Modal fibers offer superior moisture-wicking and softness, making sweaters lightweight and breathable. Wool provides excellent insulation and durability, ideal for warmth and long-lasting sweaters.
Table of Comparison
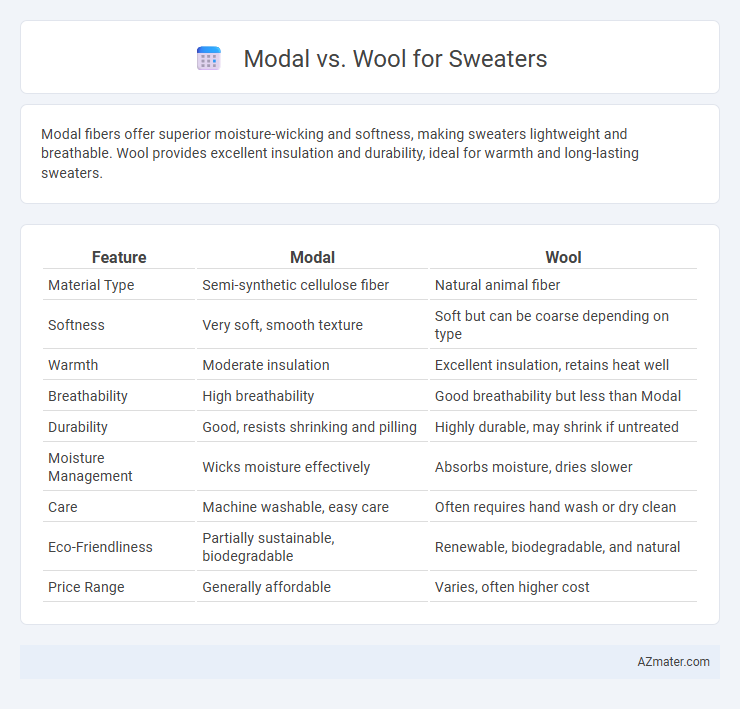
| Feature | Modal | Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Semi-synthetic cellulose fiber | Natural animal fiber |
| Softness | Very soft, smooth texture | Soft but can be coarse depending on type |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | Excellent insulation, retains heat well |
| Breathability | High breathability | Good breathability but less than Modal |
| Durability | Good, resists shrinking and pilling | Highly durable, may shrink if untreated |
| Moisture Management | Wicks moisture effectively | Absorbs moisture, dries slower |
| Care | Machine washable, easy care | Often requires hand wash or dry clean |
| Eco-Friendliness | Partially sustainable, biodegradable | Renewable, biodegradable, and natural |
| Price Range | Generally affordable | Varies, often higher cost |
Introduction to Sweater Fabrics: Modal vs Wool
Modal fabric offers a soft, smooth texture with excellent moisture-wicking properties, making it a lightweight, breathable choice for sweaters ideal for moderate climates. Wool, derived from sheep fleece, provides superior insulation and durability, excelling in warmth retention and moisture resistance, perfect for colder environments. Understanding the temperature regulation, comfort, and care requirements of Modal and Wool helps in selecting the right sweater fabric based on climate and personal preference.
What is Modal? Characteristics and Origin
Modal is a semi-synthetic fiber made from beech tree pulp, primarily known for its exceptional softness and breathability. Originating in Japan in the 1950s and refined by Croatian inventor Rudolf Damberger, Modal offers superior moisture-wicking properties and a silky texture, making it an excellent choice for sweaters. Its durability and resistance to shrinking and pilling differentiate Modal from natural fibers like wool, providing a lightweight and comfortable alternative.
What is Wool? Types and Properties
Wool is a natural fiber obtained from the fleece of sheep, renowned for its exceptional warmth, moisture-wicking abilities, and breathability, making it ideal for sweaters. Common types of wool include Merino, known for its fine, soft texture; Cashmere, prized for its luxurious softness and insulation; and Alpaca, valued for its hypoallergenic properties and durability. Wool fibers have excellent elasticity, resilience, and natural crimp, providing insulation while maintaining comfort and a cozy feel in colder temperatures.
Comfort and Softness Comparison
Modal fibers provide exceptional softness and a smooth texture, making sweaters feel luxuriously gentle against the skin. Wool offers excellent warmth and natural insulation but can sometimes be slightly coarse or itchy, depending on the type and quality. In terms of comfort, modal sweaters are ideal for those with sensitive skin, while wool sweaters excel in cold conditions due to their superior heat retention.
Warmth and Insulation: Which is Better?
Modal sweaters offer lightweight softness and moderate warmth but lack the dense insulation necessary for extreme cold. Wool excels in insulation with its natural crimped fibers trapping heat effectively, making it the superior choice for warmth in harsh weather. Wool's moisture-wicking properties also enhance thermal regulation, outperforming modal in maintaining body heat.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Modal fibers offer superior breathability compared to wool, allowing better air circulation and keeping the skin cool during wear. Wool excels in moisture management by wicking sweat away from the body and retaining warmth even when damp, making it ideal for cold and wet conditions. Modal's smooth texture enhances comfort by drying quickly, while wool's natural crimp creates insulating air pockets for temperature regulation.
Durability and Longevity
Modal fibers offer excellent durability due to their resistance to shrinkage and pilling, maintaining the sweater's shape and softness over time. Wool, especially Merino, excels in longevity thanks to its natural resilience and ability to retain warmth even after extensive wear. Both materials provide lasting quality, but wool sweaters generally endure harsh conditions better, making them a top choice for long-term use.
Ease of Care and Maintenance
Modal sweaters offer superior ease of care due to their resistance to shrinking, fading, and wrinkling, allowing for simple machine washing without special treatment. Wool sweaters, while highly insulating and breathable, require more meticulous maintenance, including hand washing or dry cleaning to prevent felting and shrinkage. Repeated care demands for wool include gentle detergents and flat drying, which contrasts with modal's durability and low-maintenance nature for everyday wear.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Modal fibers are produced from sustainably sourced beechwood trees using a closed-loop process that recycles chemicals and water, resulting in lower environmental impact compared to conventional fabrics. Wool is a natural, renewable resource with excellent biodegradability, yet its environmental footprint varies due to factors like methane emissions, land use, and water consumption associated with sheep farming. Choosing modal over wool can reduce resource-intensive farming impacts, while wool offers benefits in biodegradability and durability, making the sustainability comparison dependent on specific production practices and end-of-life management.
Which is Best for Sweaters: Modal or Wool?
Modal fibers offer exceptional softness, breathability, and moisture-wicking properties, making modal sweaters highly comfortable and ideal for sensitive skin. Wool provides superior warmth, natural insulation, and durability, perfect for cold-weather sweaters with excellent odor resistance and elasticity. Choosing between modal or wool for sweaters depends on desired use: modal suits lightweight, breathable garments, while wool excels in insulation and long-term wear.
Infographic: Modal vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com