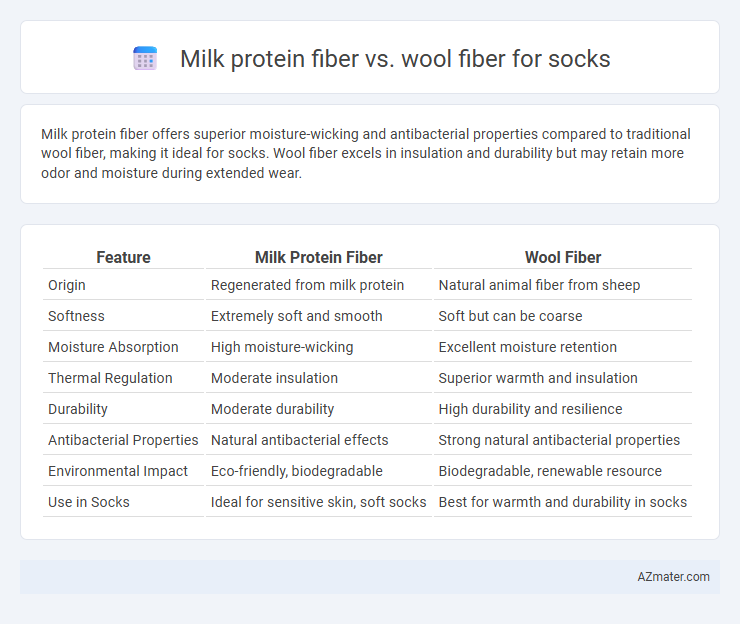
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture-wicking and antibacterial properties compared to traditional wool fiber, making it ideal for socks. Wool fiber excels in insulation and durability but may retain more odor and moisture during extended wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Wool Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Regenerated from milk protein | Natural animal fiber from sheep |
| Softness | Extremely soft and smooth | Soft but can be coarse |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture-wicking | Excellent moisture retention |
| Thermal Regulation | Moderate insulation | Superior warmth and insulation |
| Durability | Moderate durability | High durability and resilience |
| Antibacterial Properties | Natural antibacterial effects | Strong natural antibacterial properties |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, biodegradable | Biodegradable, renewable resource |
| Use in Socks | Ideal for sensitive skin, soft socks | Best for warmth and durability in socks |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Wool Fiber
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in milk, offers softness, moisture absorption, and antibacterial properties ideal for socks, while wool fiber, sourced from sheep, provides natural insulation, durability, and moisture-wicking capabilities. Milk protein fiber is hypoallergenic and promotes comfort with a silky texture, whereas wool fiber excels in temperature regulation and resilience for prolonged wear. Both fibers deliver distinct benefits in sock manufacturing, catering to different performance and comfort needs.
Composition and Production Processes
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein protein extracted from milk, undergoes chemical polymerization where milk proteins are dissolved, spun into fibers, and solidified through a drying or coagulation process, offering softness and moisture absorption. Wool fiber is obtained from the fleece of sheep through shearing, then cleaned, carded, and spun into yarn, featuring natural crimp that provides insulation and elasticity. The production of milk protein fiber involves biopolymer technology with renewable raw materials, while wool relies on animal harvesting and traditional fiber processing techniques.
Comfort and Softness Comparison
Milk protein fiber socks provide superior softness thanks to their smooth, silk-like texture that enhances comfort and reduces skin irritation. Wool fiber socks excel in warmth and moisture-wicking but can feel coarse, which may cause itchiness for sensitive skin. Choosing milk protein fiber ensures a softer, more comfortable sock experience, especially for prolonged wear.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture management for socks by efficiently wicking sweat away from the skin, keeping feet dry and comfortable during extended wear. Wool fiber naturally regulates moisture through its hygroscopic properties, absorbing and releasing moisture while maintaining breathability and insulation. While wool excels in breathability and temperature regulation, milk protein fiber provides enhanced moisture control, making it ideal for high-activity or warm-weather sock use.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Milk protein fiber and wool fiber both provide excellent thermal insulation for socks, with wool naturally excelling due to its crimped structure that traps air and retains heat efficiently. Milk protein fiber offers a smooth, soft texture with moderate insulation, leveraging protein-based polymers that provide moisture-wicking and thermal regulation benefits. Wool remains superior in maintaining warmth under varying humidity levels, making it ideal for cold-weather performance socks.
Durability and Longevity
Milk protein fiber demonstrates exceptional durability and longevity in socks due to its natural elasticity and resistance to wear, outperforming many traditional fibers. Wool fiber offers excellent resilience and moisture-wicking properties but tends to experience faster pilling and thinning with prolonged use. Choosing milk protein fiber socks ensures sustained shape retention and structural integrity, making them ideal for extended, high-frequency wear.
Allergenicity and Skin Sensitivity
Milk protein fiber offers hypoallergenic properties due to its natural amino acid composition, making it suitable for sensitive skin and reducing the risk of irritation or allergic reactions. Wool fiber, while breathable and moisture-wicking, can sometimes cause itchiness or allergic responses in individuals with wool sensitivity due to lanolin content. For socks, milk protein fiber provides a softer, smoother alternative that supports skin health and comfort in those prone to allergies or skin sensitivity.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Milk protein fiber production utilizes casein from dairy waste, significantly reducing resource consumption and landfill waste compared to traditional textiles, making it a sustainable alternative for eco-friendly socks. Wool fiber, sourced from sheep, is biodegradable and renewable but requires extensive land use, water, and methane emissions during sheep farming, contributing to a larger environmental footprint. Choosing milk protein fiber over wool for socks supports waste valorization and lowers greenhouse gas emissions, promoting a more sustainable textile industry.
Price and Market Availability
Milk protein fiber socks typically cost less than wool fiber socks due to lower raw material and production expenses. Wool fiber socks command higher prices because of their natural insulation properties and established market demand. Milk protein fiber is gaining traction in niche markets but remains less widely available compared to the more commonly stocked wool fiber socks.
Final Recommendation: Choosing the Best Fiber for Socks
Milk protein fiber offers excellent moisture-wicking properties, softness, and antibacterial benefits, making it ideal for sensitive skin and athletic socks. Wool fiber provides superior insulation, natural odor resistance, and durability, perfect for cold weather and rugged outdoor use. For versatile everyday socks, milk protein fiber suits comfort and hygiene, while wool fiber is recommended for warmth and long-lasting wear.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Wool fiber for Sock
 azmater.com
azmater.com