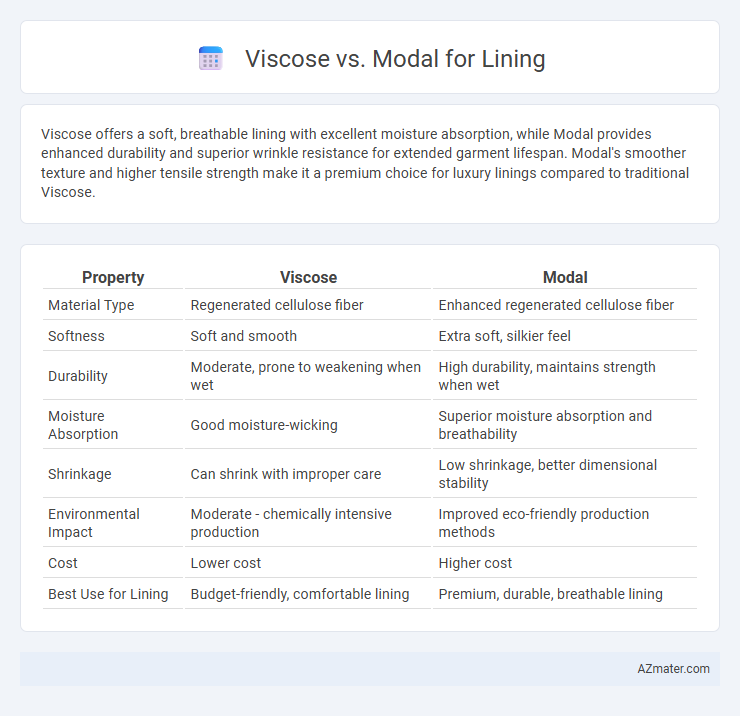
Viscose offers a soft, breathable lining with excellent moisture absorption, while Modal provides enhanced durability and superior wrinkle resistance for extended garment lifespan. Modal's smoother texture and higher tensile strength make it a premium choice for luxury linings compared to traditional Viscose.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Viscose | Modal |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Regenerated cellulose fiber | Enhanced regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Softness | Soft and smooth | Extra soft, silkier feel |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to weakening when wet | High durability, maintains strength when wet |
| Moisture Absorption | Good moisture-wicking | Superior moisture absorption and breathability |
| Shrinkage | Can shrink with improper care | Low shrinkage, better dimensional stability |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate - chemically intensive production | Improved eco-friendly production methods |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Best Use for Lining | Budget-friendly, comfortable lining | Premium, durable, breathable lining |
Introduction: Why Fabric Choice Matters for Lining
Viscose and modal are popular choices for lining fabrics due to their smooth texture and breathability, directly impacting garment comfort and durability. Modal offers superior moisture-wicking properties and greater affinity for dyes, making it more vibrant and resistant to shrinkage compared to viscose. Selecting the right fabric for lining enhances the overall garment performance by ensuring a soft touch against the skin and better structural support.
What Is Viscose?
Viscose is a semi-synthetic fiber made from regenerated cellulose, commonly derived from wood pulp, known for its soft and breathable qualities, making it an excellent choice for lining fabrics. Its smooth texture enhances comfort and drapes well, providing a luxurious feel in garments and upholstery. Viscose is highly absorbent and breathable compared to synthetic linings, making it a preferred option for moisture management in fashion and interior applications.
What Is Modal?
Modal is a type of semi-synthetic cellulose fiber derived from beech tree pulp, known for its softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making it an excellent choice for lining fabrics. Compared to viscose, modal offers superior durability and resistance to shrinkage, maintaining its shape and color even after multiple washes. Its eco-friendly production process and enhanced comfort make modal a preferred lining material in high-quality apparel and home textiles.
Fiber Source & Production Process
Viscose lining is derived from wood pulp through a chemical-intensive process involving carbon disulfide, producing a versatile fabric with moderate durability. Modal lining is made from beech tree cellulose, processed using a more eco-friendly, closed-loop system that recycles solvents and reduces environmental impact. Both fibers offer softness and breathability, but modal's sustainable production and higher wet strength often make it preferable for durable, comfortable linings.
Softness & Texture Comparison
Viscose and modal linings both offer exceptional softness, but modal is renowned for its smoother, silkier texture due to a more refined production process. Modal fibers retain softness even after multiple washes, making them ideal for garments requiring consistent comfort. In contrast, viscose provides a slightly more textured feel but remains breathable and lightweight, suitable for a wide range of lining applications.
Breathability & Moisture Wicking
Modal fabric exhibits superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to viscose, making it an ideal choice for lining in garments requiring better ventilation. The semi-synthetic nature of modal allows it to absorb and release moisture efficiently, ensuring enhanced comfort and dryness. Viscose, while breathable, tends to retain moisture longer, which can result in a less comfortable lining experience.
Durability & Strength
Modal fibers exhibit higher tensile strength and enhanced durability compared to viscose, making modal a more resilient choice for lining applications subjected to frequent wear. Viscose tends to have lower abrasion resistance and can weaken when exposed to moisture, whereas modal retains its integrity and softness even after repeated washing. For linings requiring long-lasting performance and resistance to stretching or tearing, modal provides superior strength and longevity.
Sustainability & Eco-Friendliness
Viscose and modal linings both derive from cellulose fibers, but modal boasts a more eco-friendly production process with lower water and chemical usage, enhancing its sustainability. Modal's biodegradable properties and renewable sourcing make it a preferred choice for environmentally conscious apparel manufacturers prioritizing sustainable textile options. In contrast, viscose often involves more intensive chemical processing, leading to higher environmental impact despite its popularity in linings.
Care, Maintenance & Longevity
Viscose and modal both offer soft, breathable linings, but modal excels in durability and moisture resistance, requiring less frequent washing to maintain its integrity. Modal resists pilling and shrinkage better than viscose, resulting in longer-lasting garments with minimal care. Proper care involves gentle washing and air drying for both fabrics to preserve their smooth texture and prevent fiber damage.
Which Is Better for Lining: Viscose or Modal?
Modal fabric outperforms viscose for lining due to its superior softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort in garments. Viscose tends to be less durable and can wrinkle easily, while modal retains shape and color better through washes. For luxury linings, modal's smooth texture and resilience make it the preferred choice over viscose.
Infographic: Viscose vs Modal for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com