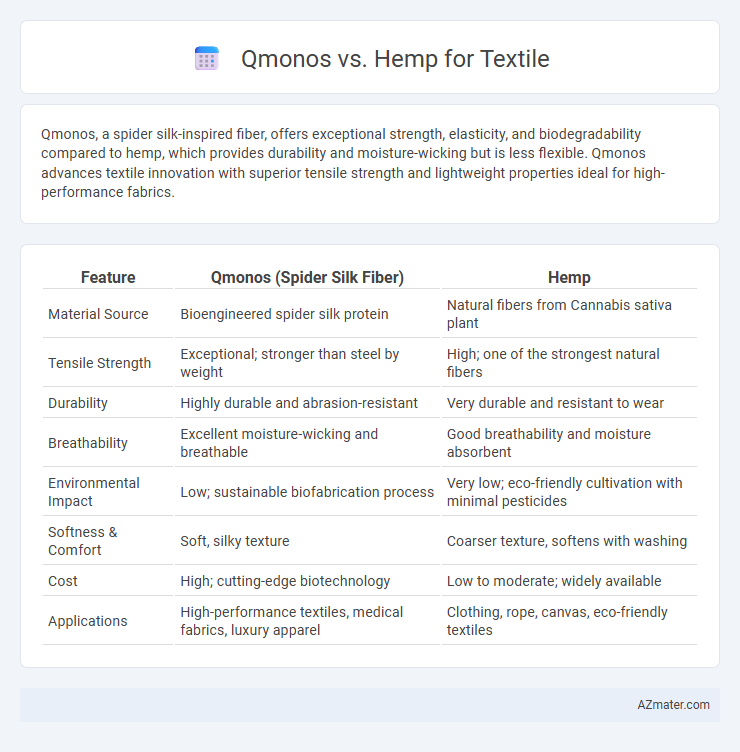
Qmonos, a spider silk-inspired fiber, offers exceptional strength, elasticity, and biodegradability compared to hemp, which provides durability and moisture-wicking but is less flexible. Qmonos advances textile innovation with superior tensile strength and lightweight properties ideal for high-performance fabrics.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Qmonos (Spider Silk Fiber) | Hemp |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Bioengineered spider silk protein | Natural fibers from Cannabis sativa plant |
| Tensile Strength | Exceptional; stronger than steel by weight | High; one of the strongest natural fibers |
| Durability | Highly durable and abrasion-resistant | Very durable and resistant to wear |
| Breathability | Excellent moisture-wicking and breathable | Good breathability and moisture absorbent |
| Environmental Impact | Low; sustainable biofabrication process | Very low; eco-friendly cultivation with minimal pesticides |
| Softness & Comfort | Soft, silky texture | Coarser texture, softens with washing |
| Cost | High; cutting-edge biotechnology | Low to moderate; widely available |
| Applications | High-performance textiles, medical fabrics, luxury apparel | Clothing, rope, canvas, eco-friendly textiles |
Introduction to Qmonos and Hemp Textiles
Qmonos is a cutting-edge synthetic fiber inspired by spider silk, known for its exceptional strength, elasticity, and lightweight properties, making it a revolutionary material in textile engineering. Hemp textiles are derived from the hemp plant, offering natural durability, breathability, and sustainability due to hemp's fast growth and minimal environmental impact. Both Qmonos and hemp represent innovative solutions for high-performance and eco-friendly textile production.
Material Origins: Qmonos vs Hemp
Qmonos, a synthetic silk fiber developed through bioengineering of silkworms, offers remarkable strength and elasticity derived from natural proteins, positioning it as a cutting-edge material in textiles. Hemp, sourced from the Cannabis sativa plant, is a bast fiber renowned for its durability, breathability, and eco-friendly cultivation with minimal pesticide use. Comparing origins, Qmonos combines biotechnology with natural protein synthesis, while hemp relies on agricultural plant fibers, highlighting a contrast between engineered biomaterials and traditional plant-based textiles.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Qmonos fibers, derived from genetically engineered silkworms, offer a sustainable alternative to traditional silk by reducing water usage and pesticide reliance, significantly lowering the environmental footprint compared to hemp cultivation. Hemp, while also eco-friendly due to its fast growth and carbon sequestration abilities, requires substantial water and land resources, and intensive processing that can impact soil health and biodiversity. Comparing the two, Qmonos presents a promising innovation with lower resource consumption and chemical inputs, positioning it as a greener choice in textile production.
Fiber Strength and Durability
Qmonos fiber exhibits exceptional tensile strength comparable to spider silk, making it one of the strongest known natural and synthetic fibers available for textile applications. Hemp fibers possess high durability, with natural resistance to wear and abrasion, making them well-suited for heavy-duty textile products. When comparing fiber strength and durability, Qmonos outperforms hemp in tensile strength, while hemp maintains superior toughness and environmental resilience.
Production Processes and Scalability
Qmonos fibers, produced through advanced genetic engineering and bioprocessing techniques, offer a highly controlled and scalable production environment compared to traditional hemp cultivation, which depends on variable agricultural conditions and longer growth cycles. The synthetic nature of Qmonos allows for consistent fiber quality and faster manufacturing times, supporting large-scale textile production with reduced environmental impact. Hemp production involves natural retting and mechanical processing, which, while sustainable, faces challenges in uniformity and scalability at industrial levels.
Sustainability and Biodegradability
Qmonos fibers, derived from genetically engineered silkworms, offer a renewable and biodegradable alternative to traditional textiles, with minimal environmental impact due to efficient production methods avoiding toxic chemicals. Hemp is widely recognized for its sustainability, requiring low water and pesticides while providing strong, durable, and fully biodegradable fibers that enrich soil health through crop rotation. Comparing both, Qmonos presents innovative biotech advantages in resource efficiency, whereas hemp delivers proven eco-friendly cultivation and biodegradability, making each suitable for sustainable textile applications depending on specific environmental priorities.
Textile Applications and Versatility
Qmonos, a synthetic spider silk fiber, offers superior tensile strength and elasticity compared to hemp, making it ideal for high-performance textile applications such as sportswear and medical fabrics. Hemp, valued for its natural durability, breathability, and antimicrobial properties, excels in producing eco-friendly, sustainable textiles like canvas, denim, and home furnishings. Both fibers demonstrate versatility, but Qmonos' advanced mechanical properties enable innovative uses demanding lightweight, flexible materials, while hemp remains favored for traditional, rugged textile products.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Qmonos fiber offers superior cost efficiency compared to hemp due to its bioengineered production process that reduces raw material expenses and enhances scalability. Hemp fibers, while abundant and naturally sustainable, often incur higher processing costs and face seasonal availability constraints impacting market supply consistency. The global textile market is increasingly adopting Qmonos for its predictable quality and lower lifecycle costs, whereas hemp remains popular in niche, eco-conscious segments despite fluctuating pricing and limited large-scale availability.
Consumer Perception and Acceptance
Qmonos fibers are praised for their superior tensile strength and durability compared to traditional hemp textiles, influencing consumer perception toward high-performance applications. Hemp is widely recognized for its eco-friendly attributes, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers despite its relatively coarser texture. Consumer acceptance of Qmonos remains niche due to higher costs, whereas hemp enjoys broader market integration driven by sustainability and natural fiber appeal.
Future Trends in Textile Innovation
Qmonos, a spider silk-based fiber developed by Kraig Biocraft Laboratories, offers extraordinary strength, elasticity, and biodegradability, positioning it as a revolutionary alternative to traditional textiles like hemp. Hemp remains a sustainable and widely used natural fiber valued for its durability, breathability, and low environmental impact, but Qmonos promises enhanced performance characteristics suited for high-tech applications such as medical textiles and advanced composites. Future trends in textile innovation point toward hybrid materials combining Qmonos' superior mechanical properties with hemp's eco-friendly profile to create next-generation fabrics that are both sustainable and high-performing.
Infographic: Qmonos vs Hemp for Textile
 azmater.com
azmater.com