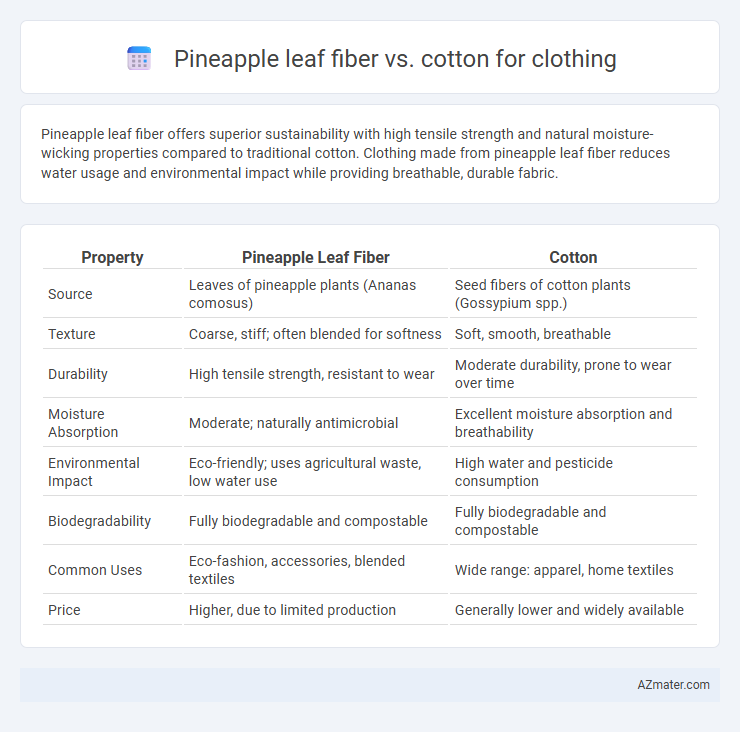
Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior sustainability with high tensile strength and natural moisture-wicking properties compared to traditional cotton. Clothing made from pineapple leaf fiber reduces water usage and environmental impact while providing breathable, durable fabric.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Pineapple Leaf Fiber | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Leaves of pineapple plants (Ananas comosus) | Seed fibers of cotton plants (Gossypium spp.) |
| Texture | Coarse, stiff; often blended for softness | Soft, smooth, breathable |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Moderate durability, prone to wear over time |
| Moisture Absorption | Moderate; naturally antimicrobial | Excellent moisture absorption and breathability |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly; uses agricultural waste, low water use | High water and pesticide consumption |
| Biodegradability | Fully biodegradable and compostable | Fully biodegradable and compostable |
| Common Uses | Eco-fashion, accessories, blended textiles | Wide range: apparel, home textiles |
| Price | Higher, due to limited production | Generally lower and widely available |
Introduction to Pineapple Leaf Fiber and Cotton
Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from the leaves of the Ananas comosus plant, offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional textiles with high tensile strength and natural luster. Cotton, a widely used natural fiber harvested from the Gossypium plant, is prized for its softness, breathability, and comfort in clothing applications. Both fibers provide unique properties that influence durability, eco-friendliness, and texture in fabric production.
Origin and Production Processes
Pineapple leaf fiber, derived from the agricultural waste of pineapple plants primarily cultivated in the Philippines and Thailand, undergoes a mechanical extraction process followed by washing and drying to produce a natural textile material. Cotton, sourced from the cotton plant predominantly grown in the United States, India, and China, is harvested through mechanical picking, then processed by ginning to separate fibers from seeds before spinning into yarn. The sustainable extraction of pineapple leaf fiber contrasts with conventional cotton cultivation, which often involves intensive water use and pesticide application.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Pineapple leaf fiber production requires significantly less water and land compared to cotton, making it a more sustainable choice for clothing. Unlike cotton, which relies heavily on pesticides and synthetic fertilizers, pineapple leaf fiber is a natural byproduct of pineapple farming, reducing agricultural waste and minimizing chemical use. The biodegradability and lower carbon footprint of pineapple leaf fiber contribute to its advantage in reducing the environmental impact associated with textile manufacturing.
Biodegradability and Sustainability
Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior biodegradability compared to conventional cotton, breaking down more rapidly without leaving harmful residues in the environment. The cultivation of pineapple leaves utilizes agricultural waste, reducing the need for additional land or water resources, thereby enhancing sustainability. Cotton farming involves significant water consumption and pesticide use, increasing environmental impact and making pineapple leaf fiber a more eco-friendly alternative for sustainable clothing production.
Texture, Feel, and Wearability
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a coarse, slightly stiff texture compared to the soft and smooth feel of cotton, making it suitable for structured garments rather than delicate wear. The natural durability and breathability of pineapple fiber enhance longevity and comfort, especially in warm climates, while cotton excels in softness and moisture absorption for everyday wearability. Pineapple fiber's unique texture provides an eco-friendly alternative with a rustic aesthetic, contrasting with cotton's classic versatility and ease of care.
Moisture Absorption and Breathability
Pineapple leaf fiber outperforms cotton in moisture absorption due to its natural hygroscopic properties, allowing it to wick sweat away efficiently and keep the skin dry. The porous structure of pineapple leaf fiber enhances breathability, promoting better airflow and ventilation compared to the denser weave of cotton fabrics. This makes pineapple leaf fiber an ideal choice for activewear and tropical climates where moisture management and comfort are critical.
Durability and Longevity
Pineapple leaf fiber offers superior durability compared to cotton, with its natural lignin content enhancing tensile strength and resistance to wear. Cotton fibers, while softer and more breathable, tend to degrade faster under repeated washing and prolonged use. Clothing made from pineapple leaf fiber demonstrates longer longevity, maintaining structural integrity and appearance better than traditional cotton garments.
Cost and Market Availability
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a sustainable alternative to cotton with a generally lower production cost due to its use of agricultural byproducts, but its processing infrastructure remains limited, affecting market availability. Cotton dominates the global textile market with well-established supply chains and wide accessibility, though increasing cultivation costs and environmental concerns impact its pricing. Emerging interest in pineapple leaf fiber clothing is driving gradual expansion in niche markets, but cotton remains the more cost-effective and readily available choice for mass-produced apparel.
Fashion Trends and Versatility
Pineapple leaf fiber, known for its sustainability and natural sheen, is gaining popularity in fashion trends as an eco-friendly alternative to cotton. Its lightweight and breathable properties offer versatility, making it suitable for both casual and formal clothing designs while reducing environmental impact compared to traditional cotton cultivation. Designers increasingly incorporate pineapple leaf fiber to create innovative textiles that appeal to eco-conscious consumers seeking stylish yet sustainable wardrobe options.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Clothing
Pineapple leaf fiber offers a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative to conventional cotton, requiring significantly less water and pesticides for cultivation, making it highly sustainable for future clothing production. Innovations in processing pineapple leaf fiber enhance its softness and durability, enabling its use in high-quality, sustainable textiles that meet growing consumer demand for eco-conscious fashion. The integration of pineapple leaf fiber in circular fashion models supports waste reduction and promotes a regenerative textile industry, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Infographic: Pineapple leaf fiber vs Cotton for Clothing
 azmater.com
azmater.com