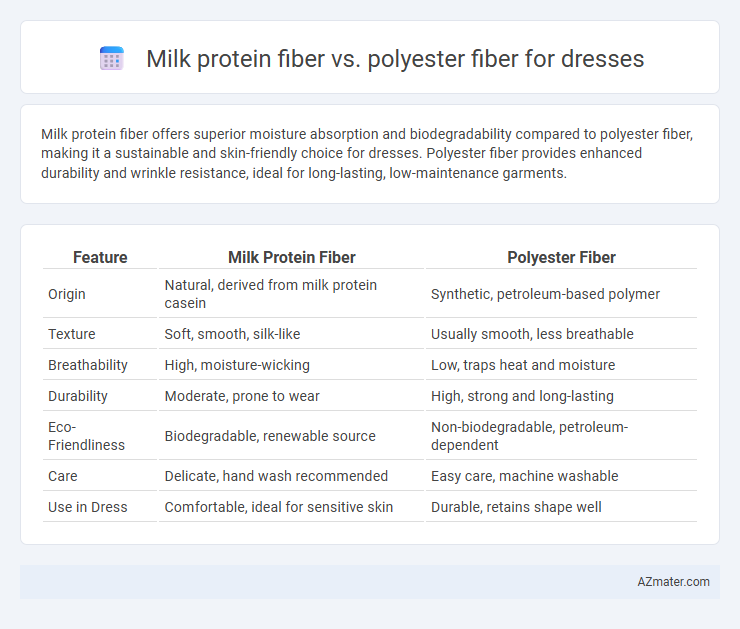
Milk protein fiber offers superior moisture absorption and biodegradability compared to polyester fiber, making it a sustainable and skin-friendly choice for dresses. Polyester fiber provides enhanced durability and wrinkle resistance, ideal for long-lasting, low-maintenance garments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Polyester Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Origin | Natural, derived from milk protein casein | Synthetic, petroleum-based polymer |
| Texture | Soft, smooth, silk-like | Usually smooth, less breathable |
| Breathability | High, moisture-wicking | Low, traps heat and moisture |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to wear | High, strong and long-lasting |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, renewable source | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-dependent |
| Care | Delicate, hand wash recommended | Easy care, machine washable |
| Use in Dress | Comfortable, ideal for sensitive skin | Durable, retains shape well |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Polyester Fiber
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein proteins found in milk, offers natural softness, breathability, and biodegradability, making it an eco-friendly alternative in textile production. Polyester fiber, a synthetic polymer made from petroleum-based products, is valued for its durability, wrinkle resistance, and moisture-wicking properties commonly used in dress fabrics. The choice between milk protein fiber and polyester fiber influences dress comfort, sustainability, and performance attributes.
Composition and Source of Milk Protein Fiber
Milk protein fiber is derived from casein, a protein found in milk, combined with natural and synthetic polymers to create a sustainable, biodegradable textile with excellent moisture absorption and softness. Polyester fiber, a synthetic material made from petrochemicals, is durable, wrinkle-resistant, and inexpensive but lacks the natural biodegradability and breathability of milk protein fiber. The unique composition of milk protein fiber captures the nourishing properties of milk, offering a hypoallergenic and eco-friendly alternative to traditional polyester used in dress fabrics.
Composition and Source of Polyester Fiber
Milk protein fiber is derived from casein proteins extracted from milk, offering natural biodegradability and a soft, moisture-absorbing composition ideal for sensitive skin. Polyester fiber, made primarily from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) synthesized through polymerization of petroleum-based raw materials, provides high durability, wrinkle resistance, and quick-drying properties in dress fabrics. The synthetic origin of polyester fiber ensures consistent strength and color retention, contrasting with the renewable and eco-friendlier source of milk protein fiber.
Environmental Impact: Milk Protein vs. Polyester
Milk protein fiber, derived from renewable milk byproducts, offers a biodegradable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic polyester fiber, which relies on petroleum and contributes to microplastic pollution. Unlike polyester, whose production emits significant greenhouse gases and requires extensive water and fossil fuel consumption, milk protein fiber production has a lower carbon footprint and enhances sustainability by repurposing waste. Biodegradability and renewable sourcing make milk protein fiber a favorable choice for environmentally conscious dress manufacturing compared to the persistent environmental impact of polyester fibers.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Milk protein fiber exhibits superior comfort and breathability compared to polyester fiber due to its natural protein structure, which allows better moisture absorption and air circulation. Polyester fiber, being synthetic, tends to trap heat and moisture, leading to less comfort during extended wear. The hypoallergenic and skin-friendly properties of milk protein fiber enhance overall garment comfort, making it ideal for sensitive skin in dress fabrics.
Durability and Longevity in Dresses
Milk protein fiber exhibits strong durability due to its high tensile strength and resistance to wear, making it suitable for long-lasting dresses. Polyester fiber is renowned for exceptional durability, retaining shape and resisting shrinking, stretching, and abrasion over extensive use. Dresses made from polyester fiber typically offer superior longevity compared to milk protein fiber, especially in high-wear situations.
Moisture-wicking and Absorbency Properties
Milk protein fiber exhibits superior moisture-wicking and absorbency properties compared to polyester fiber, making it ideal for dresses requiring breathability and comfort. Milk protein fiber naturally absorbs moisture from the skin and releases it into the air, preventing a damp or sticky feeling. Polyester fiber, while durable and quick-drying, tends to trap sweat against the skin, reducing overall comfort in warm or humid conditions.
Skin Sensitivity and Hypoallergenic Benefits
Milk protein fiber, derived from natural casein proteins, offers superior skin sensitivity benefits compared to polyester fiber due to its soft, breathable, and moisture-absorbing properties that reduce irritation and allergen buildup. Polyester fiber, a synthetic material, tends to trap heat and moisture, increasing the risk of skin irritation and allergic reactions for sensitive skin types. The hypoallergenic nature of milk protein fiber makes it an ideal choice for individuals with delicate or allergy-prone skin, promoting comfort and minimizing inflammation.
Dyeability and Color Retention
Milk protein fiber offers superior dyeability due to its excellent moisture absorption and natural amino acid structure, allowing vibrant and uniform color uptake. Polyester fiber, while durable and resistant to fading, often requires disperse dyes and high-temperature dyeing processes, which can limit color vibrancy. In terms of color retention, milk protein fiber maintains brightness and reduces color fading over time, whereas polyester fibers tend to retain color well but may show less intensity in hues.
Suitability for Different Dress Styles
Milk protein fiber offers excellent breathability and softness, making it ideal for casual and summer dresses due to its moisture-wicking properties and lightweight texture. Polyester fiber provides durability and wrinkle resistance, which suits structured and tailored dress styles, such as formal or office wear. Both fibers can be blended to balance comfort and longevity, enhancing versatility across diverse dress designs.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Polyester fiber for Dress
 azmater.com
azmater.com