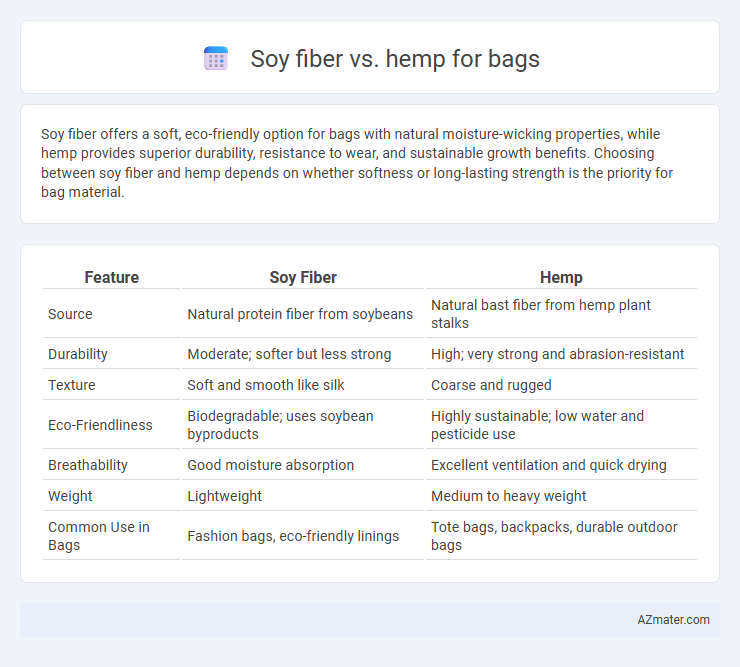
Soy fiber offers a soft, eco-friendly option for bags with natural moisture-wicking properties, while hemp provides superior durability, resistance to wear, and sustainable growth benefits. Choosing between soy fiber and hemp depends on whether softness or long-lasting strength is the priority for bag material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Soy Fiber | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural protein fiber from soybeans | Natural bast fiber from hemp plant stalks |
| Durability | Moderate; softer but less strong | High; very strong and abrasion-resistant |
| Texture | Soft and smooth like silk | Coarse and rugged |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable; uses soybean byproducts | Highly sustainable; low water and pesticide use |
| Breathability | Good moisture absorption | Excellent ventilation and quick drying |
| Weight | Lightweight | Medium to heavy weight |
| Common Use in Bags | Fashion bags, eco-friendly linings | Tote bags, backpacks, durable outdoor bags |
Introduction to Plant-Based Bag Fibers
Soy fiber and hemp are sustainable plant-based fibers increasingly favored for bag production due to their eco-friendly properties and durability. Hemp offers high tensile strength and natural resistance to moisture and UV rays, making it ideal for long-lasting bags. Soy fiber, derived from soy protein, provides a soft texture and good breathability, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal in plant-based bags.
Understanding Soy Fiber: Properties and Production
Soy fiber, derived from soybean protein through a unique wet spinning process, boasts excellent softness, moisture absorption, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly choice for bag manufacturing. It offers a silk-like texture combined with durability, suitable for both aesthetic and functional purposes. Unlike hemp, which is coarser and more rigid, soy fiber provides a lightweight and flexible alternative with natural antibacterial properties.
Hemp Fiber Overview: Strengths and Sustainability
Hemp fiber stands out for its superior tensile strength, making it ideal for durable bags that resist wear and tear over time compared to soy fiber. Its rapid growth cycle requires fewer pesticides and less water, significantly reducing its environmental footprint. The natural antimicrobial and UV-resistant properties of hemp contribute to sustainability by extending the lifespan and maintainability of hemp-based bags.
Environmental Impact: Soy Fiber vs Hemp
Hemp fiber demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact than soy fiber due to its rapid growth cycle and minimal water requirements, which reduce resource consumption and soil degradation. Hemp cultivation also absorbs more CO2 per hectare compared to soy, contributing to better carbon sequestration and enhanced soil health. In contrast, soy fiber production often depends on intensive agricultural practices and deforestation, leading to higher greenhouse gas emissions and loss of biodiversity.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Soy fiber and hemp both offer strong durability for bags, but hemp is known for its superior tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear, making it highly suitable for heavy-duty use. Hemp fibers also resist UV light and mold better than soy fiber, contributing to longer-lasting bags in diverse environmental conditions. While soy fiber provides a softer texture and some durability, hemp's robust natural composition generally ensures greater longevity and sustained structural integrity over time.
Texture and Aesthetics: How Do They Differ?
Soy fiber exhibits a smooth, silky texture with a subtle sheen, enhancing the visual appeal of bags with a refined, polished look. Hemp provides a coarse, rugged texture that contributes to a natural, earthy aesthetic, ideal for a durable and eco-friendly appearance. The contrast in fiber density and surface finish between soy and hemp significantly influences the tactile experience and overall design style of bags.
Cost and Availability of Soy and Hemp Fibers
Soy fiber offers a cost-effective alternative to hemp, with prices typically lower due to its widespread cultivation and established processing infrastructure. Hemp fiber, while generally more expensive, benefits from increasing demand in sustainable textiles but faces limited availability in some regions due to regulatory restrictions. Both fibers provide eco-friendly options, yet soy's affordability and broader market presence make it more accessible for bag manufacturing.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Soy fiber and hemp both offer excellent biodegradability, decomposing naturally within months under proper composting conditions, making them highly sustainable choices for bags. Hemp fibers possess greater durability and resistance to microbial degradation, extending the lifespan of hemp bags while still ensuring eco-friendly disposal. End-of-life scenarios for both materials prioritize industrial composting or soil integration, with hemp products contributing additional soil nutrients due to their lignin content compared to the more protein-based soy fibers.
Fashion Trends: Soy Fiber vs Hemp Bags
Soy fiber bags and hemp bags both align with the growing fashion trend toward sustainable materials, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional textiles. Hemp bags are praised for their durability and natural resistance to wear, making them a popular choice in eco-conscious fashion circles, while soy fiber bags appeal with their silky texture and biodegradability, adding a luxurious feel to sustainable accessories. The rising demand for plant-based fibers in fashion highlights soy fiber and hemp as versatile, stylish options that combine environmental responsibility with modern design.
Choosing the Right Fiber: Which is Better for Bags?
Soy fiber offers a smooth texture and natural sheen, making it ideal for lightweight, stylish bags with eco-friendly appeal. Hemp excels in durability and resistance to wear, providing a robust, long-lasting material perfect for heavy-use or outdoor bags. Choosing between soy fiber and hemp depends on the bag's intended use, balancing aesthetics with strength and sustainability requirements.
Infographic: Soy fiber vs Hemp for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com