (acid & alkali) | Excellent (acid, alkali, salts) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 700degC | Up to 800degC |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | Higher |
| Cost | Lower | Moderate to High |
| Application in Rebar | Used for lightweight, corrosion-resistant rebar | Preferred for high-strength, durable rebar in aggressive environments |
Introduction to E-fiber and Basalt Fiber Rebars
E-fiber rebars, composed of engineered glass fibers, offer high tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making them ideal for reinforcing concrete structures exposed to harsh environments. Basalt fiber rebars, derived from natural volcanic rock, provide superior durability, thermal stability, and eco-friendly attributes while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. Both materials serve as advanced alternatives to traditional steel rebars, enhancing longevity and reducing maintenance costs in construction projects.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
E-fiber, composed primarily of alumino-borosilicate glass, is manufactured through a rapid fiber-drawing process from molten glass, resulting in high tensile strength and lightweight characteristics ideal for rebar reinforcement. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic basalt rock, undergoes a melting and extrusion process that preserves its natural mineral composition, offering superior chemical resistance and thermal stability compared to E-fiber. The inherent differences in raw materials and production techniques directly impact the mechanical properties and durability of rebar made from these fibers, influencing their suitability in various construction environments.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
E-fiber rebar exhibits high tensile strength ranging from 900 to 1200 MPa and excellent corrosion resistance, making it suitable for reinforced concrete structures exposed to aggressive environments. Basalt fiber rebar offers tensile strength between 800 and 1100 MPa, superior modulus of elasticity, and enhanced impact resistance, contributing to improved structural durability and load-bearing capacity. Both fiber types provide significant advantages over traditional steel rebar, but basalt's mechanical properties often result in better stiffness and crack resistance under mechanical stress.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
E-fiber rebar exhibits superior corrosion resistance due to its non-metallic composition, making it highly durable in harsh environments and saline conditions. Basalt fiber rebar also offers excellent durability, with strong resistance to chemical attacks and high temperatures, but may be slightly less resistant to alkaline conditions compared to E-fiber. Both materials outperform traditional steel rebar in corrosion resistance, extending the lifespan of reinforced concrete structures significantly.
Weight and Density Differences
E-fiber rebar exhibits significantly lower density, typically around 1.8 g/cm3, compared to basalt fiber rebar, which ranges from 2.6 to 2.8 g/cm3, making E-fiber substantially lighter. The weight difference enhances handling and transportation efficiency for E-fiber rebar without compromising tensile strength, crucial in construction applications. Basalt fiber rebar's higher density contributes to greater stiffness and impact resistance, though at the cost of increased structural weight.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
E-fiber rebar offers superior corrosion resistance and significantly reduces carbon emissions during production compared to traditional steel rebar, enhancing sustainability in construction projects. Basalt fiber rebar, derived from natural volcanic rocks, is non-toxic, fully recyclable, and boasts a lower embodied energy, making it an eco-friendly alternative with minimal environmental impact. Both materials contribute to reducing dependence on steel, decreasing construction waste, and promoting greener building practices with their durability and recyclability.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
E-fiber rebar offers a lower initial cost compared to basalt fiber rebar, making it a more budget-friendly option for large-scale construction projects. Basalt fiber rebar, while typically more expensive, provides superior durability and corrosion resistance, often justifying the higher price in long-term applications. Market availability favors E-fiber rebar due to established production channels and wider adoption, whereas basalt fiber rebar is still expanding its presence in global markets with growing demand in specialized infrastructure sectors.
Performance in Concrete Structures
E-fiber rebar offers superior tensile strength and corrosion resistance compared to basalt fiber rebar, enhancing the durability of concrete structures in aggressive environments. Basalt fiber rebar provides excellent thermal stability and high resistance to alkali attack, making it suitable for high-temperature or chemically harsh applications. Both fibers improve structural performance, but E-fiber excels in flexural strength while basalt fiber demonstrates better long-term chemical resistance.
Applications in Construction Industries
E-fiber and basalt fiber are increasingly utilized in construction for rebar reinforcement due to their superior mechanical properties and corrosion resistance compared to traditional steel rebar. E-fiber offers high tensile strength and lightweight characteristics, making it ideal for applications such as bridge decking, floor slabs, and seismic-resistant structures. Basalt fiber, derived from volcanic rock, excels in high-temperature stability and chemical resistance, making it preferred for infrastructure exposed to harsh environments like marine constructions and industrial facilities.
Future Trends and Innovations in Fiber Rebar Technology
E-fiber and basalt fiber represent cutting-edge materials in rebar technology, with ongoing innovations aimed at enhancing durability, corrosion resistance, and tensile strength for infrastructure applications. Future trends emphasize the integration of nanotechnology and hybrid composites to optimize performance and sustainability, enabling longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in construction projects. Advances in automated manufacturing and smart sensing embedded within fiber rebar are expected to revolutionize structural health monitoring and predictive maintenance.
Infographic: E-fiber vs Basalt Fiber for Rebar
 azmater.com
azmater.com