Hemp fibers are more durable and breathable than cotton, offering superior moisture-wicking and natural antibacterial properties for T-shirts. Cotton provides a softer feel but requires more water and pesticides in cultivation compared to eco-friendly hemp.
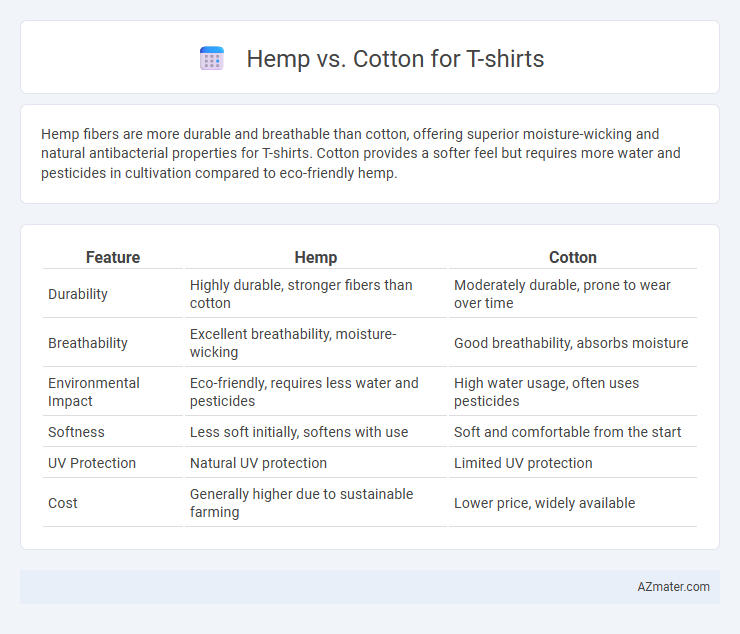
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hemp | Cotton |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, stronger fibers than cotton | Moderately durable, prone to wear over time |
| Breathability | Excellent breathability, moisture-wicking | Good breathability, absorbs moisture |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, requires less water and pesticides | High water usage, often uses pesticides |
| Softness | Less soft initially, softens with use | Soft and comfortable from the start |
| UV Protection | Natural UV protection | Limited UV protection |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable farming | Lower price, widely available |
Introduction to Hemp and Cotton Fabrics
Hemp fabric, derived from the fibers of the Cannabis sativa plant, is known for its durability, breathability, and natural resistance to UV light and mold, making it an eco-friendly choice for T-shirts. Cotton fabric, sourced from the cotton plant's seed fibers, is renowned for its softness, moisture absorption, and widespread availability, contributing to its dominance in the apparel industry. Both fabrics offer distinct benefits, with hemp providing sustainability and strength, while cotton ensures comfort and ease of care.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Cotton
Hemp requires significantly less water than cotton, using up to 50% less irrigation, which reduces strain on freshwater resources. Hemp cultivation also involves minimal pesticide and herbicide use due to its natural pest resistance, leading to lower soil and water pollution compared to cotton farming. Additionally, hemp plants have a faster growth cycle and higher yield per acre, promoting soil health through weed suppression and carbon sequestration benefits.
Water and Resource Consumption
Hemp cultivation requires up to 70% less water than cotton, making it a significantly more sustainable choice for t-shirt production. Hemp absorbs more carbon dioxide per hectare and grows faster with fewer pesticides and fertilizers, reducing environmental impact. Cotton demands extensive irrigation and chemical use, contributing to soil degradation and water scarcity concerns.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Hemp T-shirts outperform cotton in durability due to hemp fibers' natural strength and resistance to stretching, pilling, and tearing, resulting in longer-lasting garments. Cotton tends to wear out faster, especially after multiple washes, as its fibers weaken and lose shape more quickly than hemp. Choosing hemp for T-shirts ensures sustained fabric integrity and eco-friendly longevity, making it a superior option for durable clothing.
Comfort and Breathability Factors
Hemp fabric offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties compared to cotton, making it ideal for comfortable, all-day wear. The natural fibers in hemp create a lightweight, durable material that remains breathable even in hot and humid conditions. Cotton, while soft and widely used, tends to retain moisture longer, which can reduce overall comfort during prolonged activity or high temperatures.
Production Costs and Affordability
Hemp requires less water and pesticides compared to cotton, leading to lower overall production costs despite its slower growing cycle. Cotton's widespread cultivation benefits from established farming infrastructure, making raw cotton cheaper but often involves higher environmental and resource expenses. Affordability of hemp T-shirts is improving with increased demand and technological advancements, although cotton T-shirts generally remain less expensive due to scale and market familiarity.
Chemical Usage in Cultivation
Hemp cultivation requires significantly fewer pesticides and herbicides compared to cotton, reducing chemical residue on T-shirts and minimizing environmental impact. Cotton farming accounts for approximately 16% of global insecticide use despite covering only 2.5% of agricultural land, leading to high chemical runoff and soil degradation. Choosing hemp T-shirts supports sustainable agriculture due to hemp's natural pest resistance and lower water and chemical requirements.
Biodegradability and End-of-Life Options
Hemp T-shirts biodegrade more efficiently than cotton due to their natural fiber composition, breaking down within months under composting conditions without releasing harmful residues. Cotton, while also biodegradable, often requires more time and may involve pesticides or chemical residues that affect soil quality during decomposition. End-of-life options for hemp include composting, recycling, and even upcycling into other textiles, whereas cotton T-shirts typically have fewer sustainable recycling pathways, often ending up in landfills.
Market Availability and Style Options
Hemp T-shirts are gaining traction in the sustainable fashion market, with increasing availability in eco-conscious brands, though cotton remains more widely accessible in mainstream retail stores worldwide. Cotton offers a broader variety of styles, colors, and fabric blends due to its long-standing presence and versatility in the fashion industry. Hemp fabric, known for its durability and natural texture, is often featured in casual and eco-friendly collections, appealing to niche markets focused on sustainability.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Fabric for T-Shirts
Hemp fabric offers superior durability, breathability, and environmental benefits compared to cotton, making it an excellent sustainable choice for T-shirts. Cotton remains popular for its softness and affordability but often involves higher water usage and pesticide exposure during cultivation. Opting for hemp T-shirts enhances both comfort and eco-friendliness, positioning it as the best fabric choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Infographic: Hemp vs Cotton for T-shirt
 azmater.com
azmater.com