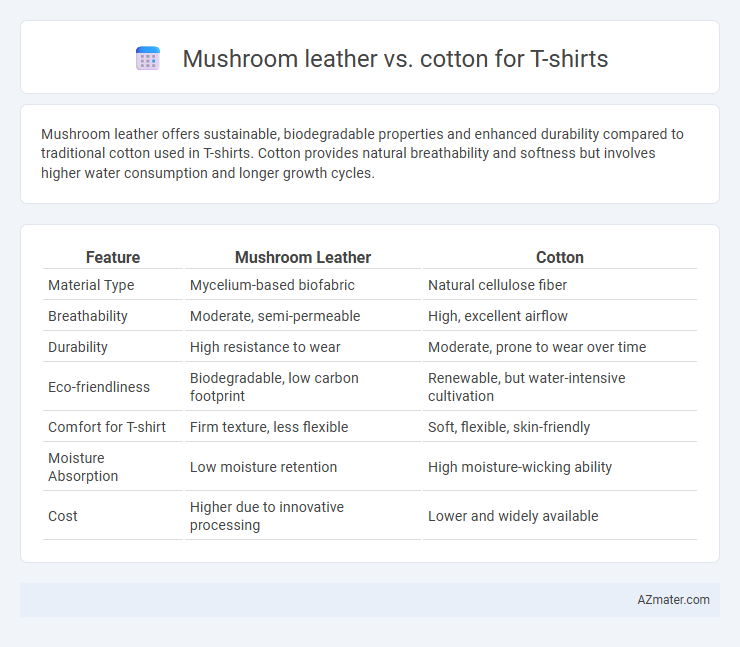
Mushroom leather offers sustainable, biodegradable properties and enhanced durability compared to traditional cotton used in T-shirts. Cotton provides natural breathability and softness but involves higher water consumption and longer growth cycles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Mushroom Leather | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Mycelium-based biofabric | Natural cellulose fiber |
| Breathability | Moderate, semi-permeable | High, excellent airflow |
| Durability | High resistance to wear | Moderate, prone to wear over time |
| Eco-friendliness | Biodegradable, low carbon footprint | Renewable, but water-intensive cultivation |
| Comfort for T-shirt | Firm texture, less flexible | Soft, flexible, skin-friendly |
| Moisture Absorption | Low moisture retention | High moisture-wicking ability |
| Cost | Higher due to innovative processing | Lower and widely available |
Introduction: Comparing Mushroom Leather and Cotton for T-Shirts
Mushroom leather offers a sustainable and biodegradable alternative to traditional materials by utilizing mycelium, the root structure of fungi, which grows rapidly with minimal environmental impact. Cotton, widely used in T-shirts, is a natural fiber valued for its breathability and softness but demands significant water and pesticide inputs during cultivation. Comparing the two highlights mushroom leather's innovative eco-friendly properties alongside cotton's established comfort and versatility in apparel.
What is Mushroom Leather?
Mushroom leather, also known as mycelium leather, is a sustainable material derived from the root structure of fungi, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional textiles. Unlike cotton, which requires extensive water and pesticide use, mushroom leather is biodegradable, renewable, and produced using minimal resources. This innovative material provides durability and a leather-like texture, making it a promising option for sustainable T-shirt production.
The Journey of Cotton: From Plant to T-Shirt
Cotton undergoes a complex transformation from seed planting, growing through several months, to harvesting, ginning, spinning, and weaving before becoming a T-shirt fabric. Mushroom leather, derived from fungal mycelium, offers a sustainable alternative with less water and pesticide use compared to cotton cultivation, which requires extensive land and resources. This shift highlights the environmental impact of traditional cotton production and the growing demand for innovative, eco-friendly textile materials like mushroom leather.
Environmental Impact: Cotton vs. Mushroom Leather
Mushroom leather offers a significantly lower environmental impact compared to conventional cotton used in T-shirts, requiring less water and land while generating fewer greenhouse gas emissions during production. Cotton farming involves intensive water use--approximately 2,700 liters per kilogram of cotton--and often relies on pesticides that harm ecosystems and soil health. In contrast, mushroom leather is biodegradable and produced from agricultural waste, making it a more sustainable alternative with a smaller carbon footprint and reduced resource consumption.
Durability and Longevity: Which Material Lasts Longer?
Mushroom leather, known for its sustainable production and natural resilience, offers superior durability compared to cotton, resisting wear and tear more effectively over time. Cotton, while breathable and comfortable, tends to degrade faster with repeated washing and exposure to sunlight, leading to fading and fiber weakening. Overall, mushroom leather's robust structure ensures a longer lifespan, making it a preferable choice for T-shirts that need to withstand extended use.
Comfort and Wearability: Feel and Fit on the Skin
Mushroom leather offers a unique texture that is soft and supple, providing a breathable surface that adapts well to body movements, enhancing comfort during wear. Cotton is naturally lightweight and highly breathable, known for its softness and ability to wick moisture, making it ideal for prolonged skin contact. While cotton generally feels more familiar and flexible, mushroom leather introduces innovative durability with a slightly distinctive tactile experience, appealing to those seeking eco-friendly alternatives with comfortable wearability.
Style and Design Flexibility
Mushroom leather offers unique texture and color variations that enhance T-shirt style with a modern, eco-friendly appeal, while cotton provides a classic, versatile canvas favored for endless design possibilities and comfort. The pliability of mushroom leather enables innovative cuts and embellishments, catering to fashion-forward designs that stand out in sustainable fashion. Cotton's breathable, lightweight nature allows for diverse printing techniques and fabric treatments, making it a preferred choice for customizable, everyday wear.
Cost Considerations: Pricing and Accessibility
Mushroom leather T-shirts typically have higher upfront costs due to sustainable production methods and limited manufacturing scale compared to widely available and mass-produced cotton T-shirts. Cotton remains more affordable and accessible, benefiting from established supply chains and economies of scale. Consumers looking for eco-friendly alternatives may face premium pricing with mushroom leather, influencing overall cost considerations.
Ethical and Social Implications
Mushroom leather offers a sustainable alternative to cotton by reducing water usage and eliminating harmful pesticides, addressing ethical concerns related to environmental impact and worker health. Cotton production often involves intensive farming practices that contribute to soil degradation and exploit labor in developing countries, raising significant social justice issues. Choosing mushroom leather for T-shirts supports cruelty-free manufacturing and promotes circular economy principles, fostering ethical consumption and improved social outcomes.
Future Outlook: The Evolution of Sustainable T-Shirt Materials
Mushroom leather offers a cutting-edge alternative to cotton by combining biodegradability and lower environmental impact with innovative fungal biotechnology, positioning it as a key material for future sustainable fashion. Cotton, while renewable and breathable, requires significant water and pesticide inputs, driving research toward eco-friendly substitutes like mycelium-based fabrics that reduce resource depletion. The ongoing evolution of sustainable T-shirt materials highlights a shift toward biofabricated textiles such as mushroom leather, which promise durability, reduced carbon footprint, and circular economy compatibility in apparel production.
Infographic: Mushroom leather vs Cotton for T-shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com