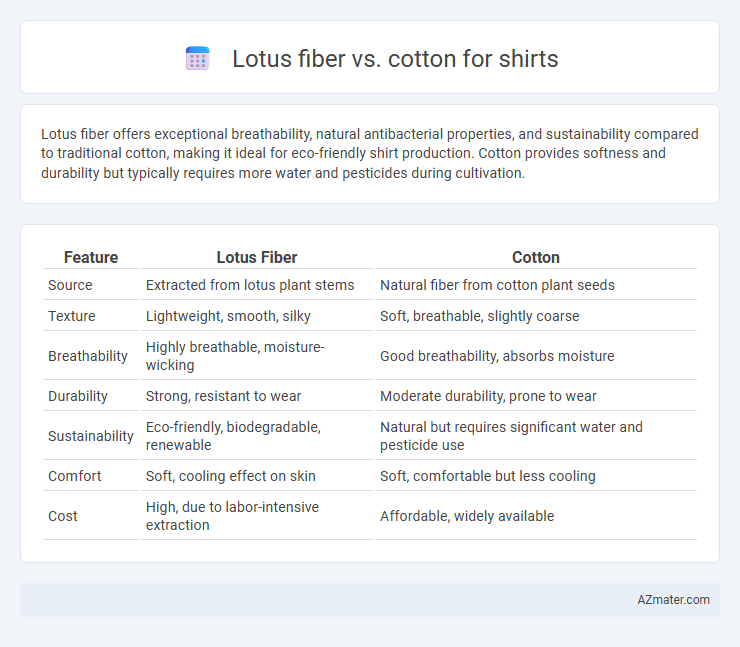
Lotus fiber offers exceptional breathability, natural antibacterial properties, and sustainability compared to traditional cotton, making it ideal for eco-friendly shirt production. Cotton provides softness and durability but typically requires more water and pesticides during cultivation.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lotus Fiber | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Extracted from lotus plant stems | Natural fiber from cotton plant seeds |
| Texture | Lightweight, smooth, silky | Soft, breathable, slightly coarse |
| Breathability | Highly breathable, moisture-wicking | Good breathability, absorbs moisture |
| Durability | Strong, resistant to wear | Moderate durability, prone to wear |
| Sustainability | Eco-friendly, biodegradable, renewable | Natural but requires significant water and pesticide use |
| Comfort | Soft, cooling effect on skin | Soft, comfortable but less cooling |
| Cost | High, due to labor-intensive extraction | Affordable, widely available |
Introduction to Lotus Fiber and Cotton
Lotus fiber, derived from the stems of lotus plants, offers a lightweight, breathable, and eco-friendly alternative to traditional cotton fabric. Cotton, a natural fiber harvested from cotton plants, is known for its softness, durability, and widespread availability in textile manufacturing. Both fibers provide unique benefits for shirts, with lotus fiber standing out for its sustainability and cotton favored for its comfort and versatility.
Origin and Production Processes
Lotus fiber originates from the stems of the lotus plant, primarily harvested in Southeast Asia through a labor-intensive process of extracting and hand-weaving the fibers, resulting in a rare and eco-friendly fabric. Cotton, derived from the cotton plant's seed hairs, undergoes mechanical ginning, spinning, and weaving, making it widely produced and globally available. The sustainable and artisanal nature of lotus fiber contrasts with the large-scale agricultural and industrial production methods typical of cotton cultivation.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Lotus fiber production requires minimal water and pesticides, making it a highly sustainable alternative to cotton, which consumes vast amounts of water and relies heavily on chemical fertilizers and pesticides. The cultivation of lotus preserves wetland ecosystems by promoting biodiversity, while conventional cotton farming often leads to soil degradation and pollution from agrochemical runoff. Biodegradable and naturally renewable, lotus fiber contributes to reducing the fashion industry's carbon footprint compared to the more resource-intensive and environmentally taxing cultivation of cotton.
Texture and Comfort Differences
Lotus fiber offers a unique texture that is naturally crisp yet soft, providing a lightweight and breathable fabric ideal for hot climates. Cotton, known for its smooth and slightly plush texture, excels in softness and moisture absorption, making it comfortable for everyday wear. While lotus fiber promotes better airflow and durability, cotton provides a familiar softness and elasticity that many prefer in shirts.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Lotus fiber offers superior breathability compared to cotton due to its natural hollow fiber structure, which enhances airflow and keeps the wearer cooler in hot climates. Cotton, while breathable, tends to retain more moisture, leading to slower drying times and reduced comfort in humid conditions. Lotus fiber excels in moisture management by wicking sweat away efficiently, maintaining dryness and freshness throughout the day.
Durability and Longevity
Lotus fiber exhibits remarkable durability due to its natural stiffness and resistance to wear, making it a superior choice for long-lasting shirts compared to cotton. Cotton, while soft and breathable, tends to degrade faster with frequent washing and exposure to sunlight. The tensile strength of lotus fiber surpasses that of cotton, contributing to enhanced longevity and reduced fabric pilling in apparel.
Allergen and Sensitivity Factors
Lotus fiber is naturally hypoallergenic and resistant to bacteria, making it an excellent choice for individuals with sensitive skin or allergies, unlike cotton which may harbor allergens due to pesticide use in conventional farming. The smooth texture of lotus fiber reduces skin irritation and itchiness often associated with cotton fibers, especially for those prone to eczema or dermatitis. Choosing lotus fiber shirts can significantly minimize allergic reactions and enhance comfort for allergy-sensitive wearers.
Style Versatility and Appearance
Lotus fiber shirts offer a unique, natural sheen and textured appearance that enhances style versatility with an elegant, eco-friendly appeal, making them ideal for both casual and formal wear. Cotton shirts provide a smooth, soft finish with a wide range of colors and patterns, allowing for diverse styling options suitable for everyday and business casual looks. The breathable nature of both fabrics adds to comfort, but lotus fiber's rarity and distinct look create a standout garment.
Cost and Accessibility
Lotus fiber shirts tend to be more expensive than cotton due to the labor-intensive extraction process and limited production scale, making them less accessible to the average consumer. Cotton is widely cultivated globally with an established supply chain, resulting in lower costs and greater availability in various markets. The price difference reflects the rarity of lotus fiber, which is often marketed as a luxury or eco-friendly alternative to traditional cotton fabric.
Choosing the Best Fabric for Shirts
Lotus fiber, derived from the lotus plant, offers exceptional breathability, natural antibacterial properties, and a silky texture, making it a sustainable and eco-friendly choice for shirts. Cotton remains widely popular for its softness, durability, and moisture-wicking abilities, ensuring comfort and versatility in various climates. Selecting the best fabric depends on prioritizing sustainability and unique texture with lotus fiber or opting for the proven comfort and affordability of cotton.
Infographic: Lotus fiber vs Cotton for Shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com