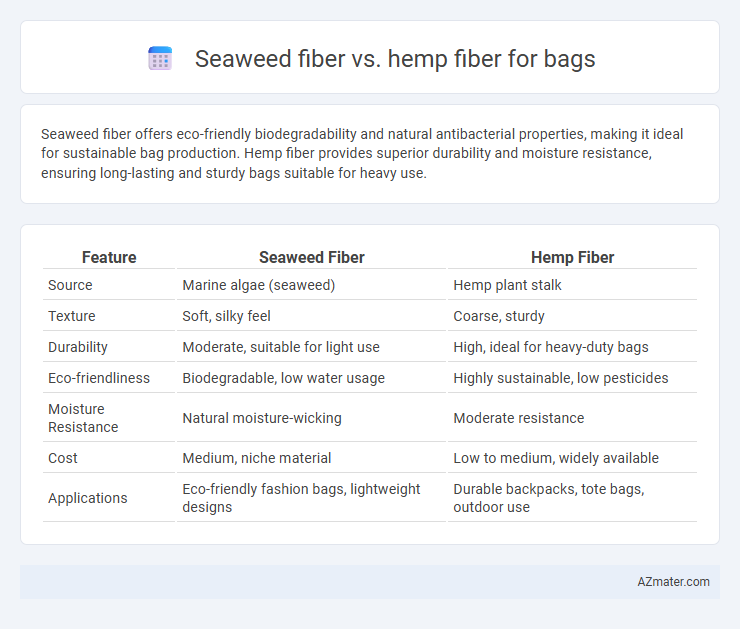
Seaweed fiber offers eco-friendly biodegradability and natural antibacterial properties, making it ideal for sustainable bag production. Hemp fiber provides superior durability and moisture resistance, ensuring long-lasting and sturdy bags suitable for heavy use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Seaweed Fiber | Hemp Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Marine algae (seaweed) | Hemp plant stalk |
| Texture | Soft, silky feel | Coarse, sturdy |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for light use | High, ideal for heavy-duty bags |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, low water usage | Highly sustainable, low pesticides |
| Moisture Resistance | Natural moisture-wicking | Moderate resistance |
| Cost | Medium, niche material | Low to medium, widely available |
| Applications | Eco-friendly fashion bags, lightweight designs | Durable backpacks, tote bags, outdoor use |
Introduction to Seaweed and Hemp Fibers
Seaweed fiber, derived from algae such as kelp, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative for fabric production with unique moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties. Hemp fiber, known for its strength and durability, is extracted from the stalks of the Cannabis sativa plant and is prized for its resistance to wear and environmental degradation. Both fibers are eco-friendly options for bag manufacturing, with seaweed providing softness and hemp offering robust structural support.
Sustainability Comparison: Seaweed vs Hemp
Seaweed fiber offers a renewable and biodegradable alternative with minimal water and land use, reducing environmental impact compared to traditional crops. Hemp fiber excels in sustainability through rapid growth, carbon sequestration, and requiring no pesticides, making it highly eco-friendly for bag production. Both fibers support circular economy principles, but hemp's durability and lower cultivation resource demands often give it a sustainability edge over seaweed fiber in large-scale applications.
Material Properties: Strength and Durability
Seaweed fiber offers natural biodegradability and a lightweight texture, but generally exhibits lower tensile strength and durability compared to hemp fiber. Hemp fiber is renowned for its exceptional tensile strength, abrasion resistance, and long-lasting durability, making it ideal for heavy-duty bags. The robust lignin and cellulose content in hemp fibers contribute to its superior structural integrity and resistance to wear over time.
Environmental Impact of Cultivation
Seaweed fiber cultivation significantly reduces environmental impact by requiring no freshwater, pesticides, or fertilizers, and it actively absorbs CO2, improving marine ecosystems. Hemp fiber farming enhances soil health through phytoremediation, requires minimal pesticides, and grows rapidly with low water input, contributing to sustainable agriculture. Both fibers offer eco-friendly alternatives to conventional materials, but seaweed's carbon sequestration and non-land-based growth provide unique environmental advantages.
Processing Methods of Seaweed and Hemp Fibers
Seaweed fiber is extracted through a wet processing method involving soaking seaweed in water, followed by mechanical pressing and drying to obtain fine, cellulose-rich fibers suitable for biodegradable bags. Hemp fiber undergoes retting, where stalks are soaked or exposed to moisture for several days to separate the bast fibers, then mechanically decorticated, combed, and spun into durable yarns ideal for sturdy bags. While seaweed processing emphasizes eco-friendly water-based techniques to preserve fiber integrity, hemp processing relies on traditional retting and decortication methods to maximize fiber strength and durability.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Considerations
Seaweed fiber offers higher biodegradability compared to hemp fiber, breaking down naturally within a few weeks in marine environments without releasing harmful residues. Hemp fiber, while slower to biodegrade, provides robust durability that extends product lifespan before disposal, decomposing fully in industrial composting facilities within several months. End-of-life considerations favor seaweed fiber for single-use or short-term bags, whereas hemp suits reusable bags requiring strength and moderate biodegradability.
Aesthetic and Functional Qualities for Bags
Seaweed fiber offers a smooth texture and natural sheen, creating bags with a sleek, eco-chic aesthetic, while hemp fiber provides a coarse, rugged look ideal for durable, rustic designs. Functionally, seaweed fiber is lightweight, moisture-wicking, and biodegradable, making bags comfortable and environmentally friendly, whereas hemp fiber excels in strength, abrasion resistance, and longevity, supporting heavy use and structural integrity. Both fibers support sustainable fashion but serve different consumer needs through their unique combinations of visual appeal and performance characteristics.
Cost Analysis: Production and Retail
Seaweed fiber production involves complex extraction processes that increase manufacturing costs compared to hemp fiber, which benefits from established agricultural and processing infrastructure, leading to lower production expenses. Retail prices of seaweed fiber bags tend to be higher due to limited supply and niche market positioning, while hemp fiber bags often offer more competitive pricing supported by mass production and widespread availability. Cost efficiency in hemp fiber is further enhanced by higher yield per hectare and stronger market demand, driving economies of scale that seaweed fiber currently lacks.
Consumer Preferences and Market Trends
Seaweed fiber offers eco-conscious consumers a sustainable, biodegradable alternative with a softer texture compared to hemp fiber, which is valued for its exceptional durability and strength in bag manufacturing. Market trends indicate growing interest in seaweed fiber-driven products due to increasing demand for marine-based, renewable resources, while hemp fiber maintains dominance in the market for its versatility and long-lasting performance. Consumer preferences lean toward seaweed fiber for luxury and eco-friendly bags, whereas hemp fiber appeals to users seeking rugged, everyday-use accessories.
Future Prospects for Seaweed and Hemp Fiber Bags
Seaweed fiber offers promising sustainability benefits due to its rapid growth and biodegradability, making it an innovative choice for eco-friendly bags as consumer demand for green products intensifies. Hemp fiber's durability, natural resistance to UV light and mold, and established supply chain position it as a strong contender for long-lasting, high-performance bags in the market. Increasing investment in research to enhance seaweed fiber processing and expanding hemp cultivation globally will drive future growth and adoption of both fibers in sustainable bag manufacturing.
Infographic: Seaweed fiber vs Hemp fiber for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com