Hemp fibers offer exceptional durability, breathability, and eco-friendliness for bags, while chitosan provides antimicrobial properties and biodegradability. Choosing hemp enhances strength and sustainability; selecting chitosan ensures odor resistance and quick decomposition.
Table of Comparison
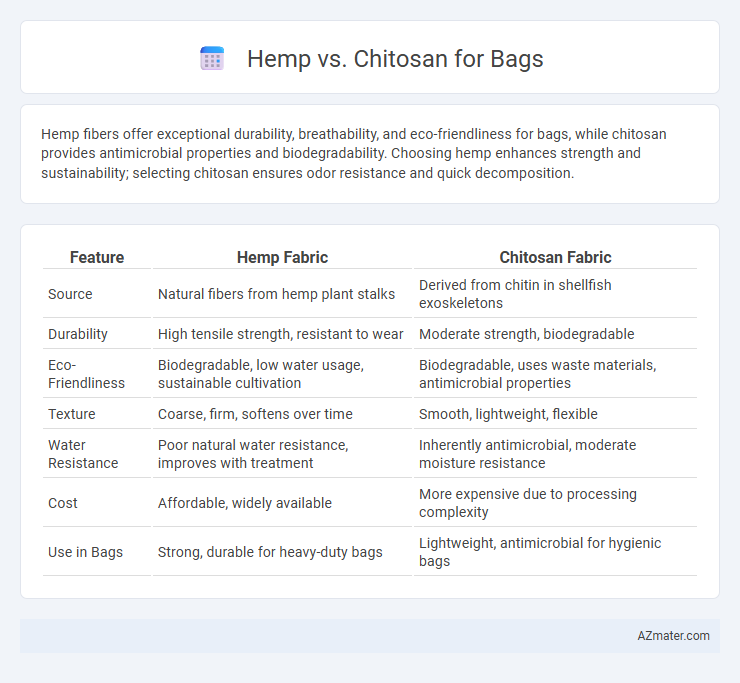
| Feature | Hemp Fabric | Chitosan Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Natural fibers from hemp plant stalks | Derived from chitin in shellfish exoskeletons |
| Durability | High tensile strength, resistant to wear | Moderate strength, biodegradable |
| Eco-Friendliness | Biodegradable, low water usage, sustainable cultivation | Biodegradable, uses waste materials, antimicrobial properties |
| Texture | Coarse, firm, softens over time | Smooth, lightweight, flexible |
| Water Resistance | Poor natural water resistance, improves with treatment | Inherently antimicrobial, moderate moisture resistance |
| Cost | Affordable, widely available | More expensive due to processing complexity |
| Use in Bags | Strong, durable for heavy-duty bags | Lightweight, antimicrobial for hygienic bags |
Introduction to Sustainable Bag Materials
Hemp fibers offer exceptional durability and biodegradability, making them a top choice for sustainable bag materials due to their low environmental impact and rapid growth cycle. Chitosan, derived from chitin in crustacean shells, provides antimicrobial properties and biodegradability, enhancing sustainability and hygiene in bag production. Both hemp and chitosan contribute significantly to reducing reliance on synthetic fibers and promote eco-friendly alternatives in the fashion industry.
What is Hemp? Overview and Benefits
Hemp is a sustainable natural fiber derived from the Cannabis sativa plant, renowned for its strength, durability, and biodegradability, making it an ideal material for eco-friendly bags. Rich in cellulose, hemp fibers provide excellent resistance to UV rays, mold, and wear, contributing to long-lasting and eco-conscious products. Its cultivation requires minimal pesticides and water compared to other crops, enhancing its environmental benefits and reducing ecological impact.
What is Chitosan? Overview and Benefits
Chitosan is a natural biopolymer derived from chitin, commonly found in the shells of crustaceans such as crabs and shrimp. It offers antimicrobial properties, biodegradability, and water resistance, making it an eco-friendly alternative for bag manufacturing compared to traditional materials like hemp. Its ability to inhibit bacterial growth and enhance durability provides significant advantages in producing sustainable, high-performance bags.
Environmental Impact: Hemp vs Chitosan
Hemp bags exhibit a significantly lower environmental impact due to their rapid growth cycle, minimal pesticide requirement, and high carbon sequestration ability compared to conventional crops. Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, is biodegradable and relies on seafood industry byproducts, reducing marine waste but limited by resource availability and potential allergenicity concerns. Overall, hemp offers a more sustainable, large-scale option for eco-friendly bag materials while chitosan provides a valuable waste-utilization alternative in niche markets.
Biodegradability and Compostability Comparison
Hemp bags exhibit high biodegradability and compostability due to their natural cellulose fibers, breaking down effectively within 3 to 6 months in industrial composting conditions. Chitosan bags, derived from chitin in shellfish shells, also biodegrade but may require specific enzymatic environments to fully compost, typically decomposing over 6 to 12 months. Both materials provide sustainable alternatives to synthetic plastics, with hemp offering faster biodegradation and chitosan presenting antimicrobial properties that enhance product preservation.
Strength and Durability of Hemp and Chitosan Bags
Hemp bags exhibit exceptional strength and durability due to the plant's fibrous structure, making them resistant to wear, tearing, and heavy loads. Chitosan bags, derived from chitin found in crustacean shells, provide moderate strength but excel in biodegradability and antimicrobial properties, which can enhance longevity in specific environments. When comparing the two, hemp offers superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, while chitosan bags prioritize eco-friendly features and potential biodegradation benefits over maximum durability.
Manufacturing Processes: Hemp vs Chitosan Bags
Hemp bags are manufactured through a process involving the harvesting, retting, and decortication of hemp fibers, followed by spinning and weaving, which results in a durable, biodegradable material ideal for eco-friendly packaging. Chitosan bags utilize chitosan derived from chitin, primarily extracted from crustacean shells through demineralization and deacetylation, then processed into films or fibers that are biodegradable and naturally antimicrobial. The manufacturing of hemp bags emphasizes fiber extraction and textile production, whereas chitosan bags rely on chemical extraction and film-forming processes, making each suited to different functional packaging requirements.
Cost and Market Availability
Hemp bags typically offer a moderate price point due to the growing availability of hemp farming and processing facilities, making them increasingly accessible in mainstream markets. Chitosan bags, derived from shellfish waste, often incur higher production costs due to complex extraction and purification processes, limiting widespread market availability. Market data indicates hemp bags dominate eco-friendly packaging sectors with broader consumer acceptance, while chitosan bags remain niche products in specialty markets.
Consumer Safety and Health Considerations
Hemp bags offer natural antimicrobial properties and are free from synthetic chemicals, reducing the risk of skin irritation and allergic reactions for consumers. Chitosan, derived from crustacean shells, provides biodegradability and antimicrobial effects but may pose allergy risks for individuals with shellfish sensitivities. Both materials promote eco-friendly alternatives, yet hemp stands out for its hypoallergenic profile and minimal health concerns in daily use.
Future Trends: Innovations in Sustainable Bag Materials
Innovations in sustainable bag materials highlight a shift toward biodegradable and eco-friendly options like hemp and chitosan, both praised for their renewable properties and durability. Hemp, derived from cannabis fibers, offers superior strength, UV resistance, and rapid growth with minimal pesticide use, making it an ideal choice for scalable eco-conscious production. Chitosan, sourced from crustacean shells, provides antimicrobial benefits and enhanced biodegradability, enabling advanced functional bags that meet rising consumer demands for sustainability and hygiene in the marketplace.
Infographic: Hemp vs Chitosan for Bag
 azmater.com
azmater.com