Milk protein fiber offers superior breathability and natural moisture-wicking properties compared to nylon, making it ideal for comfortable, hypoallergenic stockings. Nylon provides greater durability and elasticity but may lack the skin-friendly benefits of milk protein fiber.
Table of Comparison
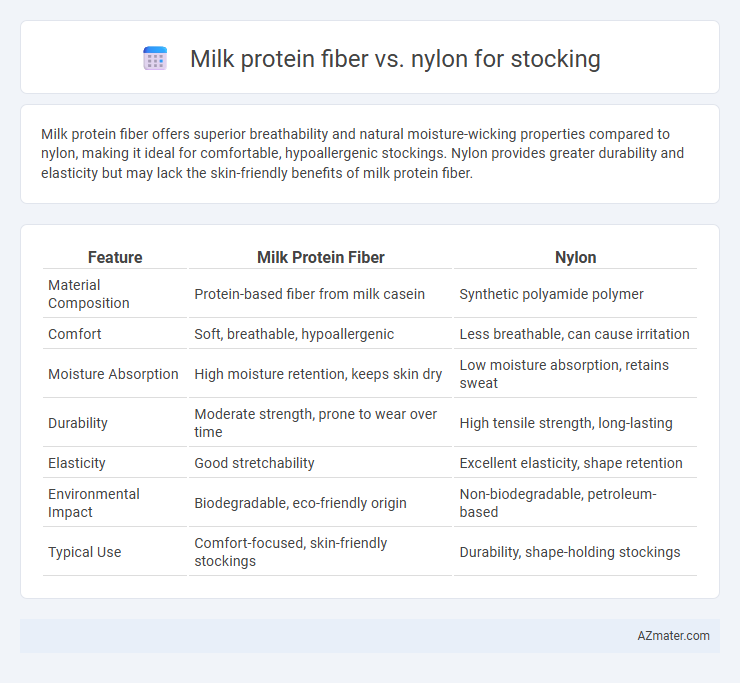
| Feature | Milk Protein Fiber | Nylon |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Protein-based fiber from milk casein | Synthetic polyamide polymer |
| Comfort | Soft, breathable, hypoallergenic | Less breathable, can cause irritation |
| Moisture Absorption | High moisture retention, keeps skin dry | Low moisture absorption, retains sweat |
| Durability | Moderate strength, prone to wear over time | High tensile strength, long-lasting |
| Elasticity | Good stretchability | Excellent elasticity, shape retention |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, eco-friendly origin | Non-biodegradable, petroleum-based |
| Typical Use | Comfort-focused, skin-friendly stockings | Durability, shape-holding stockings |
Introduction to Milk Protein Fiber and Nylon
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in milk, offers a natural, biodegradable alternative with excellent moisture absorption and softness, making it ideal for comfortable stockings. Nylon, a synthetic polymer known for its high strength, elasticity, and durability, provides superior abrasion resistance and shape retention in hosiery applications. Comparing these fibers highlights milk protein fiber's eco-friendly benefits and comfort against nylon's robustness and longevity.
Historical Background of Stocking Materials
Milk protein fiber, developed in the early 21st century, emerged as an eco-friendly alternative to traditional materials in stocking production, offering biodegradability and skin-friendly properties. Nylon, introduced in the 1930s by DuPont, revolutionized hosiery with its durability, elasticity, and affordability, quickly becoming the dominant material in stockings throughout the 20th century. The shift from silk and cotton to synthetic fibers like nylon marked a significant technological advancement, while recent innovations like milk protein fiber reflect growing consumer demand for sustainable textiles in fashion.
Composition and Manufacturing Process
Milk protein fiber is derived from casein, a protein found in milk, and is created through a process that involves extracting the protein, dissolving it in a solution, and then spinning it into fibers, resulting in a biodegradable and moisture-absorbent material. Nylon, a synthetic polyamide, is produced through a polymerization process involving the reaction of diamines and dicarboxylic acids, creating strong, elastic, and durable fibers commonly used in stockings. The natural origin and eco-friendliness of milk protein fiber contrast with nylon's petrochemical base and energy-intensive manufacturing, influencing the final texture, breathability, and environmental impact of stockings made from these materials.
Comfort and Softness Comparison
Milk protein fiber stockings offer superior comfort and softness compared to nylon due to their natural amino acid composition, which enhances moisture absorption and breathability. The protein-based structure provides a smooth, silk-like texture that reduces skin irritation and promotes all-day comfort. Nylon, while durable and elastic, tends to be less breathable and may cause discomfort during extended wear.
Durability and Longevity
Milk protein fiber exhibits excellent durability and natural elasticity, resisting wear and tear effectively, which enhances the longevity of stockings. Nylon, renowned for its strength and abrasion resistance, offers superior resilience under frequent use, maintaining shape and texture over time. When comparing both fibers, nylon generally provides longer-lasting durability, but milk protein fiber offers added comfort with reasonable durability for everyday wear.
Moisture Management and Breathability
Milk protein fiber outperforms nylon in moisture management by absorbing and wicking sweat away from the skin, enhancing comfort during prolonged wear. Its natural breathability allows air circulation that prevents overheating, while nylon tends to trap moisture and heat due to its synthetic structure. This makes milk protein fiber stockings preferable for those seeking superior moisture control and ventilation.
Skin Sensitivity and Allergenicity
Milk protein fiber offers superior skin sensitivity benefits compared to nylon, as it is naturally hypoallergenic and contains bioactive peptides that promote skin health and moisture retention. Nylon, a synthetic fiber, can cause irritation and allergic reactions in sensitive skin due to its non-breathable nature and chemical finishings. Consumers with skin allergies or sensitivities often prefer milk protein fiber stockings for their soft texture and reduced risk of dermatitis.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Milk protein fiber, derived from casein in milk, offers a biodegradable and renewable alternative to conventional nylon, reducing reliance on petroleum-based resources and lowering carbon emissions during production. Unlike nylon, which is non-biodegradable and contributes to microplastic pollution, milk protein fiber decomposes naturally, minimizing environmental waste and easing landfill burden. Its sustainable lifecycle, from renewable raw materials to eco-friendly disposal, positions milk protein fiber as a superior choice for eco-conscious stocking manufacturing.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Milk protein fiber offers a sustainable alternative to nylon in stockings, typically carrying a higher production cost due to specialized manufacturing processes and raw material sourcing. Nylon remains more cost-effective, benefiting from established supply chains and mass production efficiencies, making it widely available in global markets. Market availability of milk protein fiber stockings is currently limited, primarily found in niche or eco-friendly brands, whereas nylon stockings dominate mainstream retail channels with extensive distribution.
Final Verdict: Which Stocking Material Wins?
Milk protein fiber stockings offer superior breathability, moisture-wicking properties, and eco-friendliness compared to nylon, which tends to trap heat and cause discomfort in warm conditions. Nylon stockings excel in durability, elasticity, and affordability, maintaining shape well over prolonged use despite being less breathable. For those prioritizing comfort and sustainability, milk protein fiber is the better choice, whereas nylon remains ideal for budget-conscious consumers who need long-lasting, resilient stockings.
Infographic: Milk protein fiber vs Nylon for Stocking
 azmater.com
azmater.com