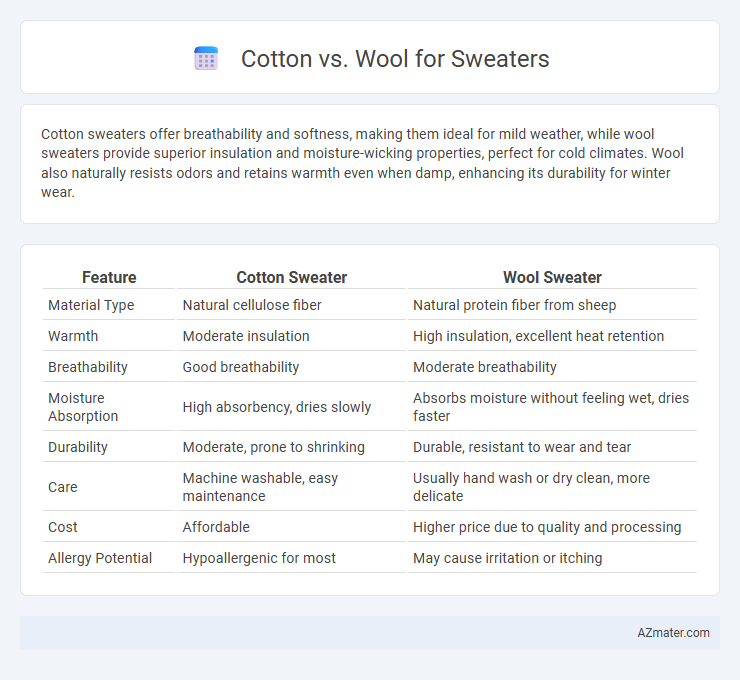
Cotton sweaters offer breathability and softness, making them ideal for mild weather, while wool sweaters provide superior insulation and moisture-wicking properties, perfect for cold climates. Wool also naturally resists odors and retains warmth even when damp, enhancing its durability for winter wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Cotton Sweater | Wool Sweater |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural cellulose fiber | Natural protein fiber from sheep |
| Warmth | Moderate insulation | High insulation, excellent heat retention |
| Breathability | Good breathability | Moderate breathability |
| Moisture Absorption | High absorbency, dries slowly | Absorbs moisture without feeling wet, dries faster |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to shrinking | Durable, resistant to wear and tear |
| Care | Machine washable, easy maintenance | Usually hand wash or dry clean, more delicate |
| Cost | Affordable | Higher price due to quality and processing |
| Allergy Potential | Hypoallergenic for most | May cause irritation or itching |
Introduction to Cotton vs Wool Sweaters
Cotton sweaters offer lightweight breathability and moisture absorption, making them ideal for mild weather and sensitive skin. Wool sweaters provide superior insulation and natural water resistance, perfect for cold climates and outdoor activities. Each fabric's unique thermal properties and texture influence comfort, durability, and maintenance requirements in sweater selection.
Natural Fiber Origins: Cotton and Wool
Cotton originates from the soft, fluffy fibers surrounding the seeds of the cotton plant, offering breathable and lightweight properties ideal for warm climates. Wool is derived from the fleece of sheep, providing superior insulation, moisture-wicking, and elasticity, making it suitable for cooler temperatures. Both fibers are renewable natural materials, with cotton favored for its softness and versatility, while wool excels in durability and thermal regulation.
Comfort and Feel: Softness and Wearability
Cotton sweaters offer a lightweight, breathable softness ideal for sensitive skin and warmer climates, while wool provides exceptional insulation with a slightly coarse texture that softens over time. Merino wool, a premium variety, stands out for its fine fibers that enhance comfort and reduce itchiness, making it more wearable for extended periods. The choice between cotton and wool depends on climate and personal sensitivity, as cotton excels in breathability and softness, whereas wool delivers superior warmth and moisture-wicking properties.
Warmth and Insulation Properties
Wool outperforms cotton in warmth and insulation due to its natural crimp, which traps air and retains body heat effectively. Cotton lacks this structure, making it less efficient at insulating and more prone to moisture absorption that reduces thermal retention. For cold weather sweaters, wool provides superior temperature regulation and moisture-wicking benefits, ensuring consistent warmth even when damp.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Cotton sweaters offer excellent breathability due to their natural fiber structure, allowing air to circulate and keep the body cool. Wool, particularly merino wool, excels in moisture management by wicking sweat away from the skin and retaining warmth even when damp. This makes wool a superior choice for regulating temperature and preventing clamminess during physical activities or fluctuating weather conditions.
Durability and Longevity
Wool sweaters offer superior durability due to natural resilience and elasticity in wool fibers, enabling them to retain shape and withstand wear over time. Cotton sweaters tend to wear out faster as fibers are less elastic and more prone to pilling or thinning after multiple washes. Investing in wool increases longevity, making it ideal for long-term use in sweaters compared to cotton options.
Care and Maintenance Requirements
Cotton sweaters require machine washing in cold water and should be air-dried to prevent shrinking, while wool sweaters need gentle hand washing or dry cleaning to maintain fiber integrity and avoid felting. Wool fibers benefit from using specialized detergents formulated for protein fibers, and sweaters should be reshaped and laid flat to dry to preserve their shape. Regular de-pilling and proper storage in a cool, dry place protect both cotton and wool garments from wear and moth damage.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Cotton sweaters typically have a larger environmental footprint due to intensive water use and pesticide application in cotton farming, whereas wool is renewable and biodegradable but can contribute to methane emissions and land degradation through sheep grazing. Organic cotton and responsibly sourced wool certified by standards like GOTS and the Responsible Wool Standard help mitigate negative environmental impacts. Choosing sweaters made from recycled fibers or integrating sustainable practices such as regenerative agriculture enhances overall sustainability in textile production.
Cost Comparison: Cotton vs Wool Sweaters
Cotton sweaters generally cost less than wool sweaters due to the lower production expenses and faster growing cycles of cotton fibers. Wool sweaters, particularly those made from high-quality merino or cashmere wool, command higher prices because of the labor-intensive harvesting and processing methods. Consumers often weigh the initial cost against durability and warmth, with wool providing better insulation but cotton offering affordability and ease of care.
Which Sweater Material is Best for You?
Cotton sweaters offer breathable comfort and are ideal for mild weather, providing softness and moisture absorption without overheating. Wool sweaters excel in insulation and moisture-wicking, making them the best choice for cold, damp conditions due to their natural warmth and durability. Choosing between cotton and wool depends on your climate, skin sensitivity, and activity level to ensure optimal comfort and performance.
Infographic: Cotton vs Wool for Sweater
 azmater.com
azmater.com