Soy fiber sweaters offer excellent breathability, moisture-wicking, and eco-friendly sustainability compared to traditional wool sweaters known for superior insulation and natural odor resistance. Both fibers provide softness, but soy fiber is lighter and hypoallergenic, making it ideal for sensitive skin.
Table of Comparison
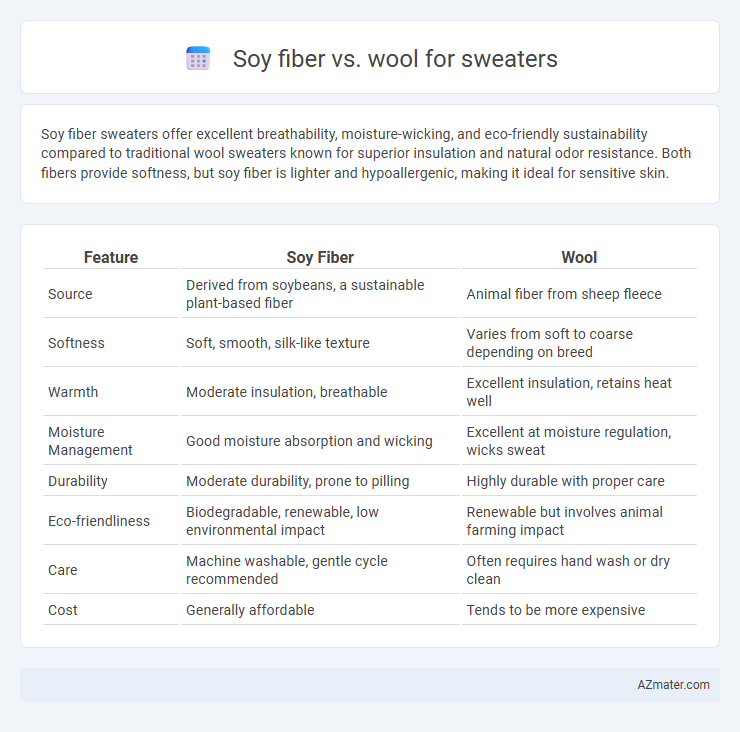
| Feature | Soy Fiber | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Derived from soybeans, a sustainable plant-based fiber | Animal fiber from sheep fleece |
| Softness | Soft, smooth, silk-like texture | Varies from soft to coarse depending on breed |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation, breathable | Excellent insulation, retains heat well |
| Moisture Management | Good moisture absorption and wicking | Excellent at moisture regulation, wicks sweat |
| Durability | Moderate durability, prone to pilling | Highly durable with proper care |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable, low environmental impact | Renewable but involves animal farming impact |
| Care | Machine washable, gentle cycle recommended | Often requires hand wash or dry clean |
| Cost | Generally affordable | Tends to be more expensive |
Introduction: Soy Fiber vs Wool Sweaters
Soy fiber sweaters offer a sustainable, eco-friendly alternative to traditional wool, boasting moisture-wicking and hypoallergenic properties ideal for sensitive skin. Wool sweaters provide superior insulation, natural breathability, and durability, making them a classic choice for cold weather garments. Comparing thermal regulation, sustainability, and comfort highlights the distinct benefits of soy fiber and wool in sweater manufacturing.
Overview of Soy Fiber and Wool Materials
Soy fiber, derived from soybean protein, is a sustainable and biodegradable material known for its softness, breathability, and natural moisture-wicking properties ideal for sweater fabrics. Wool, obtained primarily from sheep, offers excellent insulation, durability, and elasticity while retaining heat even when wet, making it a traditional choice for warm sweaters in colder climates. Both fibers cater to different needs, with soy fiber providing a smooth, lightweight feel and wool delivering superior warmth and resilience.
Environmental Impact: Sustainable Choices
Soy fiber, derived from soybean hulls, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to traditional wool in sweaters, with a lower carbon footprint and reduced water usage during production. Wool, while natural and biodegradable, often involves higher methane emissions from sheep and more intensive land use, contributing to environmental concerns. Choosing soy fiber sweaters supports sustainable fashion by utilizing agricultural byproducts and minimizing the ecological impact associated with animal farming.
Comfort and Texture Comparison
Soy fiber offers a smooth, soft texture that feels cool and breathable against the skin, making it highly comfortable for sweaters worn in mild to warm conditions. Wool provides excellent insulation and a naturally crimped texture that enhances warmth and elasticity, ideal for colder climates but can sometimes feel coarse to sensitive skin. Choosing between soy fiber and wool hinges on the desired balance between breathable softness and thermal insulation.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Soy fiber sweaters offer moderate warmth with good breathability and moisture-wicking properties, making them suitable for mild to cool weather. Wool excels in insulation due to its natural crimp, trapping air effectively to retain body heat even when damp. For maximum warmth and durability in cold conditions, wool remains the preferred choice over soy fiber.
Durability and Longevity
Soy fiber sweaters exhibit moderate durability with resistance to pilling and fading, but generally wear out faster than wool due to lower tensile strength. Wool fibers provide superior longevity, maintaining shape and insulation over years of use, thanks to their natural crimp and elasticity that enhance resilience against stretching and abrasion. Choosing wool ensures a long-lasting sweater with strong performance in durability and sustained comfort.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Soy fiber sweaters require gentle washing in cold water and air drying to maintain softness and prevent fabric weakening, with minimal pilling compared to wool. Wool sweaters demand careful hand washing or dry cleaning to avoid shrinkage and felting, along with proper storage using moth repellents to protect against damage. Both fibers benefit from avoiding high heat during drying, but wool's natural lanolin grants it some resistance to odors and dirt, reducing the frequency of washes.
Allergies and Skin Sensitivity
Soy fiber is hypoallergenic and gentle on sensitive skin, making it an excellent choice for individuals prone to allergies or skin irritation. Wool, while naturally insulating and breathable, can sometimes cause itching or allergic reactions in people with sensitive skin due to its lanolin content. Choosing soy fiber sweaters can reduce the risk of redness, itching, and discomfort associated with wool allergies.
Price and Accessibility
Soy fiber sweaters generally offer a more affordable price point compared to wool, making them accessible for budget-conscious consumers. Wool sweaters, sourced from sheep, tend to be pricier due to the labor-intensive production and natural insulating properties. Availability of soy fiber garments is increasing with the rise of sustainable fashion, while wool remains widely accessible through traditional retailers and specialty stores.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Sweater Material
Soy fiber offers superior softness and breathability, making it ideal for lightweight and eco-friendly sweaters, while wool provides exceptional warmth and durability, perfect for cold-weather garments. Consider factors such as climate, skin sensitivity, and sustainability preferences when selecting between soy fiber and wool sweaters. Prioritizing these attributes ensures optimal comfort and functionality aligned with individual needs.
Infographic: Soy fiber vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com