Spider silk offers exceptional tensile strength and lightweight softness, making it a highly durable and breathable blanket material. Wool excels in insulation and moisture-wicking properties, providing superior warmth and comfort for cold climates.
Table of Comparison
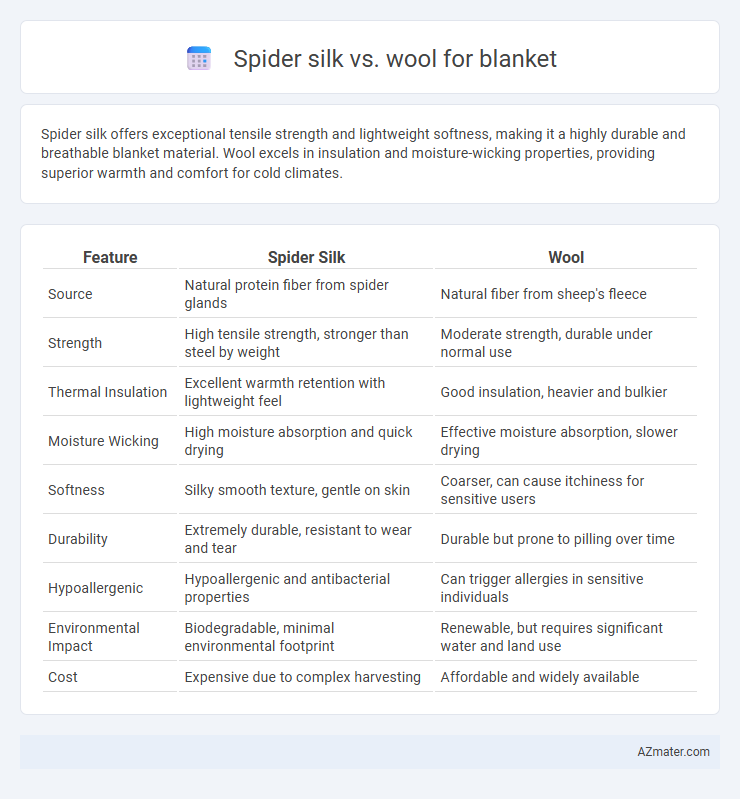
| Feature | Spider Silk | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from spider glands | Natural fiber from sheep's fleece |
| Strength | High tensile strength, stronger than steel by weight | Moderate strength, durable under normal use |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent warmth retention with lightweight feel | Good insulation, heavier and bulkier |
| Moisture Wicking | High moisture absorption and quick drying | Effective moisture absorption, slower drying |
| Softness | Silky smooth texture, gentle on skin | Coarser, can cause itchiness for sensitive users |
| Durability | Extremely durable, resistant to wear and tear | Durable but prone to pilling over time |
| Hypoallergenic | Hypoallergenic and antibacterial properties | Can trigger allergies in sensitive individuals |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, minimal environmental footprint | Renewable, but requires significant water and land use |
| Cost | Expensive due to complex harvesting | Affordable and widely available |
Introduction to Spider Silk and Wool
Spider silk, a natural protein fiber produced by spiders, is renowned for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties, making it an innovative material for blankets that offer durability and softness. Wool, derived from sheep, is a traditional textile fiber known for its excellent insulation, moisture-wicking abilities, and natural warmth, commonly used in blankets for comfort and thermal regulation. Comparing spider silk and wool highlights the contrast between advanced biomaterials and classic fibers in terms of performance and sustainability for blanket manufacturing.
Origin and Production Processes
Spider silk originates from the protein-based fibers produced by spiders, harvested through a complex and limited natural process or bioengineered synthesis involving genetically modified organisms. Wool is derived from the fleece of sheep, obtained through shearing and then cleaned, carded, and spun into yarn through well-established agricultural and textile production methods. The production of spider silk is highly specialized and labor-intensive compared to the more scalable and traditional wool manufacturing process.
Physical Properties Comparison
Spider silk exhibits exceptional tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly durable and flexible compared to wool, which is known for its insulating properties and natural moisture-wicking abilities. The lightweight and fine diameter of spider silk fibers allow for a softer, smoother texture, whereas wool fibers are thicker and coarser, contributing to bulkiness and warmth retention. While wool excels in fire resistance and breathability, spider silk offers superior thermal regulation and greater resistance to stretching and deformation.
Warmth and Insulation Capabilities
Spider silk offers exceptional warmth and insulation due to its fine protein structure, which traps heat efficiently while remaining lightweight and breathable. Wool provides robust insulation by retaining warmth even when damp, thanks to its natural crimp that creates air pockets to prevent heat loss. Compared to wool, spider silk blankets can offer superior thermal regulation and moisture-wicking properties, making them highly effective for temperature control in varying climates.
Softness and Comfort Level
Spider silk exhibits exceptional softness due to its ultra-fine fibers, offering a smooth and lightweight texture that surpasses many traditional fabrics. Wool provides natural warmth and a cozy feel but can sometimes cause itchiness or irritation for sensitive skin types. Blankets made from spider silk generally deliver superior comfort and breathability, making them ideal for those seeking luxury softness combined with moisture-wicking properties.
Durability and Longevity
Spider silk exhibits exceptional durability due to its tensile strength and elasticity, making it highly resistant to wear and tear compared to wool. Wool provides warmth and resilience but tends to degrade faster with repeated washing and exposure to moisture. Blankets made from spider silk maintain structural integrity and softness over extended periods, offering superior longevity in demanding conditions.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Spider silk exhibits superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to wool, allowing for efficient air circulation and rapid evaporation of sweat. Wool, while naturally moisture-absorbent and insulating, tends to retain dampness longer, which can reduce comfort in humid conditions. The lightweight, porous structure of spider silk fibers enhances temperature regulation and keeps sleepers dry, making it an optimal choice for breathable, moisture-managing blankets.
Hypoallergenic and Skin Sensitivity
Spider silk exhibits exceptional hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies. Unlike wool, which can sometimes cause irritation or itching due to lanolin and coarse fibers, spider silk is naturally smooth and free from common allergens. Its breathable and moisture-wicking qualities further enhance comfort for sensitive skin, promoting a gentle and irritation-free experience in blankets.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Spider silk offers a highly sustainable alternative for blankets, being biodegradable and produced through bioengineered methods that consume less water and energy compared to wool. Wool production involves significant land use and methane emissions from sheep, contributing to environmental degradation and climate change. Choosing spider silk blankets reduces reliance on animal farming, decreases greenhouse gas emissions, and supports a lower ecological footprint in textile manufacturing.
Cost and Market Availability
Spider silk blankets are significantly more expensive than wool due to the complex and labor-intensive process required to harvest and produce spider silk fibers. Wool blankets are widely available in the market, benefiting from a well-established supply chain and lower production costs, making them a cost-effective choice for most consumers. The rarity and high production costs of spider silk result in limited market availability compared to the abundant and affordable wool alternatives.
Infographic: Spider silk vs Wool for Blanket
 azmater.com
azmater.com