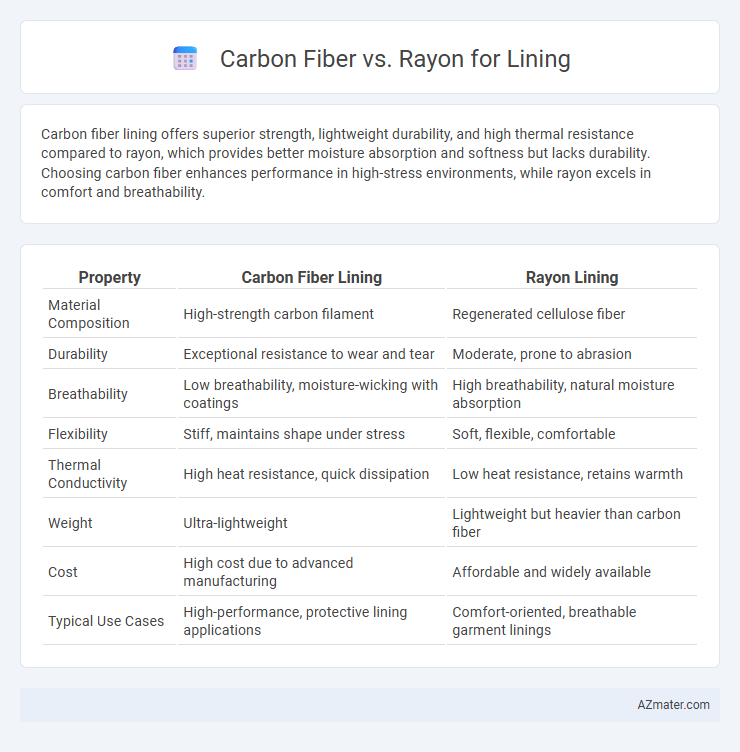
Carbon fiber lining offers superior strength, lightweight durability, and high thermal resistance compared to rayon, which provides better moisture absorption and softness but lacks durability. Choosing carbon fiber enhances performance in high-stress environments, while rayon excels in comfort and breathability.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Fiber Lining | Rayon Lining |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-strength carbon filament | Regenerated cellulose fiber |
| Durability | Exceptional resistance to wear and tear | Moderate, prone to abrasion |
| Breathability | Low breathability, moisture-wicking with coatings | High breathability, natural moisture absorption |
| Flexibility | Stiff, maintains shape under stress | Soft, flexible, comfortable |
| Thermal Conductivity | High heat resistance, quick dissipation | Low heat resistance, retains warmth |
| Weight | Ultra-lightweight | Lightweight but heavier than carbon fiber |
| Cost | High cost due to advanced manufacturing | Affordable and widely available |
| Typical Use Cases | High-performance, protective lining applications | Comfort-oriented, breathable garment linings |
Introduction to Lining Materials
Carbon fiber and rayon serve distinct roles in lining materials due to their unique properties. Carbon fiber offers exceptional strength, lightweight durability, and superior thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-performance applications. Rayon provides soft texture, breathability, and moisture-wicking capabilities, prioritizing comfort and smooth fabric feel in garment linings.
Overview of Carbon Fiber as a Lining Option
Carbon fiber as a lining material offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, providing durability and resistance to wear without adding significant bulk. Its high tensile strength and thermal stability make it ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet robust protection, outperforming traditional linings like rayon in mechanical resilience. Carbon fiber also exhibits superior moisture resistance and longevity, ensuring enhanced performance in demanding environments.
Overview of Rayon as a Lining Material
Rayon, a semi-synthetic fiber derived from cellulose, is widely used as a lining material due to its smooth texture and excellent breathability. It offers superior moisture absorption compared to synthetic fibers, contributing to enhanced comfort in clothing applications. Although less durable than carbon fiber, rayon provides a softer feel and better drape, making it a preferred choice for luxury and formal wear linings.
Strength and Durability: Carbon Fiber vs Rayon
Carbon fiber lining offers exceptional strength and durability, outperforming rayon with its high tensile strength and resistance to wear and tear. Carbon fiber's lightweight nature combined with superior impact resistance ensures long-lasting performance in demanding applications. Rayon, while flexible and comfortable, lacks the robust structural integrity and durability that carbon fiber provides in high-stress environments.
Comfort and Breathability Comparison
Carbon fiber lining offers superior durability and moisture-wicking properties, enhancing comfort by keeping the skin dry during extended wear. Rayon lining provides excellent breathability and softness, promoting airflow that helps regulate body temperature effectively. While carbon fiber excels in strength and moisture management, rayon remains preferred for its lightweight feel and natural ventilation, making both materials suitable depending on specific comfort needs.
Weight and Thickness Considerations
Carbon fiber linings offer superior strength-to-weight ratios and are significantly lighter than rayon alternatives, making them ideal for applications requiring minimal weight without compromising durability. Rayon linings tend to be thicker and heavier, which can add bulk and reduce flexibility in garments or accessories. Choosing carbon fiber enhances sleekness and performance in designs that prioritize lightweight materials and thinner profiles.
Thermal and Moisture Management
Carbon fiber linings excel in thermal regulation due to their high thermal conductivity, effectively dissipating heat and enhancing breathability for active wear. Rayon linings offer superior moisture management by absorbing and wicking sweat away from the skin, promoting dryness and comfort. While carbon fiber provides rapid heat dispersion, rayon ensures sustained moisture control, making both materials valuable for specific thermal and humidity needs in apparel design.
Cost Differences between Carbon Fiber and Rayon
Carbon fiber linings are significantly more expensive than rayon due to the complex manufacturing processes and raw material costs associated with carbon fiber production. Rayon offers a cost-effective alternative, providing affordable and versatile lining solutions suitable for budget-conscious applications. The price disparity influences material selection primarily in industries where budget constraints outweigh the performance benefits of carbon fiber.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon fiber linings offer superior durability and lightweight properties but pose significant environmental concerns due to energy-intensive production and non-biodegradability. Rayon linings, derived from cellulose fibers, provide a more sustainable alternative through biodegradability and renewable sourcing, although they may involve chemical processing with environmental risks. Choosing between carbon fiber and rayon for linings requires balancing performance needs with ecological footprint considerations.
Best Uses: Choosing the Right Lining Material
Carbon fiber lining excels in high-performance applications requiring exceptional strength, durability, and heat resistance, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and protective gear. Rayon lining offers superior moisture absorption, softness, and breathability, which suits fashion garments, formal wear, and comfort-focused apparel. Selecting the right lining material depends on the balance between structural integrity and comfort needs in the final product.
Infographic: Carbon fiber vs Rayon for Lining
 azmater.com
azmater.com