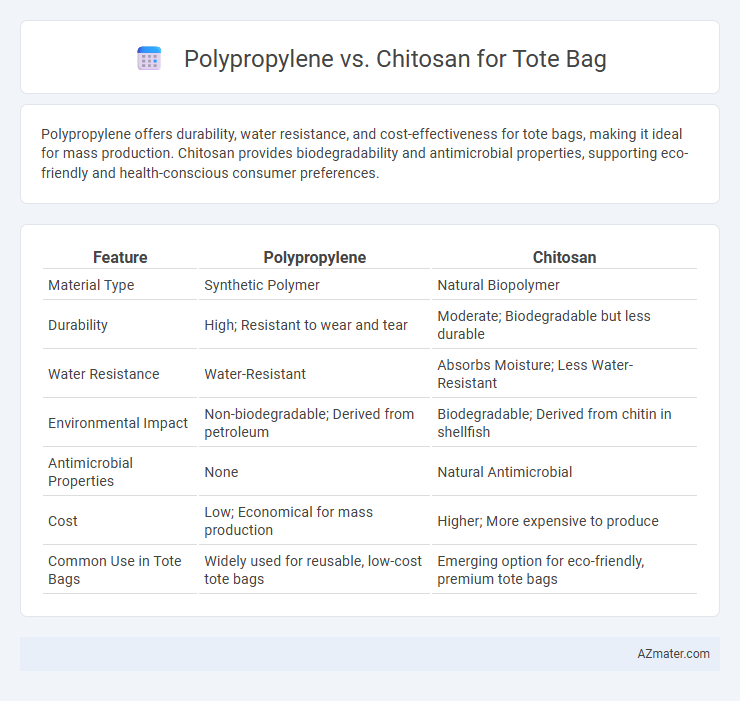
Polypropylene offers durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness for tote bags, making it ideal for mass production. Chitosan provides biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, supporting eco-friendly and health-conscious consumer preferences.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polypropylene | Chitosan |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic Polymer | Natural Biopolymer |
| Durability | High; Resistant to wear and tear | Moderate; Biodegradable but less durable |
| Water Resistance | Water-Resistant | Absorbs Moisture; Less Water-Resistant |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable; Derived from petroleum | Biodegradable; Derived from chitin in shellfish |
| Antimicrobial Properties | None | Natural Antimicrobial |
| Cost | Low; Economical for mass production | Higher; More expensive to produce |
| Common Use in Tote Bags | Widely used for reusable, low-cost tote bags | Emerging option for eco-friendly, premium tote bags |
Introduction to Tote Bag Materials
Polypropylene and chitosan represent two distinct materials commonly used in tote bag production, each offering unique benefits. Polypropylene, a synthetic polymer, is favored for its durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for reusable shopping bags. Chitosan, derived from natural sources like crustacean shells, provides biodegradable and antimicrobial properties, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives.
Overview of Polypropylene
Polypropylene is a durable, lightweight thermoplastic polymer widely used for tote bags due to its high tensile strength and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Its cost-effectiveness and recyclability make it an eco-friendly option compared to traditional plastics. Polypropylene totes offer excellent wear resistance, making them suitable for repeated use while maintaining structural integrity.
Overview of Chitosan
Chitosan is a biodegradable, natural polysaccharide derived from chitin, commonly found in crustacean shells, making it an eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials like polypropylene for tote bags. It offers antimicrobial properties, enhanced breathability, and excellent biodegradability, contributing to sustainable fashion and reducing plastic pollution. Chitosan's ability to be chemically modified allows for versatile applications, including water resistance and improved mechanical strength in textile products.
Environmental Impact: Polypropylene vs Chitosan
Polypropylene tote bags, made from non-biodegradable fossil fuel-based polymers, contribute significantly to plastic pollution and persist in ecosystems for hundreds of years. In contrast, chitosan tote bags, derived from renewable crustacean shell waste, offer biodegradable and compostable properties, drastically reducing landfill burden and microplastic contamination. The environmental footprint of chitosan bags is further minimized by their lower carbon emissions during production compared to polypropylene manufacturing.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Polypropylene tote bags exhibit superior durability and strength due to their synthetic fibers, offering resistance to wear, moisture, and heavy loads. In contrast, chitosan, derived from natural sources, provides moderate strength and biodegradability but is less resistant to prolonged stress and environmental elements. Polypropylene's tensile strength typically ranges from 30-50 MPa, while chitosan composites usually have lower mechanical properties, making polypropylene more suitable for long-term, heavy-duty tote bag use.
Biodegradability and Sustainability
Polypropylene tote bags are widely used due to their durability and cost-effectiveness but pose significant environmental concerns since they are non-biodegradable and contribute to plastic pollution. In contrast, chitosan tote bags, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, offer excellent biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, making them a sustainable alternative in eco-friendly packaging. The choice between polypropylene and chitosan significantly impacts sustainability goals, with chitosan supporting reduced landfill waste and enhanced compostability.
Cost Efficiency and Market Availability
Polypropylene tote bags offer superior cost efficiency with prices typically 30-50% lower than chitosan alternatives, making them ideal for large-scale production and budget-conscious consumers. Market availability of polypropylene is widespread due to its mass production and established supply chains, ensuring consistent stock and diverse style options worldwide. In contrast, chitosan tote bags, derived from natural biopolymers, present higher costs and limited availability, primarily targeting niche markets focused on biodegradability and eco-friendly materials.
Health and Safety Aspects
Polypropylene tote bags are durable and water-resistant but may release microplastics and harmful chemicals during production and disposal, posing environmental and health risks. Chitosan, derived from natural sources like shellfish, offers antimicrobial properties and biodegradability, reducing potential health hazards associated with prolonged use or contamination. Choosing chitosan bags enhances safety by minimizing chemical exposure and supporting eco-friendly waste management.
Consumer Preferences and Trends
Consumers prefer polypropylene tote bags for their durability, water resistance, and affordability, making them ideal for daily use and mass distribution. Chitosan tote bags attract eco-conscious buyers due to their biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, aligning with growing trends in sustainable fashion. Market analysis reveals a rising demand for biodegradable alternatives like chitosan as environmental awareness influences purchasing decisions.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material
Polypropylene offers durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for long-lasting tote bags used in various weather conditions. Chitosan provides biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, appealing to eco-conscious consumers seeking sustainable alternatives. Selecting the right material depends on balancing environmental impact, use-case durability, and consumer preferences for functionality versus sustainability.
Infographic: Polypropylene vs Chitosan for Tote Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com