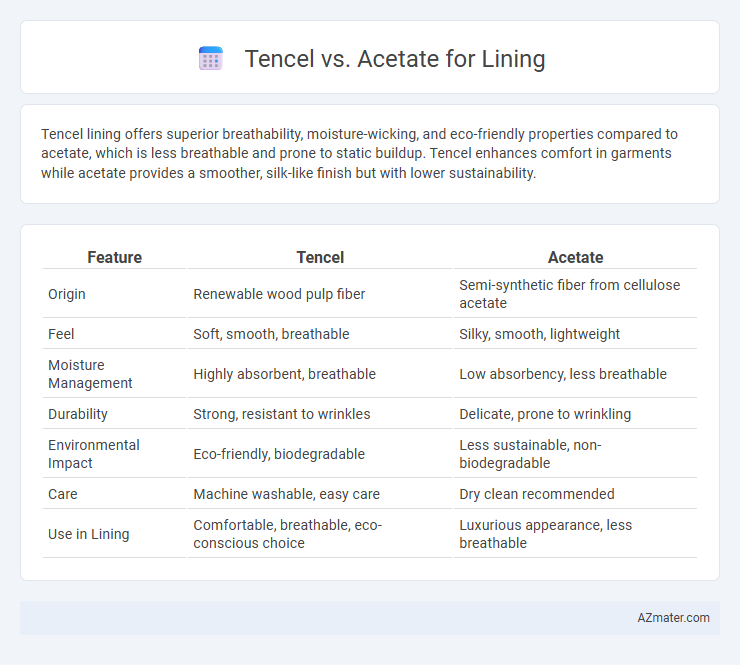
Tencel lining offers superior breathability, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly properties compared to acetate, which is less breathable and prone to static buildup. Tencel enhances comfort in garments while acetate provides a smoother, silk-like finish but with lower sustainability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Tencel | Acetate |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Renewable wood pulp fiber | Semi-synthetic fiber from cellulose acetate |
| Feel | Soft, smooth, breathable | Silky, smooth, lightweight |
| Moisture Management | Highly absorbent, breathable | Low absorbency, less breathable |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wrinkles | Delicate, prone to wrinkling |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Less sustainable, non-biodegradable |
| Care | Machine washable, easy care | Dry clean recommended |
| Use in Lining | Comfortable, breathable, eco-conscious choice | Luxurious appearance, less breathable |
Introduction: Why Lining Fabric Matters
Lining fabric plays a crucial role in garment comfort, durability, and breathability, influencing the overall wearing experience. Tencel, known for its moisture-wicking and eco-friendly properties, offers a soft, breathable option ideal for sensitive skin. Acetate provides a smooth, luxurious finish with excellent drape and sheen but lacks the moisture management and sustainability features of Tencel.
What is Tencel?
Tencel is a sustainable fabric made from cellulose fibers derived from eucalyptus wood, known for its softness, moisture-wicking properties, and eco-friendly production process. It offers excellent breathability and durability, making it an ideal choice for clothing linings that require comfort and long-lasting wear. Compared to acetate, Tencel is biodegradable and less prone to static, providing a more natural and comfortable lining experience.
What is Acetate?
Acetate is a synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, commonly used in linings for its smooth texture and resistance to wrinkles. It is known for its lustrous appearance and excellent drape, making it a popular choice in garment linings compared to natural or semi-synthetic fibers like Tencel. While acetate offers breathability and softness, it is less durable and less moisture-absorbent than Tencel, affecting its performance in long-lasting or moisture-wicking linings.
Key Differences Between Tencel and Acetate
Tencel and acetate differ significantly in fiber origin and sustainability, with Tencel derived from wood pulp and known for its eco-friendly production, while acetate is a semi-synthetic fiber made from cellulose acetate and involves chemical-intensive processing. In terms of comfort and performance, Tencel offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making it ideal for linings in garments requiring comfort, whereas acetate provides a smooth, glossy finish with excellent drape but lacks breathability. Durability also varies, as Tencel is more resistant to wrinkles and wear, whereas acetate can be prone to shrinkage and damage from heat and solvents.
Comfort and Softness Comparison
Tencel fibers provide superior moisture-wicking properties and exceptional breathability, making linings comfortable and soft against the skin. Acetate linings offer a smooth, silk-like feel but tend to retain heat and moisture, reducing overall comfort during prolonged wear. Tencel's eco-friendly production also enhances its appeal in sustainable fashion while maintaining softness comparable to acetate.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Tencel excels in breathability and moisture management due to its natural fibers that effectively absorb and release moisture, keeping the skin dry and comfortable. Acetate, while smooth and luxurious, tends to trap heat and moisture, making it less breathable and less effective at moisture wicking. For linings, Tencel is preferred in performance and comfort-focused garments, especially in warm or active environments.
Durability and Wear Performance
Tencel linings offer superior durability and wear performance due to their moisture-wicking and breathable properties, which help maintain fabric integrity over time. Acetate linings, while smooth and luxurious, tend to be less durable, prone to stretching and deterioration with frequent wear and washing. Choosing Tencel for lining ensures longer-lasting garments with enhanced comfort and resilience during daily use.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Tencel, derived from sustainably sourced wood pulp, offers superior environmental benefits compared to acetate due to its biodegradable properties and closed-loop production process that minimizes water and chemical use. Acetate, a cellulose-based synthetic fiber, involves more energy-intensive manufacturing and releases harmful chemicals, leading to a higher environmental footprint. Choosing Tencel for lining promotes eco-friendly fashion by reducing landfill waste and supporting renewable resource cycles.
Care and Maintenance of Tencel vs Acetate Linings
Tencel linings require gentle washing with mild detergents and should be air-dried to maintain their smooth texture and breathability, whereas acetate linings are more delicate and often need dry cleaning to prevent fabric damage and preserve their lustrous finish. Tencel's natural moisture-wicking properties make it less prone to odor retention and easier to freshen between washes compared to acetate, which can become brittle or lose sheen if improperly cleaned. Proper care of Tencel results in longer-lasting linings with minimal shrinkage, while acetate demands careful handling to avoid fabric puckering and color fading.
Which is Better for Lining: Tencel or Acetate?
Tencel offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to acetate, making it ideal for linings in garments that require comfort and temperature regulation. Acetate, while providing a smooth and shiny finish, lacks the durability and eco-friendly benefits that Tencel delivers. For linings prioritizing sustainability, softness, and longevity, Tencel is the better choice over acetate.
Infographic: Tencel vs Acetate for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com